QuickLogic Open Reconfigurable Computing (QORC) SDK provides components needed to get started on the QuickLogic's EOSS3 device and open source development boards such as Quickfeather.
Currently, the following boards are supported:
Easiest way to get started on quickfeather development kit is to build and run example application projects included in this SDK on a quickfeather development kit.
Install the items listed in Pre-requisites section below. Clone this QORC SDK
repository using
git clone https://github.com/QuickLogic-Corp/qorc-sdk
- Firmware
- ARM GNU GCC toolchain Version 7.2.1 or later.
Refer Launchpad Ubuntu for details to install the toolchain on Ubuntu Linux system.sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:team-gcc-arm-embedded/ppa sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install gcc-arm-embedded
- ARM GNU GCC toolchain Version 7.2.1 or later.
- Gateware
- QuickLogic Symbiflow: Refer QuickLogic Symbiflow to install the QuickLogic Symbiflow toolchain
-
Flash programmer: TinyFPGA programmer
- To install clone the repository and install the dependancy
git clone --recursive https://github.com/QuickLogic-Corp/TinyFPGA-Programmer-Application.git pip3 install tinyfpgabOn Ubuntu the lsusb command should display something similar to the following:
lsusb Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub Bus 002 Device 029: ID 1d50:6140 OpenMoko, Inc.If the OpenMoko device is not present (it could also have ID 1d50:6130) then run the following commands.
pip3 install apio apio drivers --serial-enable Serial drivers enabled Unplug and reconnect your boardRecommend adding an alias to simplify programming:
Using the editor of your choice add the following line to ~/.bashrc:
alias qfprog="python3 ~/TinyFPGA-Programmer-Application/tinyfpga-programmer-gui.py"and then source that file:
source ~/.bashrc
-
Terminal application program such as: putty
sudo apt-get install putty -y -
Miscellaneous: GNU make 3.8.1 or equivalent
- Quickfeather development kit
- A micro USB cable
- [Optional] A serial-to-USB cable
- [Optional] J-Link Debug probe
This section describes how to build and run the qf_helloworldsw project.
-
Navigate to qf_helloworldsw build folder and run make
cd qorc-sdk/qf_apps/qf_helloworldsw/GCC_projects make -
Reset QuickFeather board and press ‘user button’ while blue LED is flashing.
Should switch to mode where green LED is breathing.
If green LED not breathing, press reset again and ‘user button’ within 5 seconds of releasing reset (while blue LED is still flashing) -
With green LED breathing, program qf_helloworldsw app into QuickFeather:
qfprog --port /dev/ttyXX --m4app output/bin/qf_helloworldsw.binreplace /dev/ttyXX with the actual device path.
-
After programming has completed, reset the QuickFeather board and do not press the user button.
Blue LED should flash for 5 sec and then load the m4app and run it. -
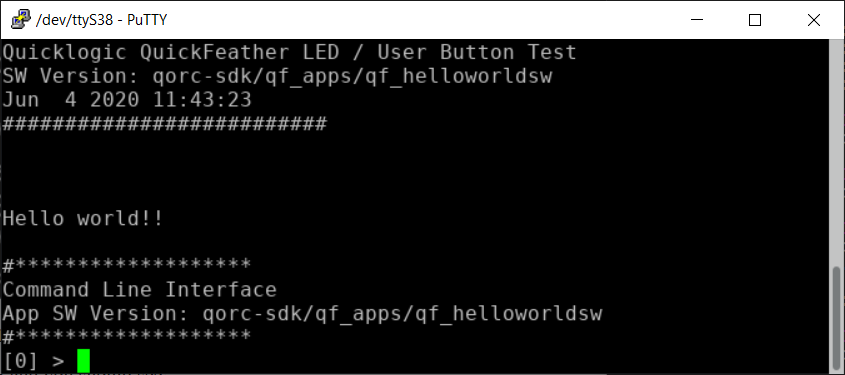
Run PuTTY or some other terminal emulator and attach to the QuickFeather (NOTE: the port name will most probably be different than the port name used for programming).
