A package to help estimate some of the (linear) spatial and spatio-temporal autogressive models discussed in Cook, Hays and Franzese (2020, 2021). The package provides tools to create geographic (k-nearest neighbor) spatial weights matrices for estimating Spatial AutoRegressive (SAR) models, Spatial Error Models (SEM), and Spatial Autocorrelation (SAC) models. The package is designed to work with unbalanced Country-Year Time-Series-Cross-Section (TSCS) datasets.
The package can be installed using devtools
# The development version from GitHub:
library(devtools); devtools::install_github("judechays/STADL", dependencies = TRUE)
TSCS spatial weights matrices can be created for any cross-section of
countries in the international system up until the year 2019, using the
cshapes package. The cross-sections can change across years to account
for country entry into and exit from the international system.
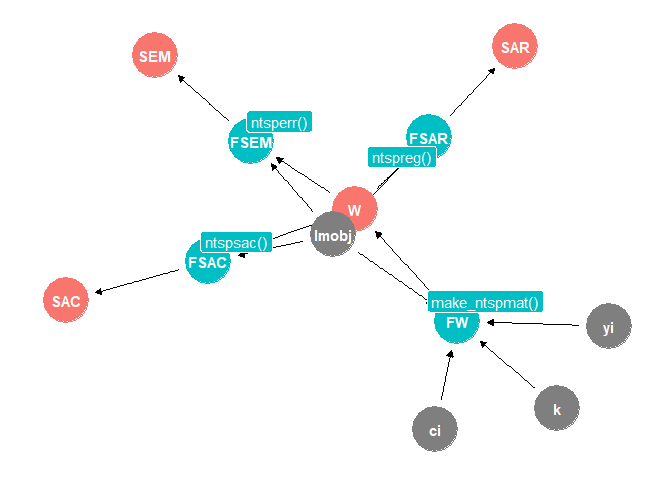
| Object | Method | Variables | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weights Matrix | k-nearest neighbor |
ols country_name year k |
make_ntspmat(lmobj, ci, yi, k=4) |
| Spatial AutoRegressive (SAR) | spatialreg::lagsarlm |
ols W |
ntspreg(ols, W) |
| Spatial error model (SEM) | spatialreg::errorsarlm |
ols W |
ntsperr(ols, W) |
| Spatial Autocorrelation (SAC) | spatialreg::sacsarlm |
ols W |
ntspsac(ols, W) |
The syntax for creating a k-nearest neighbor spatial weights matrix is
W <- make_ntspmat(lmobj = ols, ci = country_name, yi = year, k=4)where ols refers to the object returned from a linear regression,
using the lm function (lm(formula = y ~ x, data = data)).
country_name is the variable that identifies the sample countries,
and year is the variable that identifies the sample years. The
parameter k is the number of nearest neighbors you want to include
the spatial weights matrix, W.
The package also provides convenient wrapper functions to estimate the
SAR, SEM and SAC models using the spatial weights matrix,
W. The wrappers call the largsarlm, errorsarlm, and sacsarlm
functions from the spatialreg package. The main advantage of the
wrapper functions is that they process the weights matrix created by
make_ntspmat for use with the spatialreg functions.
The syntax for estimating the SAR model is
ntspreg(ols, W) where ols again refers to the object returned from a linear
regression using the lm function (lm(formula = y ~ x, data = data)),
and W is the spatial weights matrix created using the make_ntspmat
function.
ntsperr(ols, W) ntspsac(ols, W) -
Functions (blue)
The package includes four functions: make_ntspmat(), ntspreg(), netsperr(), and ntspsac(). These functions take inputs (arguments) and return outputs (lists).
-
Inputs (grey)
The functions take four inputs: country names ci, years yi, number of neighbors k, and the returned list from calling the linear model (lm) function lmobj.
-
Outputs (orange)
Each function returns an output. The function make_ntspmat() returns a k-nearest neighbor spatial weights matrix. The functions ntspreg(), netsperr(), and ntspsac() return lists of results from the estimation of their respective spatial regression models.
One of the challenges when using make_ntspmat() to create a spatial
weights matrix is matching the country names from your data to the ones
used in cshapes. The package includes some helper functions that make
this recoding process easier. These functions are discussed and
illustrated below.
| Object | Description | Input | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Country name list | List of all country names in cshapes |
names_list() |
|
Country information: cowcode |
Provides country information in cshapes, if you know cowcode. It gives: country name, start date, and end date. |
cowcode |
name_code(cowcode) |
Country information: country_name |
Provides country information in cshapes, if you know country_name. It gives: cowcode, start date, and end date. |
country_name |
name_text("Country name") |
If you run make_ntspmat and receive a message saying that Some of
your Country-Years are not Matched you can use the helper functions
above to fix the problem.
names_list()This returns a list with all country names which looks like this:
#> [1] "United States of America"
#> [2] "Canada"
#> [3] "Bahamas"
#> [4] "Cuba"
#> [5] "Haiti"
#> [6] "Dominican Republic"
#> [7] "Jamaica"
For example, if you have the United States in your data, and you know
cowcode==2, then you can check exact country name used in cshapes.
name_code(2)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "United States of America"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "Start date"
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] "1886-01-01" "1959-01-03" "1959-08-21"
#>
#> [[4]]
#> [1] "End date"
#>
#> [[5]]
#> [1] "1959-01-02" "1959-08-20" "2019-12-31"From this output, we can see that the country name used by cshapes is
“United States of America.” We also see that there are three separate
entries and thus three start and end dates. The start date for cshapes
is 1886-01-01. The two additional entries for the United States
correspond to the extensions of statehood to Alaska and Hawaii
respectively.
