The original LAB git repository is not ready for Docker and has some errors in compiler settings. I added a new Dockerfile, fixed some errors, and added a script to copy the training and testing datasets.
LAB uses Caffe and modified it to add new implementations. Here, a Dockerfile is prepared for LAB. Note that the original Caffe docker file (docker/gpu/Dockerfile) cannot be used. Also, note that README.md in the docker folder is outdated, so do not use it.
nvidia-docker is required. Refer to this link.
- Decide a base folder. In my case, I created the
LABfolder inside~/Documents/. Then create a Dockerfile.
$ vim Dockerfile
Copy the following text and paste to the Dockerfile. Then save it and quit vim.
FROM nvidia/cuda:8.0-cudnn6-devel-ubuntu16.04
LABEL maintainer caffe-maint@googlegroups.com
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
build-essential \
vim \
cmake \
git \
wget \
libatlas-base-dev \
libboost-all-dev \
libgflags-dev \
libgoogle-glog-dev \
libhdf5-serial-dev \
libleveldb-dev \
liblmdb-dev \
libopencv-dev \
libprotobuf-dev \
libsnappy-dev \
protobuf-compiler \
python-dev \
python-numpy \
python-pip \
python-setuptools \
python-scipy && \
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
ENV CAFFE_ROOT=/wywu/LAB
WORKDIR $CAFFE_ROOT
# FIXME: use ARG instead of ENV once DockerHub supports this
# https://github.com/docker/hub-feedback/issues/460
# ENV CLONE_TAG=1.0
# RUN git clone -b ${CLONE_TAG} --depth 1 https://github.com/BVLC/caffe.git . && \
RUN git clone https://github.com/jrkwon/LAB.git . && \
pip install --upgrade pip && \
cd python && for req in $(cat requirements.txt) pydot; do pip2 install $req; done && cd .. && \
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/nccl.git && cd nccl && make -j install && cd .. && rm -rf nccl && \
mkdir build && cd build && \
cmake -DUSE_CUDNN=1 -DUSE_NCCL=1 -DUSE_OPENMP=1 .. && \
make -j"$(nproc)"
ENV PYCAFFE_ROOT $CAFFE_ROOT/python
ENV PYTHONPATH $PYCAFFE_ROOT:$PYTHONPATH
ENV PATH $CAFFE_ROOT/build/tools:$PYCAFFE_ROOT:$PATH
RUN echo "$CAFFE_ROOT/build/lib" >> /etc/ld.so.conf.d/caffe.conf && ldconfig
WORKDIR $CAFFE_ROOT/workspace
- Create a local workspace folder to be shared with a Docker container that we will create.
$ mkdir workspace
Make sure that you are at the base folder (~/Documents/LAB) where the Dockerfile resides.
$ docker build . -t wywu/lab
Then, run the docker image to create a container named lab.
docker run --runtime=nvidia --rm --name lab -v $PWD/workspace:/wywu/LAB/workspace -it wywu/lab
After length installation process from the previous step, if you see the prompt like below,
root@0c01adc1d7e7:/wywu/LAB/workspace#
Now, LAB is ready to be used.
I prepared the training and test WFLW datasets and modified scripts for you in the Docker image.
Simply copy them to your corrent workspace folder.
root@0c01adc1d7e7:/wywu/LAB/workspace# cp -r ../workspace_temp/. .
Tada! You're all set.
Then, now you can test the model. As of the moment that I am writing this, not all test were successful.
bash ./scripts/test/run_test_on_wflw.sh final
root@0c01adc1d7e7:/wywu/LAB/workspace# cp -r ../scripts .
root@0c01adc1d7e7:/wywu/LAB/workspace# mkdir ./scripts/copy
root@0c01adc1d7e7:/wywu/LAB/workspace# vim ./scritps/copy/copy_wflw_images.sh
Then, copy the text below and save it.
# Copy images from ~/Download and untar
FILE=$1
TARGET_DIR=./datasets/$FILE
mkdir -p $TARGET_DIR
cp ~/Downloads/${FILE}_images.tar.gz $TARGET_DIR/.
