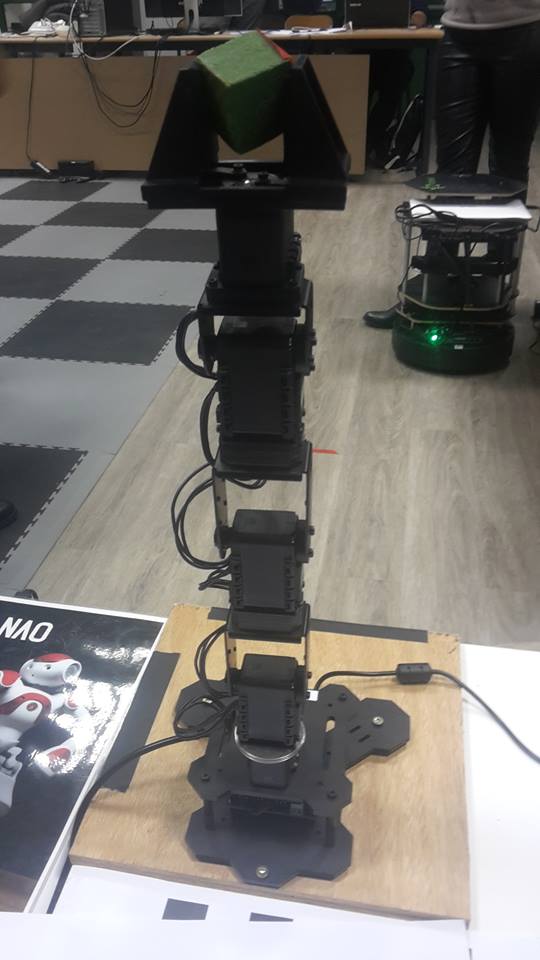
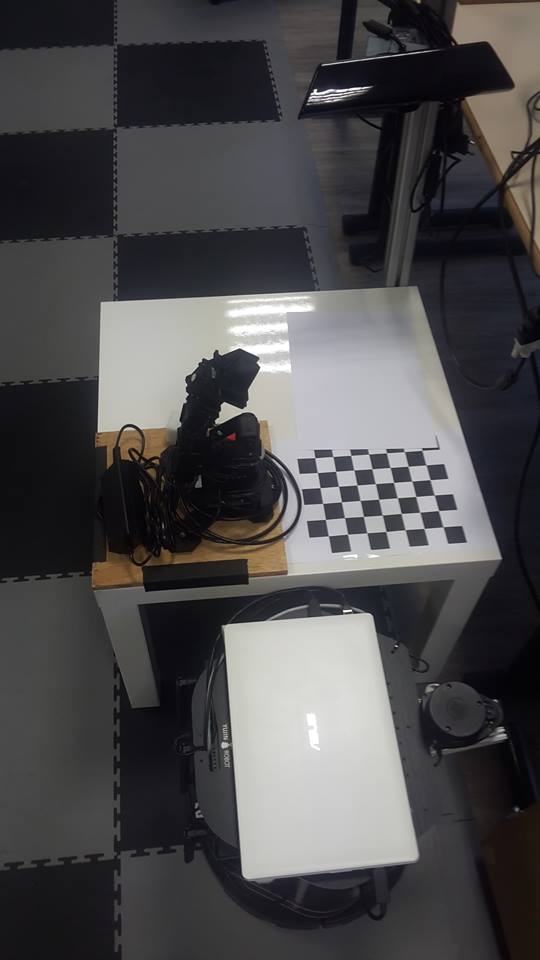
This project is part of larger project, where multiple robit is working together to implement a larger scenario. First the turtlebot have to navivate to the loading area. When the robot is at the right spot, an arm must pick a green cube and put it on the robot base. Then the robot must navigate to the drop area. When in place the green cube must take the cube and place it in the drop area. We focus on the pick and place tasks. The phantom pincherX is a controllable robotic arm but there is no camera on itself. We use the kinect sensor to locate the object and do the pick and place task.
- Turtlebot with PincherX project
- Packages installation and setup
- Getting started
- Calibration
- Path planning
- Block detection and manipulation:
- Videos:
- Contributions problems and conclusion
The ROS packages in the repository :
-
turtlebot_arm
The turtlebot arm meta package
More info at http://ros.org/wiki/turtlebot_arm -
turtlebot_arm_block_manipulation
The turtlebot_arm_block_manipulation contains our working demo, as well as, a demo allowing the TurtleBot arm to manipulate small blocks on a level surface using interactive markers.