If you have a country’s name, but you are uncertain whether the period
you are analyzing is covered by cshapes, you can check using the
name_text function.
name_text("Uruguay")
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "Correlates of War Code"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] 165
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] "Start date"
#>
#> [[4]]
#> [1] "1886-01-01"
#>
#> [[5]]
#> [1] "End date"
#>
#> [[6]]
#> [1] "2019-12-31"The data used in this example come from Acemoglu, D., Johnson, S., Robinson, J. A. & Yared, P. (2008), “Income and democracy,” American Economic Review 98(3), 808–42. The dataset includes a global sample of countries’ GDPs and their democracy scores (Polity IV scores) for the period 1960–2000 (5-year averages). A more extensive re-analysis is presented in Cook, Hays, and Franzese (2021).
The dependent variable, democracy (polity4), is the Polity IV Democracy Index. The main independent variable is GDP per capita (in PPP) lrgdpchL.
We start by matching country names and creating the spatial weights matrix. Then we estimate spatio-temporal versions of the SAR, SEM, and SAC models. These models account for global waves of democratization with period fixed effects and over-time persistence in democracy scores by including the temporally lagged dependent variable, polity4L, as a regressor.
data<-read.csv("./inst/extdata/aer_5year_APSR_full.csv")reg<-lm(formula = polity4 ~ polity4L + lrgdpchL + as.factor(year), data = data)W <- make_ntspmat(reg,country,year,10)In this dataset, there are 29 countries with names that do not match the
country names used in cshapes. We can solve this problem by re-naming
these countries. For example “Cote d’Ivoire” should be “Cote D’Ivoire”.
The country names used in cshapes are provided by the helper function
names_list(). We can also check the start (entry) and end (exit) dates
using name_text("Country Name") and name_code(cowcode) helper
functions.
=======================================
Data Country Name Data Start Year
---------------------------------------
1 Belarus 2000
2 Burkina Faso 1965
3 Cambodia 2000
4 Congo, Dem. Rep. 1970
5 Congo, Rep. 1965
6 Cote d'Ivoire 1965
7 Egypt, Arab Rep. 1960
8 Ethiopia -pre 1993 1960
9 Ethiopia 1993- 2000
10 Gambia, The 1970
11 Germany 1995
12 Iran 1960
13 Italy 1960
14 Korea, Rep. 1960
15 Macedonia, FYR 2000
16 Madagascar 1965
17 Pakistan-post-1972 1980
18 Pakistan-pre-1972 1960
19 Romania 1965
20 Russia 2000
21 Sri Lanka 1960
22 Syrian Arab Republic 1970
23 Tanzania 1970
24 Turkey 1970
25 United States 1960
26 Venezuela, RB 1960
27 Vietnam 1995
28 Yemen 2000
29 Zimbabwe 1975
---------------------------------------
Fixing country names
The following code, using the recode_factor function from the dplyr
package, re-names the unmatched countries.
library (dplyr)
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Belarus"="Belarus (Byelorussia)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Burkina Faso"="Burkina Faso (Upper Volta)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Cambodia"="Cambodia (Kampuchea)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Congo, Dem. Rep."="Congo, Democratic Republic of (Zaire)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Congo, Rep."="Congo")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Cote d'Ivoire"="Cote D'Ivoire")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Egypt, Arab Rep."="Egypt")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Ethiopia -pre 1993"="Ethiopia")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Ethiopia 1993-"="Ethiopia")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Gambia, The"="Gambia")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Germany"="German Federal Republic")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Iran"="Iran (Persia)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Italy"="Italy/Sardinia")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Korea, Rep."="Korea, Republic of")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Macedonia, FYR"="Macedonia (FYROM/North Macedonia)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Madagascar"="Madagascar (Malagasy)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Pakistan-post-1972"="Pakistan")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Pakistan-pre-1972"="Pakistan")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Romania"="Rumania")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Russia"="Russia (Soviet Union)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Sri Lanka"="Sri Lanka (Ceylon)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Syrian Arab Republic"="Syria")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Tanzania"="Tanzania (Tanganyika)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Turkey"="Turkey (Ottoman Empire)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"United States"="United States of America")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Venezuela, RB"="Venezuela")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Vietnam"="Vietnam, Democratic Republic of")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Yemen"="Yemen (Arab Republic of Yemen)")
data$country<-recode_factor(data$country,"Zimbabwe"="Zimbabwe (Rhodesia)")reg<-lm(formula = polity4 ~ polity4L + lrgdpchL + as.factor(year), data = data)
summary(reg)
#>
#> Call:
#> lm(formula = polity4 ~ polity4L + lrgdpchL + as.factor(year),
#> data = data)
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
#> -0.73614 -0.08293 -0.01148 0.06733 0.69875
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) -0.257342 0.062472 -4.119 4.17e-05 ***
#> polity4L 0.748899 0.021605 34.663 < 2e-16 ***
#> lrgdpchL 0.053035 0.008012 6.619 6.42e-11 ***
#> as.factor(year)1965 -0.055404 0.033306 -1.663 0.0966 .
