- Docker
- Jenkins
- See Install Docker Engine on Linux.
- if you want to use docker without
sudo:- Remember to add yourself to the
dockergroup.sudo groupadd docker && sudo gpasswd -a $USER docker - Restart the daemon:
- In Ubuntu:
sudo service docker restart - Other distributions:
sudo systemctl restart docker
- In Ubuntu:
- Remember to add yourself to the
Note: All commands should run with sudo permission unless you have set the docker group.
- Container: VM-like instance running processes.
- Image: Disk image for containers. Defined by a Dockerfile. You can get a lot of images from Docker Hub
- Volume: A host directory that can be mount into container directory.
- Show current running containers:
docker ps - Show all containers:
docker ps -a. This includes exited dockers. - Show available docker images:
docker images - Show all volumes:
docker volume ls - To delete a container / image / volume:
- Use 1. to 4. to get ID / NAME (something like
9e24d7d5a3beorjenkins_workspace). - Container:
docker rm [ID] - Image:
docker rmi [ID] - Volume:
docker volume rm [NAME]
- Use 1. to 4. to get ID / NAME (something like
- Tip: to remove all unused containers:
docker ps -a | awk '{print $1}' | xargs docker rm
$ docker run [Options] [Docker Image] [Command]
$ docker run -v [host path / volumne name]:[container path] -it --rm [docker image] [command]
$ # Example:
$ docker run -v rvm:/home/jenkins/.rvm -v jenkins_workspace:/home/jenkins/workspace -it --rm joshua5201/jenkins-slave-rails /bin/bash- Pull image:
docker pull joshua5201/jenkins-slave-rails - Create volume for RVM:
docker volume create --name rvm - Create volume for Workspace:
docker volume create --name jenkins_workspace - Install RVM in docker:
docker run -v rvm:/home/jenkins/.rvm -it joshua5201/jenkins-slave-rails /bin/bash - Inside docker:
su -l jenkinscurl -sSL https://get.rvm.io | bash -s stable
- You can just mount rvm volume whenever you add a docker image (~/.rvm must exists).
joshua5201/jenkins-slave-rails: basic runtimejoshua5201/jenkins-slave-rails-pg: with postgresql installed. postgres user: jenkins, no password.
- Follow the default steps and create first administrator user
- Manage jenkins -> Manage plugins -> Available -> install docker rvm
- Manage jenkins -> Configure system -> Add a new cloud (choose docker) ref: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Docker+Plugin
