Based on the convolutional recurrent neural network, make an image sequence prediction. For example, input 16 consecutive image frames, the image size (3,128,128). Encoder feature extraction is performed on each consecutive 16 images using a convolutional network, and then the extracted feature sequence is input into the recurrent neural network (LSTM), and then the decoder is deconvolved into troch (3,128,128) of the original image size. It can also be regarded as the 17th frame image generated based on the first 16 frames, and the 17th frame image of the original sequence is used as the label to calculate the loss....
Sort the data in the following way:
Use creat_pathtxt.py to save the image path into a txt file for easy extraction during training. A sequence extracted from each line in txt. During training, each line of pictures is iterated in a loop, encoded and sent to LSTM training. The generated txt file is as follows:
The parameter seqsize can be changed in creat_pathtxt.py, the last picture of each sequence is the label by default, and the loss is calculated.
Set the training parameters in train.py, the main parameters are described as follows:
BATCH_SIZE: the number of pictures in each batch of training;
SEQ_SIZE: The number of pictures used for prediction in the sequence, which is 1 less than the number of pictures in each line of txt (note);
learning_rate: Trying this parameter several times works well;
epochs: The number of iterations, one hundred is enough.
Using GeForce RTX 2060 to train 100 rounds of 2000 images, it takes about 20 minutes.
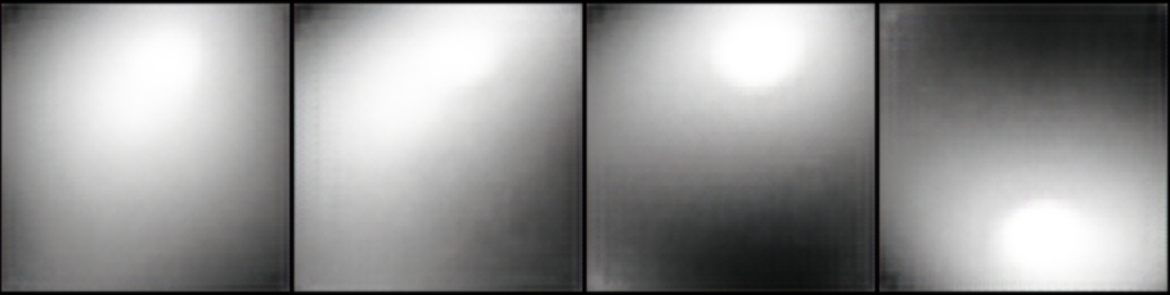
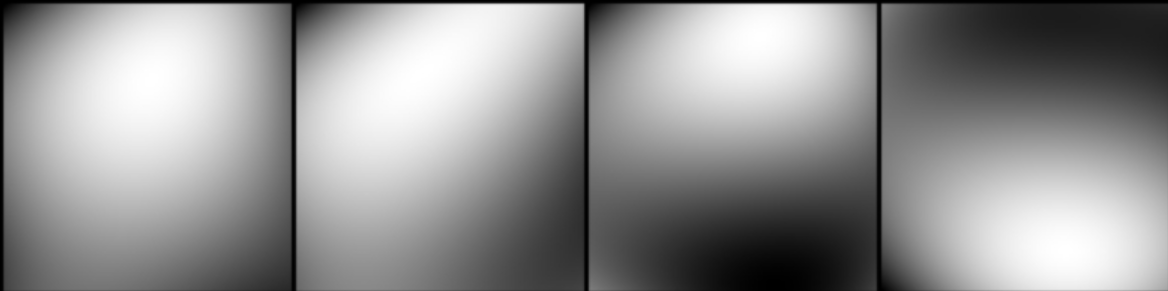
Run train.py, the decoded pictures and original pictures will be saved every 5 epochs of training, and stored in the folder conv_autoencoder. The following is a set of decoded pictures and original pictures:
decode_image
raw_image