More info at http://ros.org/wiki/turtlebot_arm_block_manipulation -
turtlebot_arm_bringup
Provides launch files for starting the drivers for the TurtleBot arm.
More info at http://ros.org/wiki/turtlebot_arm_bringup -
turtlebot_arm_description
This package contains URDF files and meshes for the TurtleBot arm.
More info at http://ros.org/wiki/turtlebot_arm_description -
turtlebot_arm_ikfast_plugin
IKFast61 plugin for closed-form kinematics
More info at http://ros.org/wiki/turtlebot_arm_ikfast_plugin -
turtlebot_arm_kinect_calibration
This package, allows calibration of a kinect to a TurtleBot arm, including a kinect on-board and off-board the TurtleBot for more precise manipulation. More info at http://ros.org/wiki/turtlebot_arm_kinect_calibration -
turtlebot_arm_moveit_config
An automatically generated package, using movit wizard, with all the configuration and launch files for using the turtlebot_arm with the MoveIt Motion Planning Framework
More info at https://github.com/turtlebot/turtlebot_arm and http://moveit.ros.org/ -
turtlebot_arm_moveit_demos
The turtlebot_arm_moveit_demos package contains scripts to start playing with a turtlebot arm and MoveIt. More info at http://ros.org/wiki/turtlebot_arm_moveit_demos
All the packages is compatible with the ros indigo distribution. Arbotix must be at V10.0 or better.
The repository also contains tmux scripts to automatate sessions in folder scripts, bash and zsh configuration files in the same folder. Also, the images direcory contains images used in this readme.
The repository must be cloned first and the packages must be compiled at the target machine. On target machine a ros indigo installation with moveit, rviz, arbotix and alll required packages must be installed first. An indigo compatible ubuntu based distribution is recomended.
cd ~/ros/indigo/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/jtsagata/turtlebot_arm
cd .. && catkin_make
We had issues with the robot description so this repository is a merge from code taken from
The setup is composed of several parts. We have a table where is disposed the robotic arm, this table will be our station where we will let the object to be picked up. We also have the kinect on a stake to have the view on our robot table. The last object used will be a turtlebot, for us the turtlebot will be another work platform. It will be considered as a motionless platform because we are not supposed to manage the robot movement on this project. The hardware setup is showed in the figure.
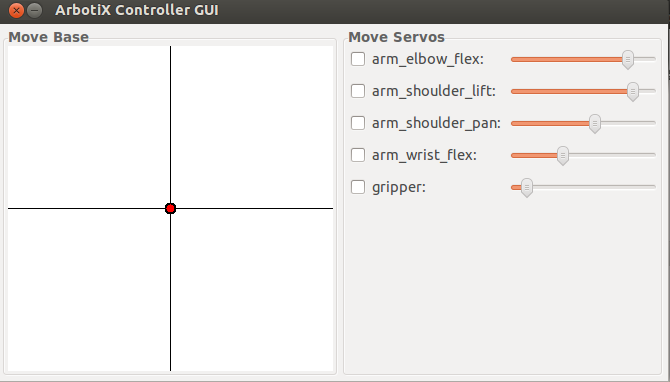
The arm architecture is described in a yaml file. USB port, number of joints, limits...
port: /dev/ttyUSB0
read_rate: 15
write_rate: 25
joints: {
arm_shoulder_pan_joint: {id: 1, neutral: 205, max_angle: 180, min_angle: -60, max_speed: 90},
arm_shoulder_lift_joint: {id: 2, max_angle: 150, min_angle: -150, max_speed: 90},
arm_elbow_flex_joint: {id: 3, max_angle: 150, min_angle: -150, max_speed: 90},
arm_wrist_flex_joint: {id: 4, max_angle: 100, min_angle: -100, max_speed: 90},
gripper_joint: {id: 5, max_angle: 0, min_angle: -180, max_speed: 90}
}
controllers: {
arm_controller: {type: follow_controller, joints: [arm_shoulder_pan_joint,
arm_shoulder_lift_joint, arm_elbow_flex_joint, arm_wrist_flex_joint],
action_name: arm_controller/follow_joint_trajectory, onboard: False }
}
The port parameter must be the correct one. One way to find it if to run the command
tail -f /var/log/syslog
and connect the arm to the controlling PC. The device port must be writeable and redaable by the user, by a custom udev rule, or by issuing the command, at the beggining of every user session, with the correct TTY device.
sudo chmod a+rw /dev/ttyUSB0
For more information, see ROS by examples vol.2 (http://wiki.ros.org/Books/ROSbyExampleVol2) for further information.