- set name, docker url (usually
unix:///var/run/docker.sock)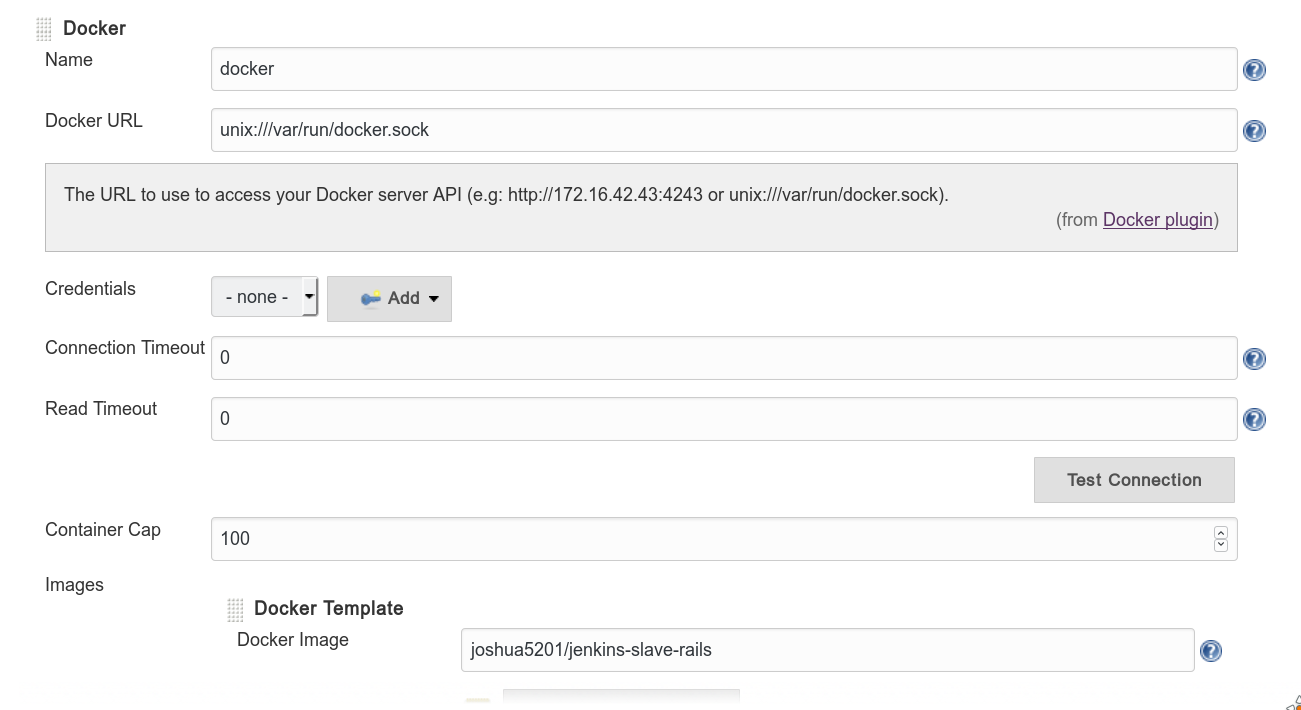
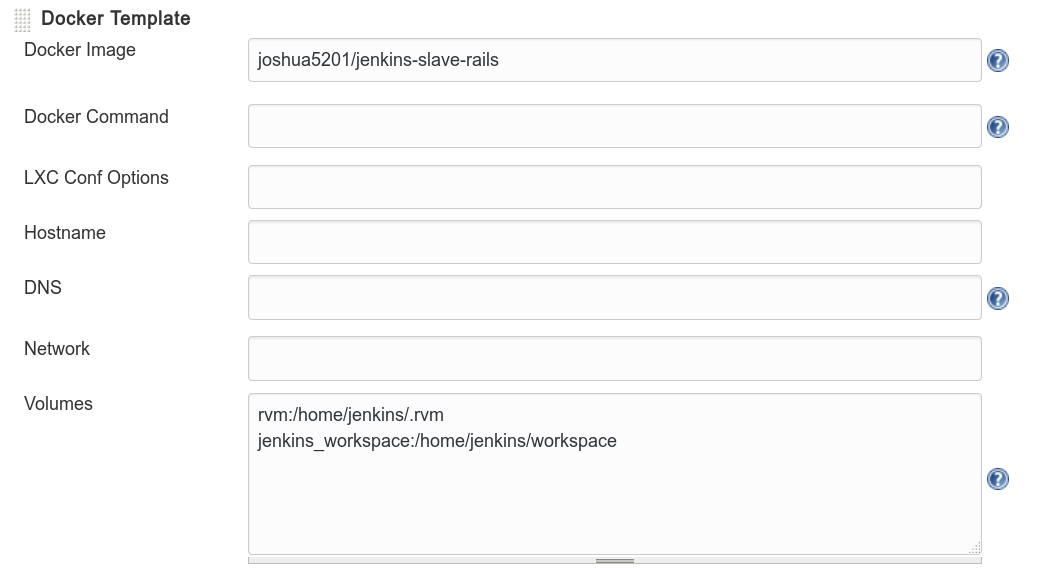
- Add docker template
- Docker image: joshua5201/jenkins-slave-rails
- Container settings -> Volumes: rvm:/home/jenkins/.rvm jenkins_workspace:/home/jenkins/workspace
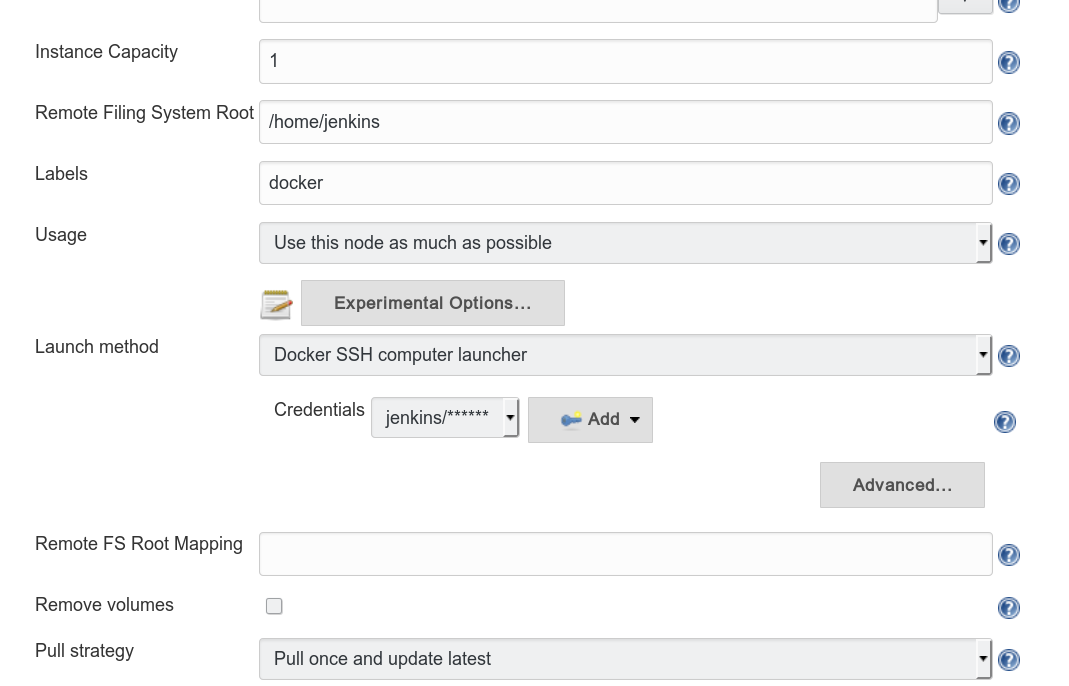
- Remote File System Root: /home/jenkins
- Labels: docker
- Add Credentials -> username with password -> jenkins/jenkins
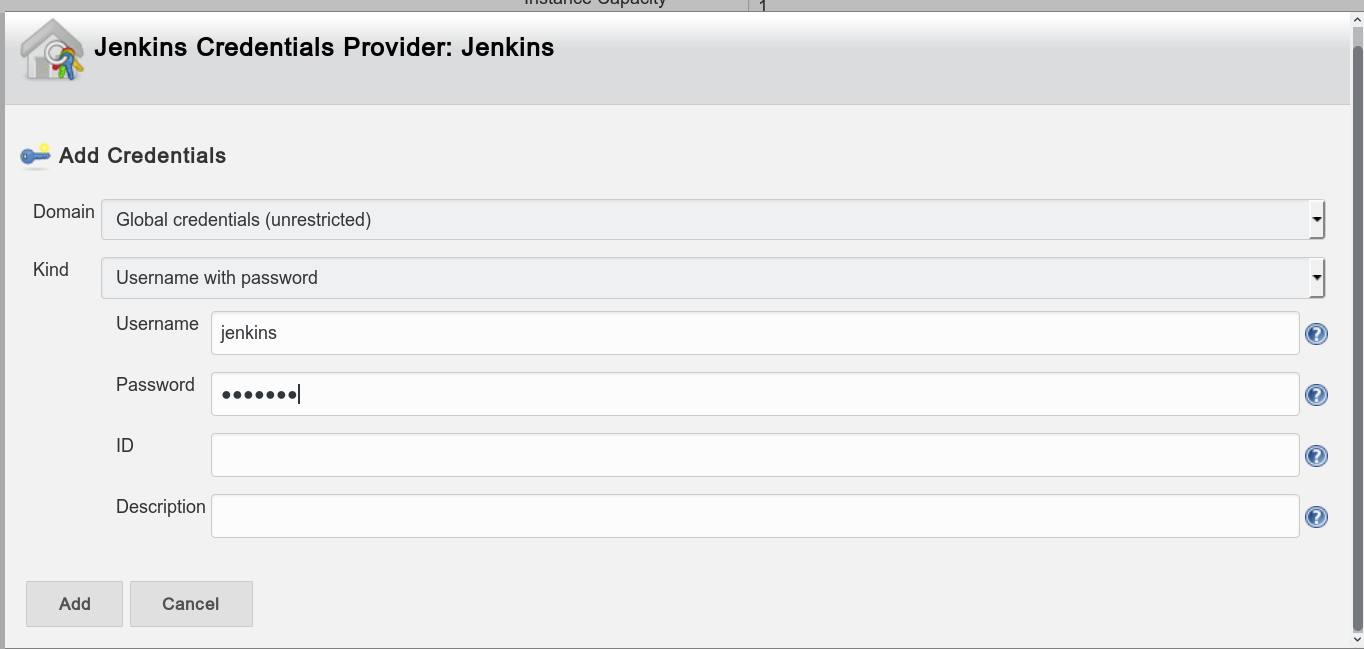
- set name, docker url (usually
- When adding other images like jenkins-slave-rails-pg, just change the Docker image and Labels above. (e.g. docker-pg)
- New Item -> Enter name -> Choose freestyle item
- General -> Advanced -> Custom Workspace: jenkins_workspace:/home/jenkins/workspace
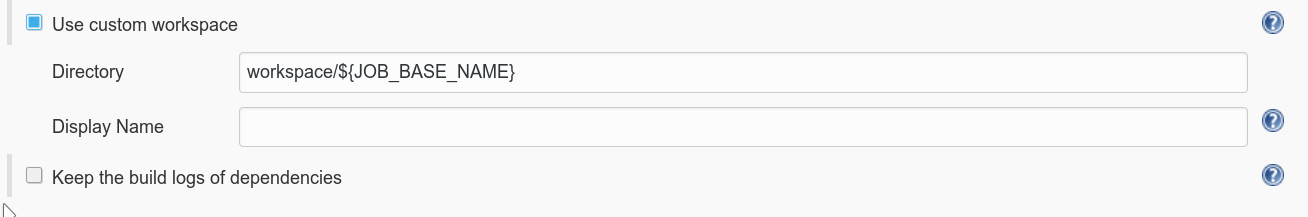
- Restrict where this project can be run: docker (or whatever labels you set for your docker image)
- Source Code Management: git -> set repo url -> add credentials (ssh private key with username 'git')
- Build Environment: Run the build in a RVM-managed environment -> choose your implementation (e.g.
