Scripts created for post-processing X-shooter reductions.
If you find any bugs or missing features, please let me know at jselsing@nbi.ku.dk
The two main scripts in the package are XSHcomp.py and XSHextract.py. These take care of combinations of individual exposures and 1D-extractions respectively. The idea is that the ESO X-shooter pipeline, http://www.eso.org/sci/software/pipelines/, is used to reduce all observations in STARE-mode, and then the scripts provided here, do combinations and extractions where the X-shooter pipeline can be improved.
Install the ESO pipelines through macports. Install instructions are available at https://www.eso.org/sci/software/pipelines/installation/macports.html.
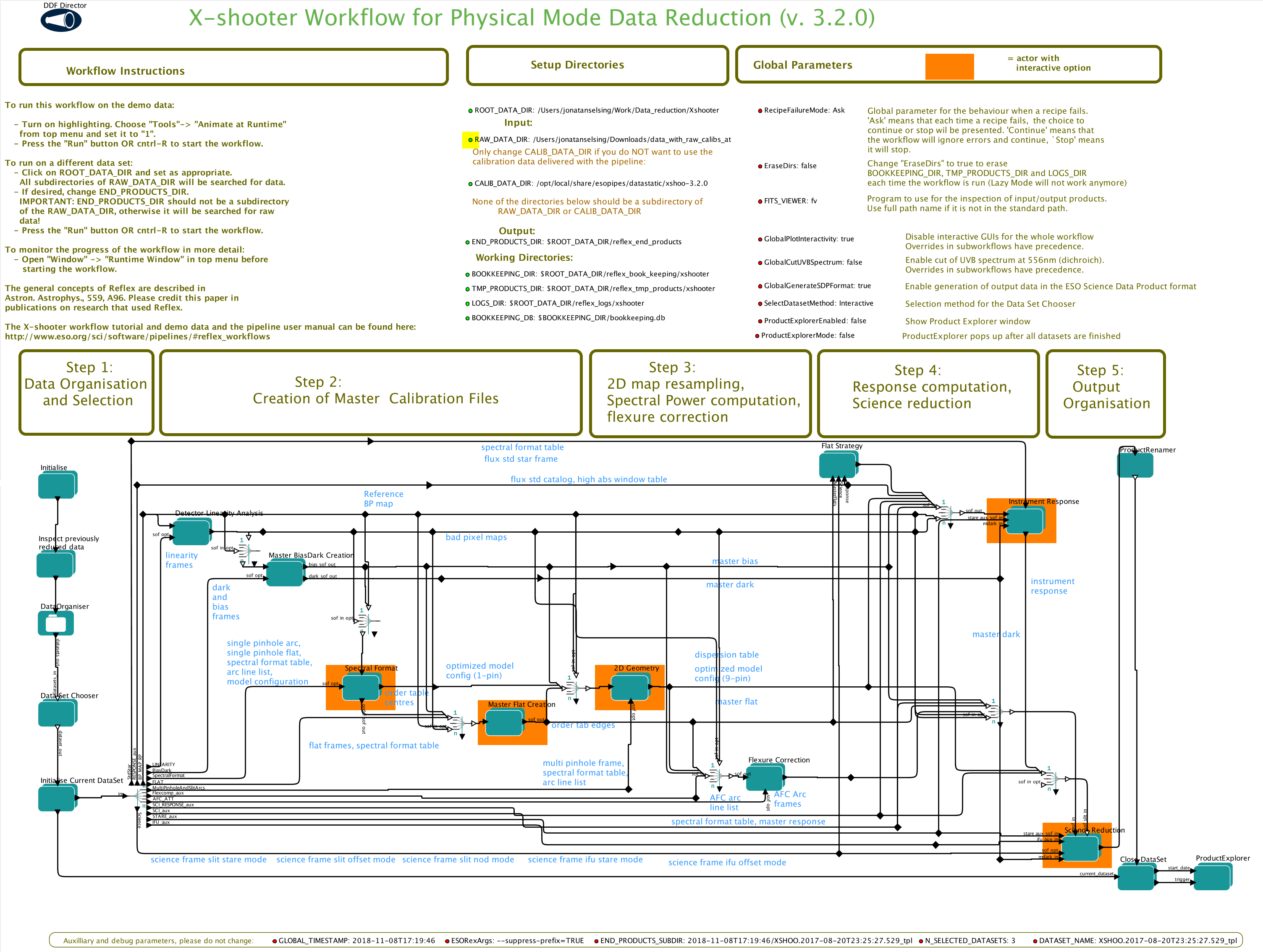
The workflow used for these X-shooter reductions can be downloaded from this repository. The file ESO/xsh_workflow_320.kar contains a workflow. When esoreflex and installed and the workflow is loaded into Kepler (ESO workflow engine), it should look something like this:
Follow the instrutions printed on the workflow. Most importantly set the RAW_DATA_DIR to the folder containing your unzipped data. The workflow provided here has been preconfigured to reduce the observations in STARE-mode.