Choose a launcher
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_bringup arm.launch
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_bringup arm_sim.launch
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_bringup arm_calibrated.launch
and then
rosrun arbotix_python arbotix_gui
The first time the robot is uncalibrated so choose the arm_sim.launch for running a simulation or arm.launch to control the real robot.
The PincherX have no camera attached. So a calibration step is nessesery in order to calculate camera extrinsic parameters and then provide a tf transform from the object coordinates for the object detection to PincherX coordinate system.
-
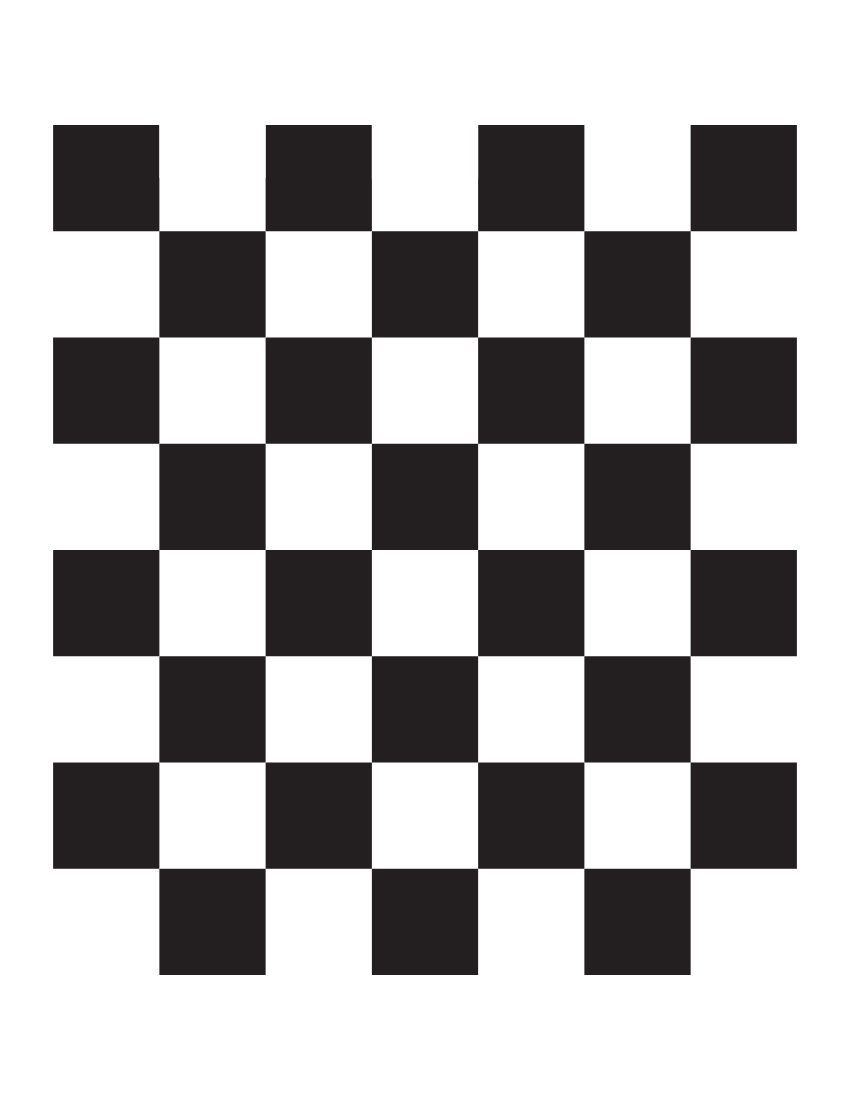
Calibration checkerboard (7x6 27mm) witch can be downloaded from the repository here.
Be sure to print the pdf version and measure it before use. -
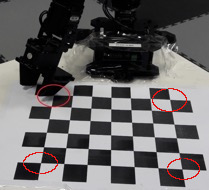
The complete checkerboard have to be in the kinect field of view
-
Verify that the arm can reach every point on the checkerboard
-
Verify that servo-motors for the wrist and the one for the shoulder spin on the same side.
-
Use the left side of the gripper for calibrating the setup
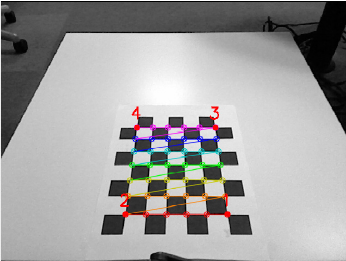
For our task,to do the arm calibration we have to move the arm to 4 possitions in a checker board pattern. From the state of the arm we can calculate the coordinate transformation.