-
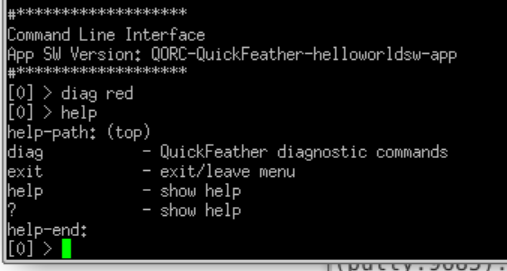
The prompt ‘[0]’ indicates that you are level 0 in the CLI menus system. Type
diag redand you should see the red LED on QuickFeather light up -
Which lists what is in the top-level CLI menu:
- diag is a user defined sub-menu
- the others are there by default
-
Type
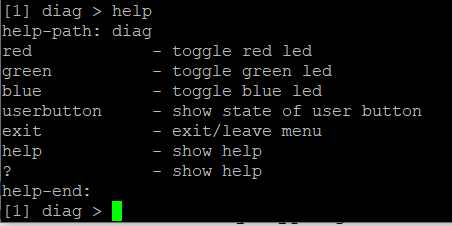
diagto enter the diag sub-menu:
You should see
Where the [1] diag indicates that you are in a 1st level submenu called diag
-
You can try these by typing red (should turn the red led off), green and so forth. Note that if you are level 0, you can access submenu elements by typing
submenuname submenu action, which is what we did earlier when we typeddiag red
-
Using the editor of your choice, edit
qorc-sdk/qf_apps/qf_helloworldsw/src/main.c. Change the line
dbg_str(“\n\nHello world !!\n\n”)
to say something else. Save the changes -
Now naviagte to qf_helloworldsw build folder and run make.
cd qorc-sdk/qf_apps/qf_helloworldsw/GCC_projects make -
Reset QuickFeather board and press ‘user button’ while blue LED is flashing.
- Should switch to mode where green LED is breathing
- If green LED not breathing, press reset again and ‘user button’ within 5 seconds of releasing reset
-
With green LED breathing, program the updated qf_helloworldsw app into QuickFeather:
qfprog --port /dev/ttyXX --m4app output/bin/qf_helloworldsw.bin -
After programming has completed, reset the QuickFeather board and do not press the user button.
- Blue LED should flash for 5 sec and then load the m4app and run it
-
Run PuTTY or some other terminal emulator and attach to the QuickFeather (NOTE: the port name will most probably be different than the port name used for programming).
-
You should see a banner and then your changed message.
- Navigate to qf_helloworldsw build folder and run make.
cd qorc-sdk/qf_apps/qf_helloworldhw/GCC_projects make - Reset QuickFeather board and press ‘user button’ while blue LED is flashing.
- Should switch to mode where green LED is breathing
- If green LED not breathing, press reset again and ‘user button’ within 5 seconds of releasing reset
- With green LED breathing, program qf_helloworldhw app into QuickFeather:
qfprog --port /dev/ttyXX --m4app output/bin/qf_helloworldhw.bin - After programming has completed, reset the QuickFeather board and do not press the user button.
- Blue LED should flash for 5 sec and then load the m4app which will load the FPGA and run that
- You should see the green LED flashing about 3 times/second.
- You will not see QuickFeather mounted on USB, because now the FPGA is used for the custom FPGA code, not the standard USB2SERIAL code. And because of this you cannot use PuTTY to monitor the application. (See Lesson#3 for how to monitor applications while running custom FPGA code).