During processing of the workflow, two quality-control windows are shown. The flux-standard reduction where the response function is computed and the science object reduction. The flux-standard window should be inspected for agreement between the blue and the green lines, signifying that the standard star has been adequately calibrated. The blue line is the nightly, flux-calibrated standard star and the green line tabulated flux for this star.
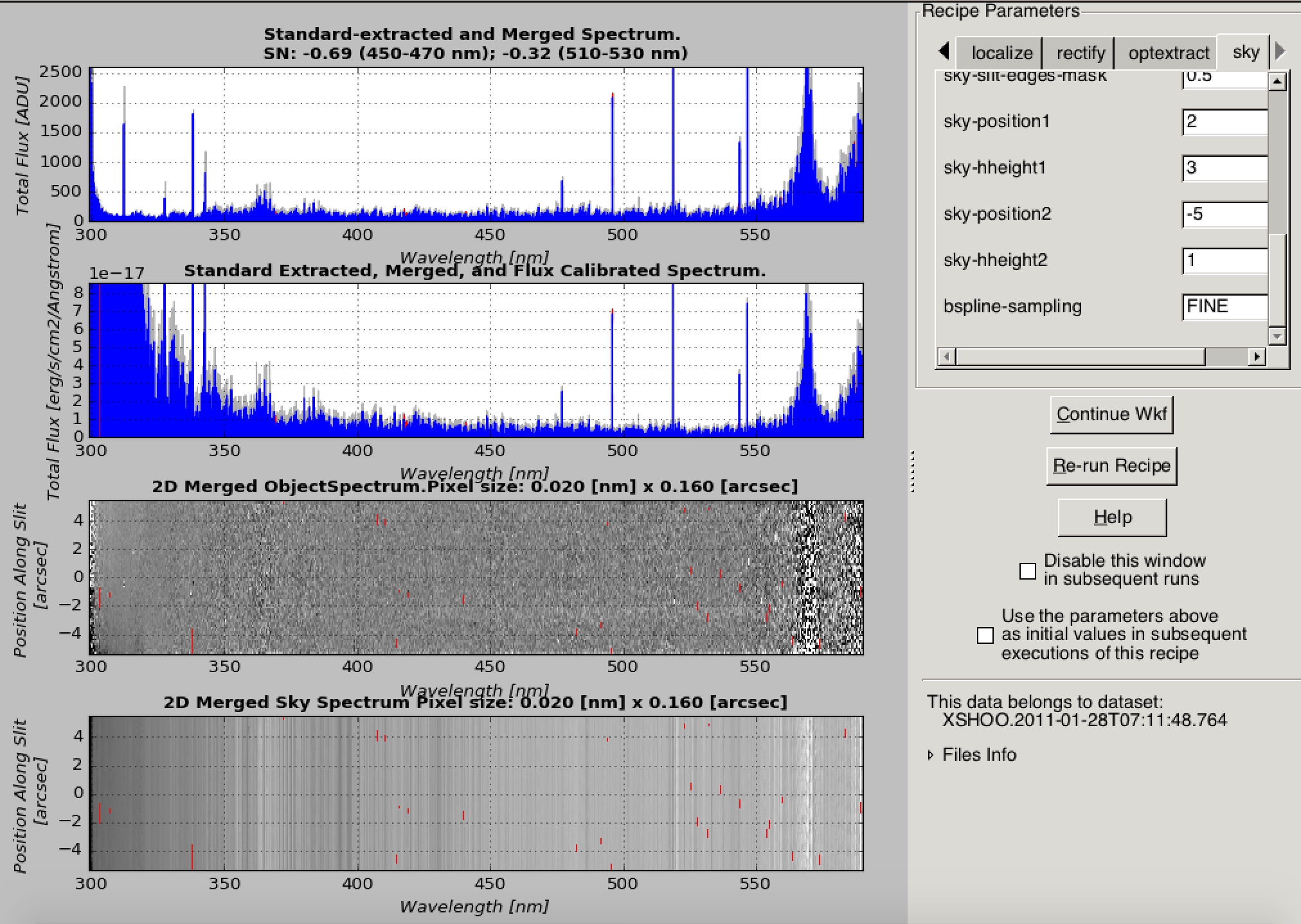
For the science reduction, mainly the sky regions should be set for each element in the nodding sequence. It could look something like this, where a faint trace of the afterglow is visible, centered at -2.5 arcsec. The sky is specified using the sky_position and sky-hheight. For this example, two sky windows have been chosen, one at 2 arcsecond with a half-height of 3 arcseconds, and one at -5 arcsec with a 1 arcsec half-height.