TAR_FILE_ANNO=$TARGET_DIR/${FILE}_images.tar.gz
tar -zxvf $TAR_FILE_ANNO -C $TARGET_DIR
rm $TAR_FILE_ANNO
Download WFLW training and test datasets.
- WFLW Training and Testing images [Google Drive] [Baidu Drive]
Then, run the script below to copy the datasets and untar into a proper location.
bash ./scritps/copy/copy_wflw_images.sh WFLW
Download WFLW annotation datasets
bash ./scripts/download/download_wflw_annotation.sh WFLW
Download pretrained models:
bash ./scripts/download/download_wflw_model.sh WFLW
Replace the test script with followings. (The original test script has some errors).
#!/usr/bin/env bash
## parameter description
# --input_file_1: ground truth list of 98 landmarks
# --input_file_2: precomputed meanpose
# --input_folder: path of testing images
# --model_path: path of pretrained model
# --output_file_1: predicted list of 98 landmarks
# --label_num: 2 * num of landmarks
# --thread_num: number of threads
MODEL=$1
INPUT_FILE_1_DIR=./datasets/WFLW/WFLW_annotations/list_98pt_test
mkdir -p ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result
./build/tools/alignment_tools run_test_on_wflw --input_file_1=$INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_largepose.txt --input_file_2=../meanpose/meanpose_71pt.txt --input_folder=./datasets/WFLW/WFLW_images/ --model_path=./models/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}/ --output_file_1=./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_largepose.txt --label_num=196 --thread_num=12
echo "list 1 done"
./build/tools/alignment_tools run_test_on_wflw --input_file_1=$INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_expression.txt --input_file_2=../meanpose/meanpose_71pt.txt --input_folder=./datasets/WFLW/WFLW_images/ --model_path=./models/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}/ --output_file_1=./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_expression.txt --label_num=196 --thread_num=12
echo "list 2 done"
./build/tools/alignment_tools run_test_on_wflw --input_file_1=$INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_illumination.txt --input_file_2=../meanpose/meanpose_71pt.txt --input_folder=./datasets/WFLW/WFLW_images/ --model_path=./models/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}/ --output_file_1=./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_illumination.txt --label_num=196 --thread_num=12
echo "list 3 done"
./build/tools/alignment_tools run_test_on_wflw --input_file_1=$INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_makeup.txt --input_file_2=../meanpose/meanpose_71pt.txt --input_folder=./datasets/WFLW/WFLW_images/ --model_path=./models/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}/ --output_file_1=./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_makeup.txt --label_num=196 --thread_num=1
echo "list 4 done"
./build/tools/alignment_tools run_test_on_wflw --input_file_1=$INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_occlusion.txt --input_file_2=../meanpose/meanpose_71pt.txt --input_folder=./datasets/WFLW/WFLW_images/ --model_path=./models/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}/ --output_file_1=./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_occlusion.txt --label_num=196 --thread_num=12
echo "list 5 done"
./build/tools/alignment_tools run_test_on_wflw --input_file_1=$INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_blur.txt --input_file_2=../meanpose/meanpose_71pt.txt --input_folder=./datasets/WFLW/WFLW_images/ --model_path=./models/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}/ --output_file_1=./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_blur.txt --label_num=196 --thread_num=12
echo "list 6 done"
./build/tools/alignment_tools run_test_on_wflw --input_file_1=$INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test.txt --input_file_2=./meanpose/meanpose_71pt.txt --input_folder=./datasets/WFLW/WFLW_images/ --model_path=./models/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}/ --output_file_1=./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_test.txt --label_num=196 --thread_num=12
echo "list 7 done"
cat $INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_largepose.txt $INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_expression.txt $INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_illumination.txt $INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_makeup.txt $INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_occlusion.txt $INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test_blur.txt $INPUT_FILE_1_DIR/list_98pt_test.txt > ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/gt_release.txt
cat ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_largepose.txt ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_expression.txt ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_illumination.txt ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_makeup.txt ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_occlusion.txt ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_blur.txt ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_98pt_test.txt > ./evaluation/WFLW/WFLW_${MODEL}_result/pred_release.txt
Then, now you can test the model. As of the moment that I am writing this, not all test were successful.