2.3.0) - Add build steps: Execute shell
gem install rubygems-bundler
sudo /etc/init.d/redis-server start # if you need Redis
bundle install
bundle exec rake db:test:prepare
bundle exec rspec - To avoid SSH problems, please use the same key for GitHub repo deploy key and the key for SSH login to staging / production server.
- Follow the same steps as build job.
- At Build Environment -> Use secret text(s) or file(s) -> Varialble: DEPLOY_KEY -> Upload a secret file (id_rsa PRIVATE key)
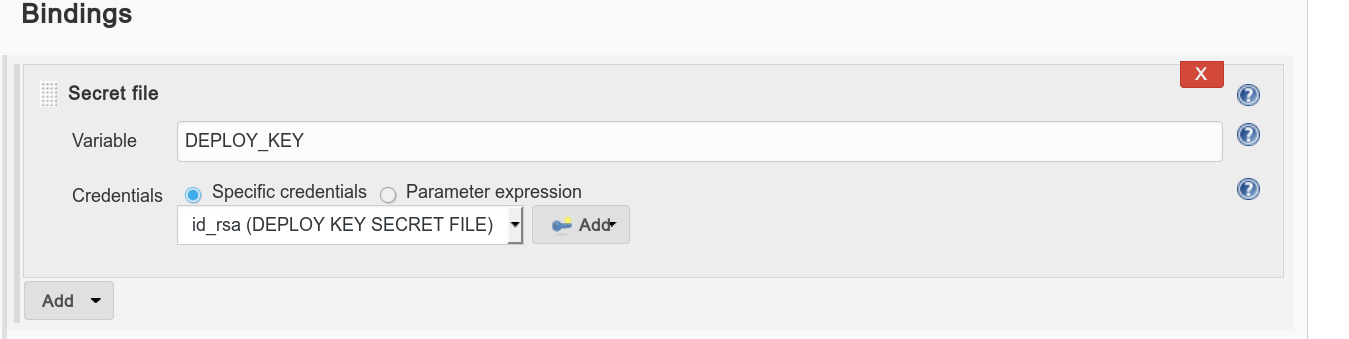
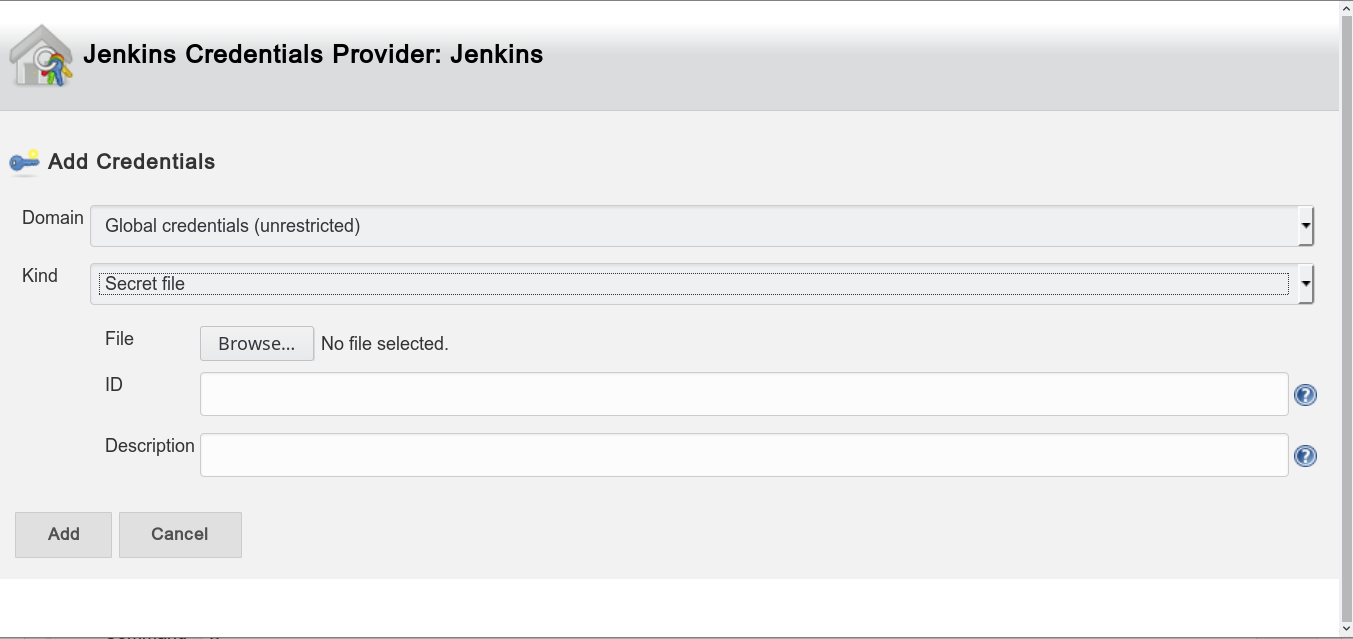
- Use the following shell script template:
# Prepare bundler
gem install rubygems-bundler
bundle install