First start up the kinect and the arm
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_bringup arm.launch
and then launch the calibration program
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_kinect_calibration calibrate.launch
First, this should detect the checkerboard and pop up the calibration image , with the calibration pattern edges overlaid and four points marked on the image.
Follow the terminal instructions say, move the right part of the open gripper to the four specified points.
[ INFO] [1507636573.094797721]: [calibrate] Initialized.
[ INFO] [1507636573.464054472]: [calibrate] Got image info!
Got an image callback!
Is the checkerboard correct?
Move edge of gripper to point 1 in image and press Enter
[....]
After moving to the fourth point, the calibration script will output something like the following:
Resulting transform (camera frame -> fixed frame):
0.103775 0.992602 0.0630181 -0.202959
0.841407 -0.0538294 -0.537714 0.153275
-0.530344 0.108825 -0.840769 1.01224
0 0 0 1
Resulting transform (fixed frame -> camera frame):
-0.530344 0.108825 -0.840769 1.01224
-0.103775 -0.992602 -0.0630182 0.157959
-0.841407 0.0538295 0.537714 -0.153275
4.59135e-41 4.58869e-41 4.58869e-41 1
Static transform publisher (use for external kinect):
rosrun tf static_transform_publisher x y z qx qy qz qw frame_id child_frame_id period_in_ms
rosrun tf static_transform_publisher 0.424262 0.0548834 0.943436 -0.480766 -0.00262613 0.874737 0.0607612 /base_link /camera_link 100
URDF output (use for kinect on robot):
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot>
<property name="turtlebot_calib_cam_x" value="0.424262" />
<property name="turtlebot_calib_cam_y" value="0.0548834" />
<property name="turtlebot_calib_cam_z" value="0.943436" />
<property name="turtlebot_calib_cam_rr" value="-0.116664" />
<property name="turtlebot_calib_cam_rp" value="0.998702" />
<property name="turtlebot_calib_cam_ry" value="2.9392" />
<property name="turtlebot_kinect_frame_name" value="base_link" />
</robot>
In directory turtlebot_arm/turtlebot_arm_kinect_calibration/launch/ it will create 2 files
-
calibration_properties_calibrated.xml
-
transformation_calibrated.launch
The generated launcher is then inserted in other launch files and the tf transformation is automaticaly applied by the _caliberated launchers.
The ROS package called MoveIt! addresses almost all aspects of mobile manipulation including Motion Planning, Kinematics, Collision Checking, Grasping, Pick and Place, and Perception. The commands given bellow allow us to move the end effector to a given possition, calculate the kinematics and issue the commads to the arm. The URDF files and the turtlebot_arm_moveit_config package that have been created provides the arm description that MoveIt needs.
The kinematics.yaml file configures the kinematics solver.
kinematics_solver: turtlebot_arm_arm_kinematics/IKFastKinematicsPlugin
kinematics_solver_search_resolution: 0.005
kinematics_solver_timeout: 0.005
kinematics_solver_attempts: 3
To do path planning in simulation mode issue the commands
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_moveit_config arm_sim.launch
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_moveit_config turtlebot_arm_moveit.launch
To do path planning with the real robbot issue the commands
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_bringup arm_calibrated.launch
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_moveit_config turtlebot_arm_moveit.launch
MoveIt can also controlled from the command line using the following command
rosrun moveit_commander moveit_commander_cmdline.py
This BlockDetectionServer takes the detection map from the kinect, and filter it by height, leaving only the points between the table height and the predetermined block size value. Then the points if filterd to in order to get only the elements that are on top of the table. By clustering the remaining points we get a list of possible objects and select the target based on his dimensions. Because the algorithm can detect also the arm itself before we move the arm out of the view.
The InteractiveManipulationServer class which will show some 3D representations of the detected blocks in RViz and the user can click an object to order to grab the choosen object.
The algorithm steps is
-
Open gripper, so it can pick the object
-
Rotate arm towards block’s position
The arm is moved at the xy position of the block, while keeping the arm Z position higher than the block. -
Move arm down to block’s z position
-
Close gripper and tightly grab the block.
-
Lift arm up
-
Rotate arm towards the turtlebot position
-
Move arm down to final z’s position
-
Open gripper and release the object
-
Lift arm up and allow the turtlebot to move
To luanch the pick and place demo.
roslaunch turtlebot_arm_block_manipulation block_manip_complete.launch
We had problems with the robot model, and we spend alot of time figuring how the parts or the ros ecosystem is connected. So we had limited time left to tune the procedure. Our main contributions is on the automation of the launcher files and provide a working move it configuration.