#! ./scripts/test/run_test_on_wflw.sh
bash ./scripts/test/run_test_on_wflw.sh final
bash ./scripts/test/run_test_on_wflw.sh wo_mpThe testing results will be saved to text files here: ./evaluation/WFLW/.
Created by Wayne Wu at Tsinghua University.
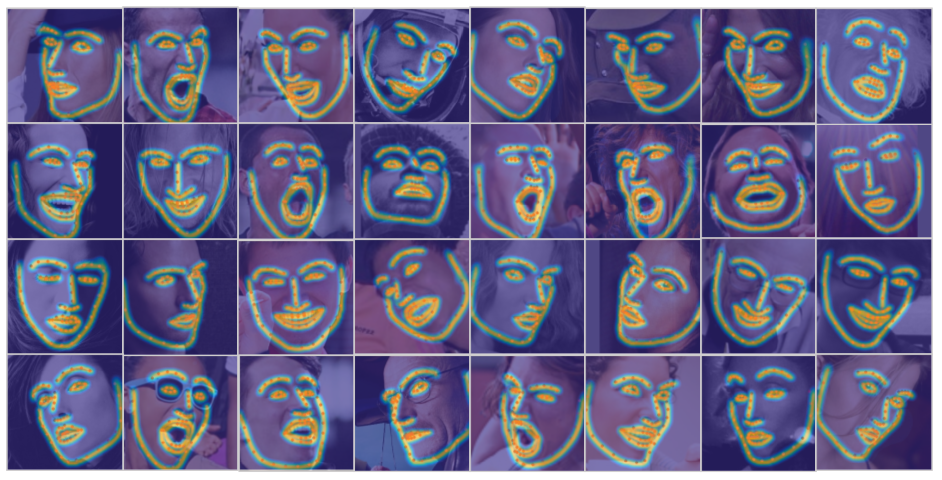
We present a novel boundary-aware face alignment algorithm by utilising boundary lines as the geometric structure of a human face to help facial landmark localisation. Unlike the conventional heatmap based method and regression based method, our approach derives face landmarks from boundary lines which remove the ambiguities in the landmark definition. Three questions are explored and answered by this work: 1. Why use boundary? 2. How do you use boundary? 3. What is the relationship between boundary estimation and landmarks localisation?
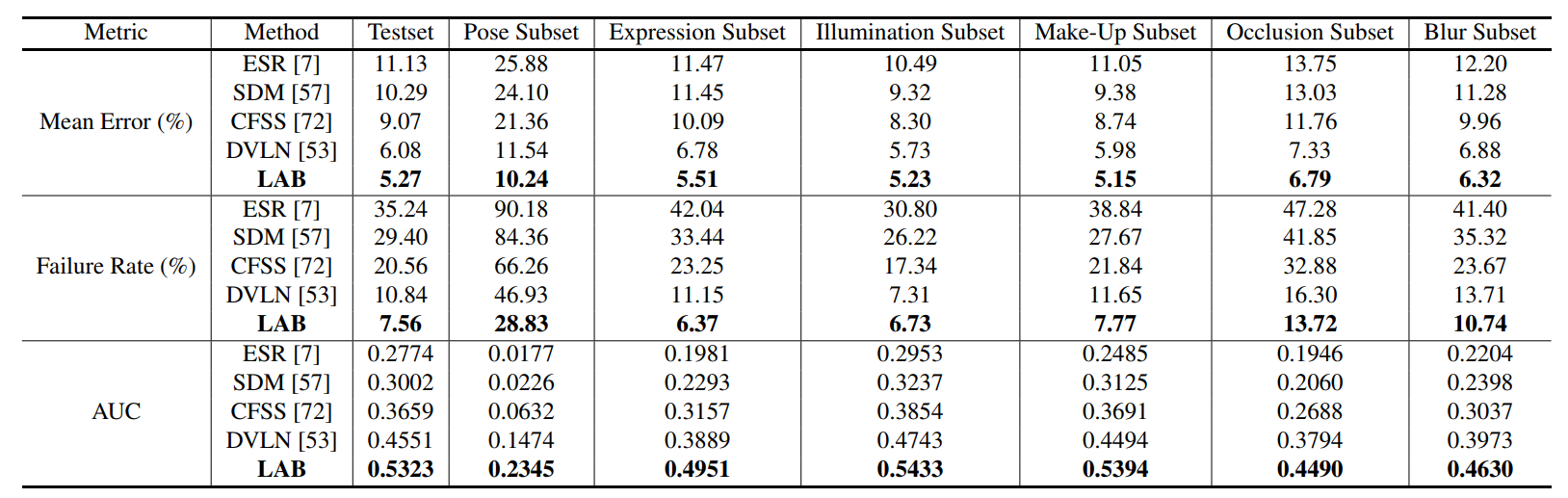
Our boundary-aware face alignment algorithm achieves 3.49% mean error on 300-W Fullset, which outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin. Our method can also easily integrate information from other datasets. By utilising boundary information of 300-W dataset, our method achieves 3.92% mean error with 0.39% failure rate on COFW dataset, and 1.25% mean error on AFLW-Full dataset. Moreover, we propose a new dataset Wider Facial Landmark in the Wild (WFLW) to unify training and testing across different factors, including poses, expressions, illuminations, makeups, occlusions, and blurriness. A detailed description of the system can be found in our paper.
If you use this code or WFLW dataset for your research, please cite our papers.
@inproceedings{wayne2018lab,
author = {Wu, Wayne and Qian, Chen and Yang, Shuo and Wang, Quan and Cai, Yici and Zhou, Qiang},
title = {Look at Boundary: A Boundary-Aware Face Alignment Algorithm},
booktitle = {CVPR},
month = June,
year = {2018}
}
- Linux
- Python 2 or 3
- CPU or NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN
- Install prerequisites for Caffe (http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/installation.html#prequequisites)
- Modified-caffe for LAB (https://github.com/wywu/LAB.git)
Wider Facial Landmarks in-the-wild (WFLW) is a new proposed face dataset. It contains 10000 faces (7500 for training and 2500 for testing) with 98 fully manual annotated landmarks.
- WFLW Training and Testing images [Google Drive] [Baidu Drive]
- WFLW Face Annotations
- Unzip above two packages and put them on './datasets/WFLW/'
Simply run this script to download annotations of WFLW
#! ./scripts/download/download_wflw_annotation.sh
bash ./scripts/download/download_wflw_annotation.sh WFLWWe supply two pretrained models:
WFLW_final: The final model evaluated on WFLW in the paper.
WFLW_wo_mp: The simplified model without Message Passing layer which is much easier to read.
- Download pretrained models: WFLW_final and WFLW_wo_mp.
#! ./scripts/download/download_wflw_model.sh
bash ./scripts/download/download_wflw_model.sh WFLW- Test the model:
#! ./scripts/test/run_test_on_wflw.sh
bash ./scripts/test/run_test_on_wflw.sh final
bash ./scripts/test/run_test_on_wflw.sh wo_mpThe testing results will be saved to text files here: ./evaluation/WFLW/.
For company security considerations, it is with regret that we are not allowed to release the training scripts. However, for training, all you need to do is using this released code and adding data augmentation described in the paper. Taking the released prototxt file as reference and using the hyper-parameters described in the paper, we think it is easy to reproduce the reported performance. If you have any question about the training process, please feel free to contact us.
Supported dataset
- Wider Facial Landmark in the Wild (WFLW)
- Annotated Facial Landmarks in the Wild (AFLW)
- Caltech Occluded Faces in the Wild (COFW)
- 300 Faces In-the-Wild (300W)
Supported models
Please contact wuwenyan0503@gmail.com