Using Google cloud types along with artifacts allow users to store metadata automatically as they are created.
In pipelines-with-metadata, users will create two custom components
- The first component will create a BQTable artifact subclass
- The second component will read the data and store a csv extract to gcs in the form of a custom artifact
@component(
base_image='python:3.9',
packages_to_install=[
'google.cloud.bigquery'
,'google.cloud.storage'
,'pandas'
,'google_cloud_pipeline_components'
,'db-dtypes'
],
)
def save_schedule_to_gcs(
bq_table: Input[BQTable],
project_id: str,
bucket_name: str,
destination_blob_name: str,
region: str = 'us-central1'
) -> NamedTuple('outputs'
, pandas_data=Artifact)
...
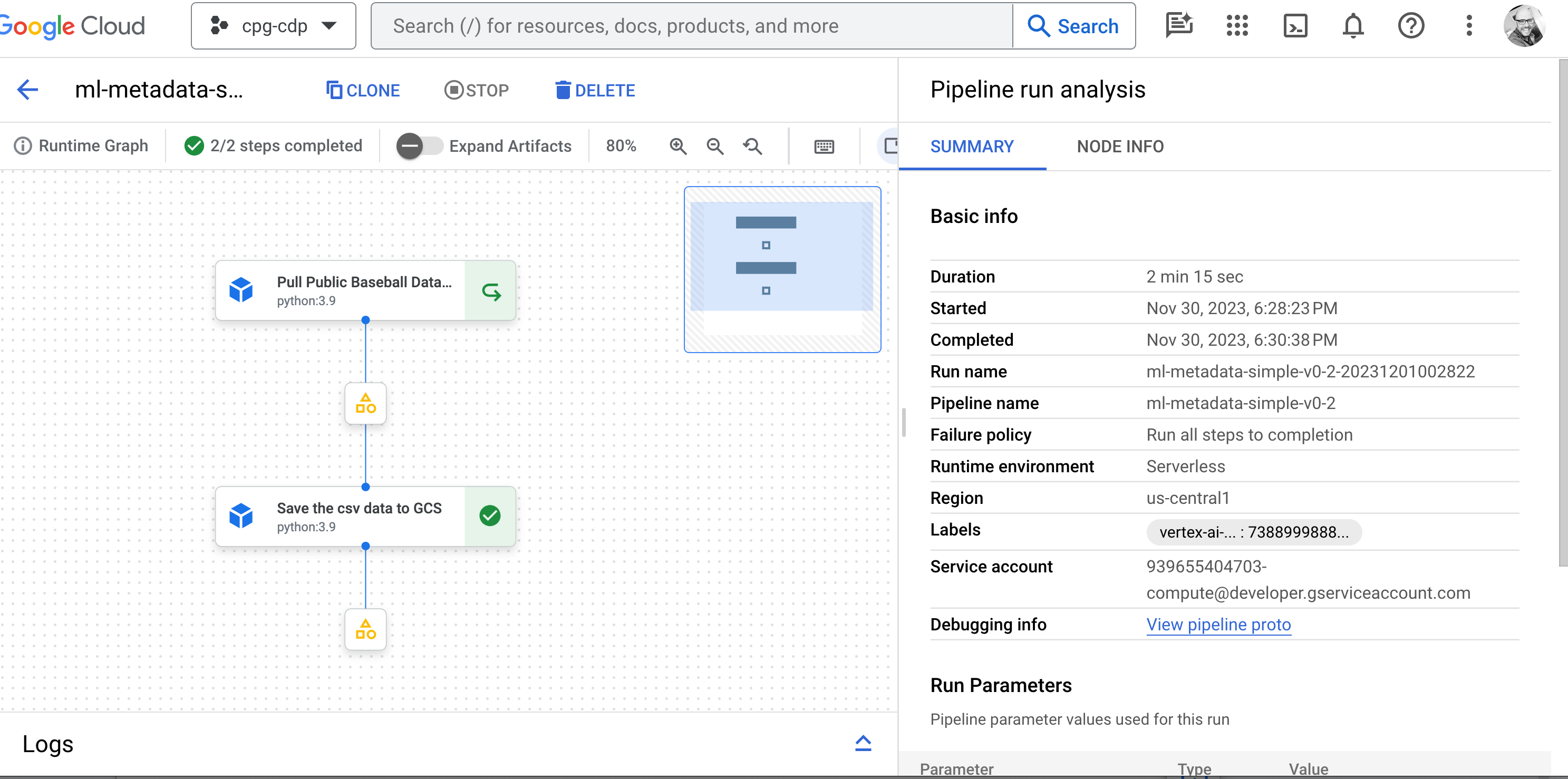
return (pandas_data, )To get an understanding of how the pipeline components connect, the DAG is developed using outputs and inputs:
pull_baseball_data_op = pull_baseball_data(
year = year,
project_id = project_id,
dataset_id = dataset_id,
output_table_name = output_table_name
).set_display_name("Pull Public Baseball Data Schedules")
save_schedule_pandas_gcs_op = save_schedule_to_gcs(
bq_table = pull_baseball_data_op.outputs['bq_table'],
project_id = project_id,
bucket_name = bucket_name,
destination_blob_name = destination_blob_name
).set_display_name("Save the csv data to GCS")pull_baseball_data_op.outputs['bq_table'] is an example of pulling the output artifact from the component.