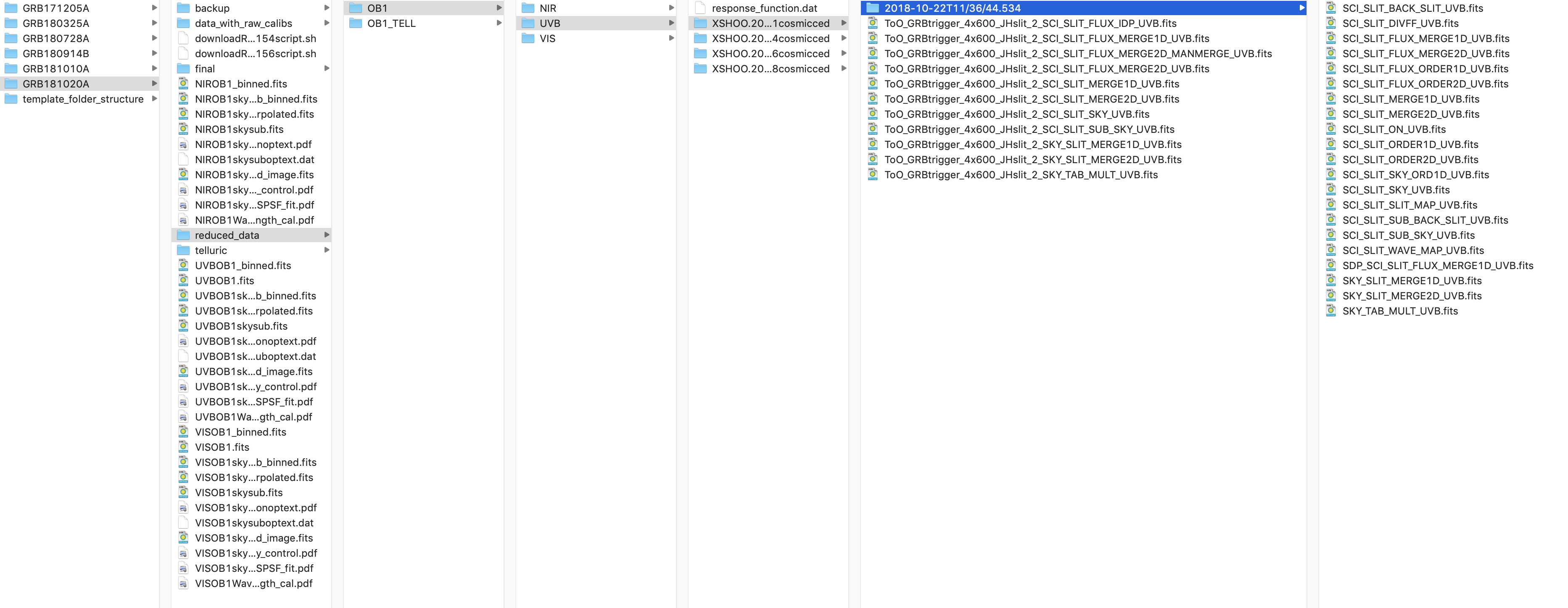
Each complete nodding sequence will produce 4 individual reductions for each arm. The scripts aims at combining these reductions. A specific directory structure makes the combinations much easier. The structure is shown here.
This is a bit cumbersome, as we need to work with files that ESO puts in the reflex_tmp_products/xshooter/xsh_scired_slit_stare_1 and in reflex_end_products. It is easiest to keep track of the files if the files from each
When this directory structure is used, the scripts can be used.
To use the script, clone and download this repository (or download the .zip).
There are a few dependences, which using https://www.anaconda.com/download/, can be easily set up.
The included conda environment file can be setup using:
conda-env create -f xsh_env.yml
This will create a anaconda environment named xsh_env.
Activate the conda environment using:
conda activate xsh_env
There is single dependence, which must be installed. With the xsh_env active, run:
pip install git+https://github.com/karllark/dust_extinction.git
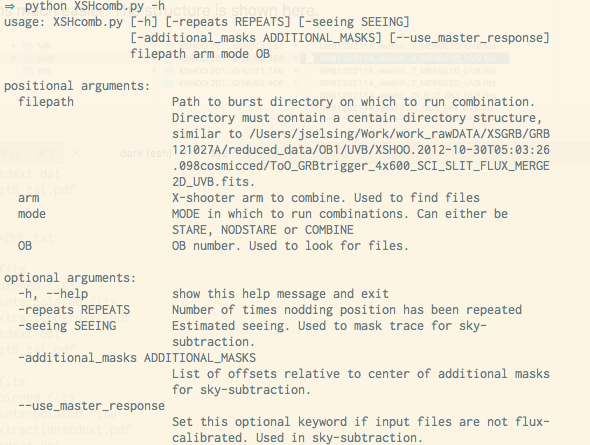
example usage
$ python XSHcomb.py /Users/jonatanselsing/Work/work_rawDATA/Crab_Pulsar/ UVB STARE OB9 $
and
$ python XSHextract.py /Users/jonatanselsing/Work/work_rawDATA/Crab_Pulsar/UVBOB9skysub.fits --optimal $
Copyright 2016-2020 Jonatan Selsing and contributors.
These scripts are free software made available under the GNU License. For details see the LICENSE file.