- How does this work:
- If you look at main.c you will find the following code fragment:
load_fpga(sizeof(axFPGABitStream),axFPGABitStream); // Load bitstream into FPGA S3x_Clk_Enable(S3X_FB_21_CLK); // Start FPGA clock S3x_Clk_Enable(S3X_FB_16_CLK);
- The array, axFPGABitStream, is located in fpga/rtl/helloworldfpga_bit.h which is generated from the Verilog by ql_symbiflow
- What the
load_fpga()does is take the bitstream from array axFPGABitSTream and program the FPGA - What the
S3x_Clk_Enable(S3X_FB_21_CLK)does is to enable CLK 21 which is one of two clocks from the M4 that drive the FPGA - The frequency of the clock is specified in src/s3xd_pwrcfg.c to be 48MHz
[CLK_C21] = { .name = "C21", .clkd_id = CLK_C21, .type = SRC_CLK, .sync_clk = SYNC_CLKD (0, 0, 0), .cru_ctrl = CRU_CTRL (0x34, 0x1fe, 9, 0x38, 0x70, 0x1, 8), .def_max_rate = (F_48MHZ), .init_state = INIT_STATE(F_48MHZ, 1, INIT_GATE_OFF),},
- Using the editor of your choice, edit qf_apps/qf_helloworldhw/fpga/rtl/helloworldfpga.v
- Change the terminal counter from 4000000 to 2000000
- Change the assign greenled = led to assign redled = led
- Save the changes
- Navigate to qf_helloworldhw build folder and run make (note: for make use ql_symbiflow you will
have to activate the ql_symbiflow conda)
cd qf_apps/qf_helloworldhw/GCC_projects conda activate make conda deactivate - Reset QuickFeather board and press ‘user button’ while blue LED is flashing
- Should switch to mode where green LED is breathing
- If green LED not breathing, press reset again and ‘user button’ within 5 seconds of releasing reset
- With green LED breathing, program the updated qf_helloworldhw app into QuickFeather:
qfprog --port /dev/ttyXX --m4app output/bin/qf_helloworldhw.bin - After programming has completed, reset the QuickFeather board and do not press the user button
- Blue LED should flash for 5 sec and then load the m4app which loads the new FPGA code and runs it
- You should see the red LED flashing about 6 times/second
- You will not see QuickFeather mounted on USB, because now the FPGA is used for the custom FPGA code, not the standard USB2SERIAL code. And because of this you cannot use PuTTY to monitor the application. (See Lesson#3 for how to monitor applications while running custom FPGA code
- Go to directory qf_apps/qf_advancedfpga/GCC_projects
- Activate conda, run make and deactivate conda
- Connect to the QuickFeather UART
- Connect a serial-to-USB cable to the QuickFeather board
- Connect PuTTY to the serial port associated with the serial-to-USB cable
- Set baud rate to 115200
- Reset QuickFeather board and press ‘user button’ while blue LED is flashing
- Should switch to mode where green LED is breathing
- If green LED not breathing, press reset again and ‘user button’ within 5 seconds of releasing reset
- With green LED breathing, program m4 app into QuickFeather
- python tinyfpgaprogrammer - -port /dev/ttyXX - -m4app output/bin/qf_helloworldhw.bin
- After programming has completed, reset the QuickFeather board and do not press the user button
- Blue LED should flash for 5 sec and then load the m4app and run it
- The banner should be printed on PuTTY and then the CLI prompt
- Switch to the ledctlr sub-menu by entering ‘ledctlr’
- Set the color for timeslot 0 to blue by ‘color0 1’ – led should go blue
- Set the color for timeslot 1 to green by ‘color1 2’ – no visible change
- Set the color for timeslot 2 to red by ‘color2 4’ – no visible change
- Set the duration of timeslot 0 to 500ms by ‘duration0 500’
- Set the duration of timeslot 1 to 500ms by ‘duration1 500’
- Now the LED should display green for 500ms, then blue for 500ms and repeat
- Set the duration of timeslot 2 to 1000ms by ‘duration2 1000’
- Now LED should be blue for 500ms, green for 500ms and red for 1000ms and repeat
To create an application start by cloning the existing helloworldsw application project.
create_newapp.py python script may be used to quickly create a new application.
Run the following command from a command shell in the qf_apps/ folder.
python create_newapp.py --source qf_helloworldsw --dest MyNewApplication
The above would create a folder named MyNewApplication with sources and project workspaces
cloned from qf_helloworldsw.