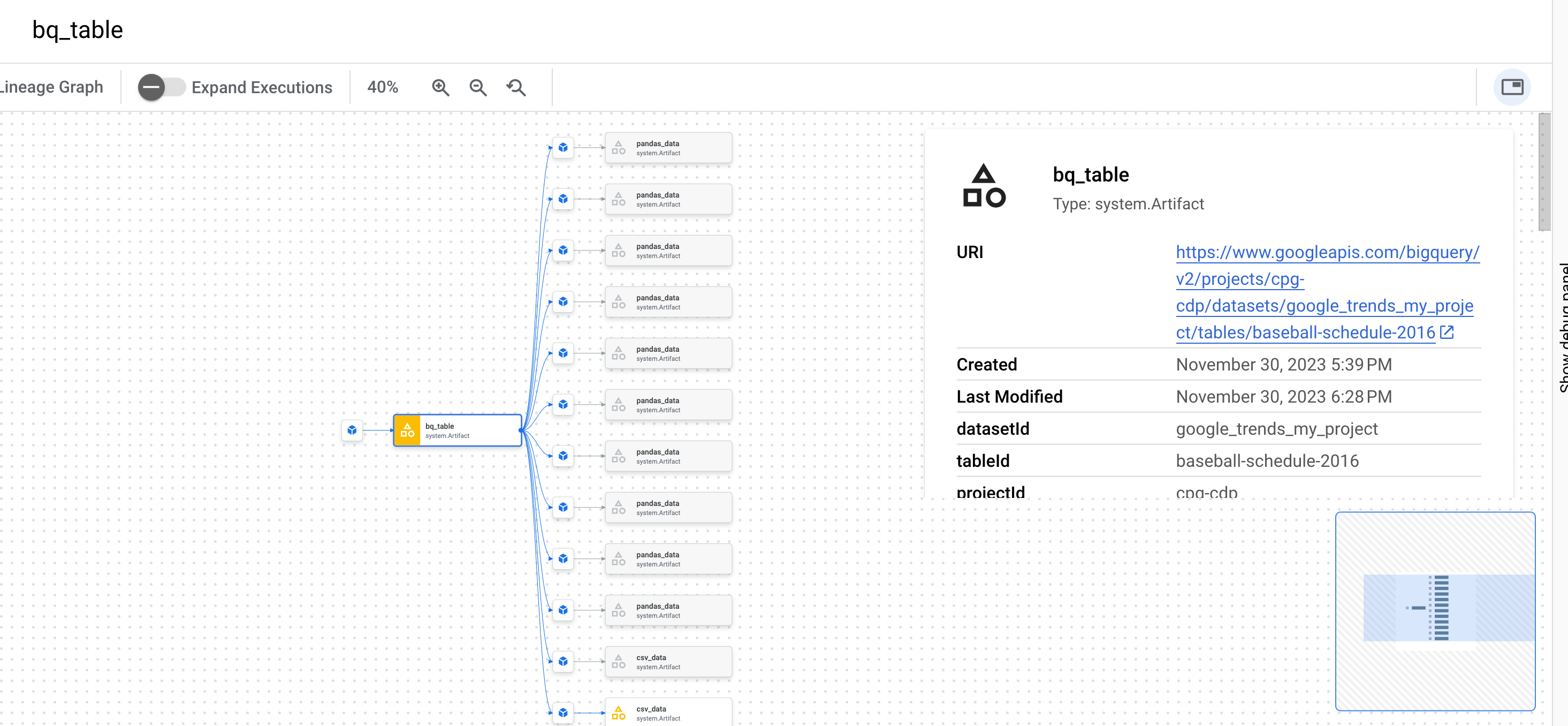
Be sure to select an artifact and click on view lineage:
Official guide here Notebook [here](./Intro to Vertex Pipelines.ipynb)