# Setting up ssh-agent for capistrano
eval `ssh-agent`
ssh-add $DEPLOY_KEY
# Deploy scripts here
bundle exec cap staging deploy
# Kill ssh-agent
kill $SSH_AGENT_PID- You can create new job based on old ones.
- If you want Jenkins to integrate with GitHub:
- Go to https://github.com/settings/tokens to generate your token
- Manage Jenkins -> Configure System
- GitHub -> Add GitHub Server
- Credentials: Secret Text -> Input your token here
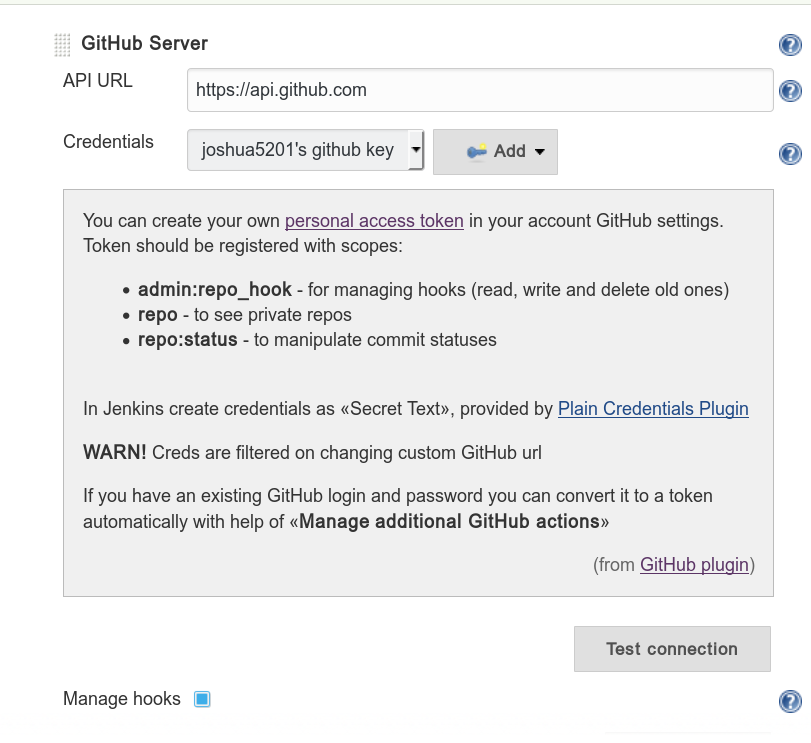
- Project configuration tips:
- If you want to bypass CI in commit message like [ci skip], install this plugin ci-skip
- If any packages are needed to be installed, email: joshua841025@gmail.com or fork my Dockerfile.