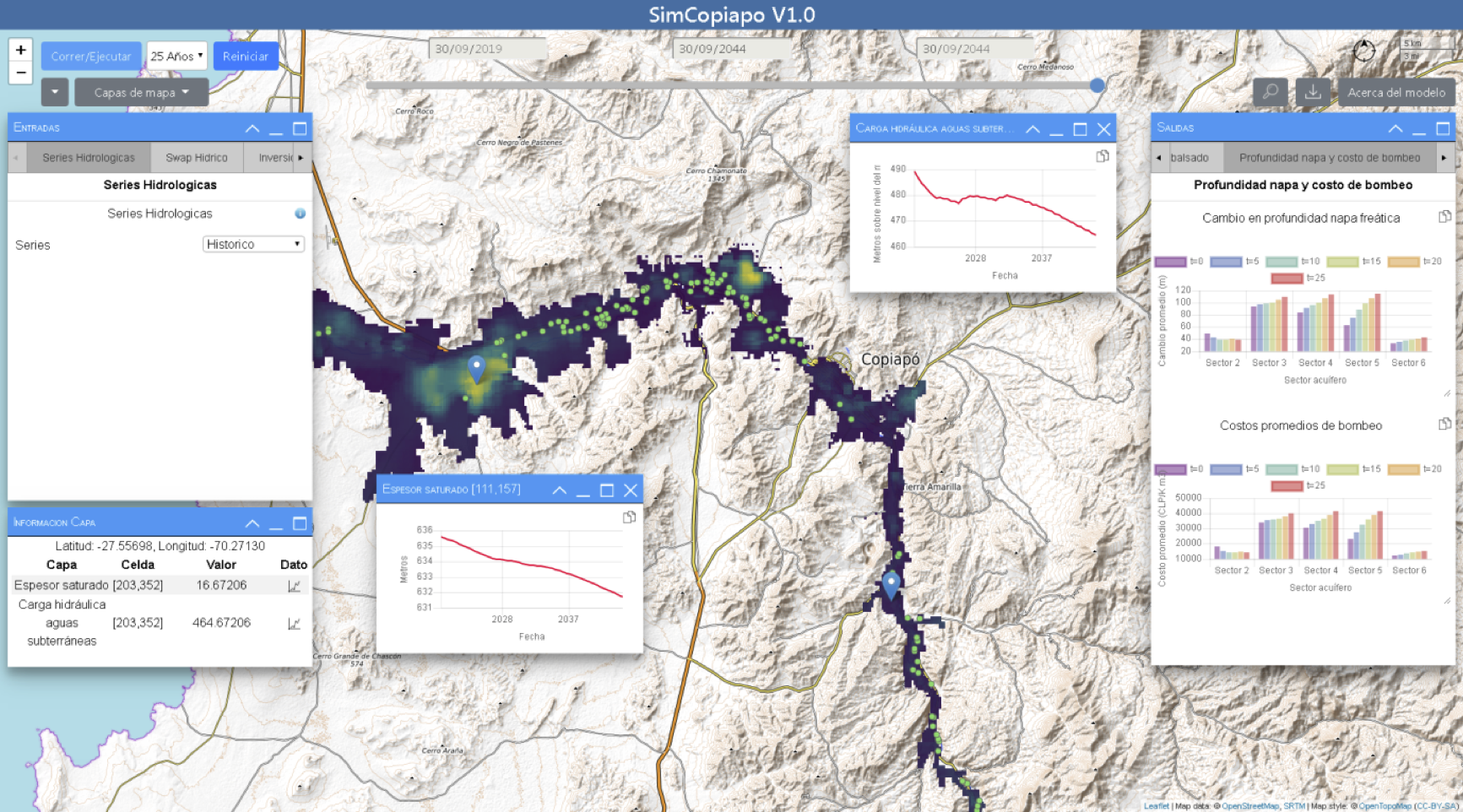
Effective stakeholder engagement and participation—the promise that stakeholder’s contributions can influence important environmental management decisions—is essential to tackle the complex socio-environmental issues of the Anthropocene. Although environmental models offer valuable guidance to support policy, planning, and management of the coupled human-natural systems at stake, their increasing sophistication often provides limited practical value and leads to poor comprehension by end-users. In this context, participatory modelling can increase the relevance and utility of traditional modelling efforts by promoting early and frequent interaction between model developers and decision-makers. The level of engagement and interaction that is needed to describe, disentangle, and debate the outputs of increasingly large and complex simulations during participatory modelling, however, demands flexible and extensible software that can quickly evolve and adapt in response to stakeholder requirements. To address this need, we introduce Pyticipate, an open-source software development kit that enables interactive scenario exploration and model-based decision support during collaborative modelling processes. Pyticipate provides a lightweight, parsimonious, reusable, and highly extensible framework to create customised web-based steering environments for distributed environmental models. Model developers (e.g., a scientist or engineer with a primary background in environmental modelling) do not need to know or have any previous experience using web-based technologies—they just need to write Python code. To this end, Pyticipate provides a range of predefined input/output objects and spatial layer types defined through a Python base class that handles the instantiation of model parameters and scenarios and automates the display of model outputs on a web interface. Pyticipate also supports exporting datasets from individual output controls to the clipboard and generating on-demand, customised scenario reports (in pdf or Word format) via the user interface. We demonstrate the features and capabilities of the framework through a real-world application, where Pyticipate was used to integrate legacy hydrologic models and guide a collaborative planning process in the drought-stricken Copiapo Basin in Chile. The resulting integrated socio-hydrology model allowed stakeholders to openly explore the viability and impacts of a wide range of infrastructure and policy scenarios, ending decades of paralyzing stalemate over water scarcity, water management, and climate change adaptation negotiations.
juancastilla/Pyticipate
An open-source, web-based steering environment to support interactive scenario exploration in participatory environmental modelling
HTML