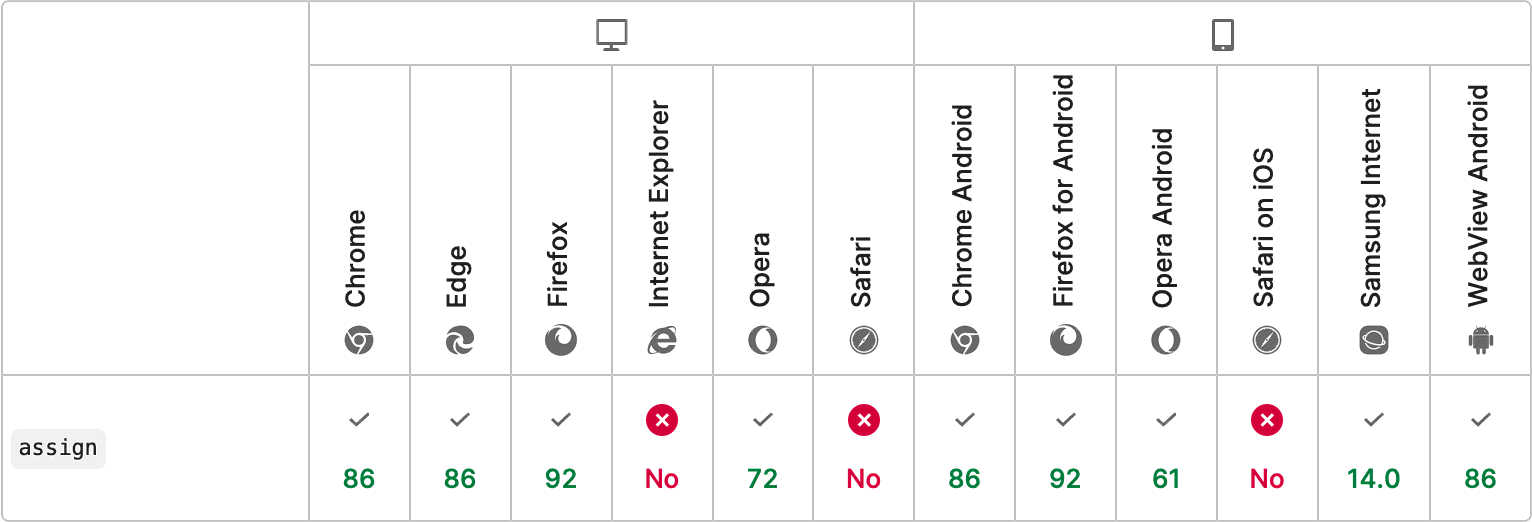
DOM Slot Assign is a polyfill that allows you to use imperative slot assignment, following the HTML specification.
Include DOM Slot Assign in your project.
import "https://unpkg.com/dom-slot-assign@0.1"<script src="https://unpkg.com/dom-slot-assign@0.1"></script>If you're ok with slightly reduced browser support, you can include it conditionally, only when needed:
if (!globalThis?.HTMLSlotElement?.prototype.assign) {
await import("https://unpkg.com/dom-slot-assign@0.1");
}You can also use npm:
// npm install dom-slot-assign
import "dom-slot-assign"That’s it. Now use imperative slotting in your project.
This example creates a <content-tabs> element. From its children, any <h1> - <h6> element generates a new <details> / <summary> in its shadow dom, with the heading slotted into the summary. Any content after that heading and before the next heading is added as content to the current details.
customElements.define('content-tabs', class extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
let host = super()
let root = host.attachShadow({ mode: 'open', slotAssignment: 'manual' })
root.innerHTML += '<style>::slotted(:is(h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6)) { display: contents; pointer-events: none; }</style>'
if (host.childNodes.length) host.contentChangedCallback()
new MutationObserver(() => host.contentChangedCallback()).observe(host, { childList: true })
}
contentChangedCallback() {
let root = this.shadowRoot
let [ style ] = root.childNodes
let details, summary, content
// clear the shadow root
root.replaceChildren(style)
// for each slottable child
for (let node of this.childNodes) {
// ignore leading text nodes
if (!details && node.nodeType !== 1) continue
// create new summary details with headings
if (node instanceof HTMLHeadingElement) {
details = root.appendChild(document.createElement('details'))
summary = details.appendChild(document.createElement('summary'))
summary.appendChild(document.createElement('slot')).assign(node)
content = undefined
} else {
// put adjacent comments in summary details below headings
content = content || details.appendChild(document.createElement('slot'))
content.assign(...content.assignedNodes(), node)
}
}
}
})When the <slot> element lacks an assign() method, the polyfill is activated.
An assign() method works by detecting whether the given slot belongs to a shadow root with manual slot assignment
If it does, it assigns a unique name to the given slot, which is never actually used.
Then, each assigned Element node has its slot set a separate, private slot, which is then appended to the given slot.
<#shadow-root>
<!-- public slot created by the user -->
<slot name="">
<slot style="display:contents!important" name="">
<!-- private slot for the first element -->
</slot>
<slot style="display:contents!important" name="">
<!-- private slot for the second element -->
</slot>
<slot style="display:contents!important" name="">
<!-- private slot for the N element -->
</slot>
</slot>
</#shadow-root>Assigned Text nodes are cloned and each clone is placed inside a private slot, which is also appended to the given slot.
The original text nodes are observed for DOMCharacterDataModified and DOMNodeRemoved to update or remove the clone.
<#shadow-root>
<!-- public slot created by the user -->
<slot name="">
<slot style="display:contents!important" name="">
<!-- private slot for the first element -->
</slot>
<slot style="display:contents!important" name="">
<!-- private slot for the second element -->
</slot>
<slot style="display:contents!important" name="">
A cloned text node.
</slot>
<slot style="display:contents!important" name="">
<!-- private slot for the N element -->
</slot>
</slot>
</#shadow-root>A new assignedNodes() method returns an array of all nodes privately assigned to the slot that are still connected.
A new assignedElements() method returns an array of all elements privately assigned to the slot that are still connected.
An overriding attachShadow() method detects the slotAssignment: "manual" option and enables slot elements within the given shadow root to support the assign method.
To prevent any accidental ‘named’ slot assignments, the shadow root is observed for slotchange to enforce the manual assignment.