#> as.factor(year)1970 -0.071326 0.032185 -2.216 0.0269 *
#> as.factor(year)1975 -0.074252 0.031657 -2.345 0.0192 *
#> as.factor(year)1980 -0.043703 0.031617 -1.382 0.1673
#> as.factor(year)1985 -0.029291 0.031616 -0.926 0.3545
#> as.factor(year)1990 0.041154 0.031359 1.312 0.1898
#> as.factor(year)1995 0.073656 0.031238 2.358 0.0186 *
#> as.factor(year)2000 0.013973 0.030396 0.460 0.6458
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error: 0.1828 on 843 degrees of freedom
#> Multiple R-squared: 0.7725, Adjusted R-squared: 0.7698
#> F-statistic: 286.2 on 10 and 843 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16Once we have corrected the country names, we can re-estimate the
non-spatial linear regression model and create the spatial weights
matrix using make_ntspmat.
reg<-lm(formula = polity4 ~ polity4L + lrgdpchL + as.factor(year), data = data)
summary(reg)
#>
#> Call:
#> lm(formula = polity4 ~ polity4L + lrgdpchL + as.factor(year),
#> data = data)
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
#> -0.73614 -0.08293 -0.01148 0.06733 0.69875
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) -0.257342 0.062472 -4.119 4.17e-05 ***
#> polity4L 0.748899 0.021605 34.663 < 2e-16 ***
#> lrgdpchL 0.053035 0.008012 6.619 6.42e-11 ***
#> as.factor(year)1965 -0.055404 0.033306 -1.663 0.0966 .
#> as.factor(year)1970 -0.071326 0.032185 -2.216 0.0269 *
#> as.factor(year)1975 -0.074252 0.031657 -2.345 0.0192 *
#> as.factor(year)1980 -0.043703 0.031617 -1.382 0.1673
#> as.factor(year)1985 -0.029291 0.031616 -0.926 0.3545
#> as.factor(year)1990 0.041154 0.031359 1.312 0.1898
#> as.factor(year)1995 0.073656 0.031238 2.358 0.0186 *
#> as.factor(year)2000 0.013973 0.030396 0.460 0.6458
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error: 0.1828 on 843 degrees of freedom
#> Multiple R-squared: 0.7725, Adjusted R-squared: 0.7698
#> F-statistic: 286.2 on 10 and 843 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
W <- make_ntspmat(reg,country,year,10)The make_ntspmat function generates the weights matrix year by year.
While running, each year’s cross-section, with sample countries
identified by COW codes, will be displayed. If the function stops before
the end of the sample you will be able to recognize the problematic
cross-section (year). If all of the countries in a given cross-section
match with cshapes, you will see a message saying “All of your
Countries are Matched.”
#> [1] 1960
#> [1] 900 305 211 140 20 225 155 710 100 94 390 42 130 651 230 530 375 220 200
#> [20] 350 90 91 750 205 630 395 666 325 663 740 732 780 70 93 210 385 920 770
#> [39] 95 135 840 235 150 92 380 800 713 165 2 101 560
#> [1] 1965
#> [1] 160 900 305 211 434 439 145 140 482 20 225 155 710 437 471 484 100 94 390
#> [20] 130 651 230 530 375 220 481 200 452 438 350 90 91 850 750 205 630 395 666
#> [39] 325 663 740 732 780 600 580 70 432 435 820 436 475 93 210 385 790 920 770
#> [58] 95 135 840 235 150 360 433 92 380 483 461 800 713 165 2 101 560
#> [1] All of your Countries are Matched.
#> [1] 1970
#> [1] 160 900 305 211 434 439 145 140 482 20 225 155 710 437 471 484 100 94 390
#> [20] 615 130 651 230 530 375 220 481 200 452 438 420 350 90 91 850 750 205 630
#> [39] 395 666 325 51 663 740 501 732 780 600 580 70 432 435 553 820 436 475 93
#> [58] 210 385 790 920 95 135 840 235 150 360 517 433 830 451 92 380 652 483 461
#> [77] 800 52 616 640 713 510 500 165 2 101 560 490 551
#> [1] All of your Countries are Matched.
#> [1] 1975
#> [1] 160 900 305 516 211 434 439 145 140 571 482 20 225 155 710 437 471 484 100
#> [20] 94 352 390 42 615 130 651 530 375 950 220 481 200 452 438 420 411 350 90
#> [39] 110 91 41 310 850 750 205 630 395 666 325 51 663 740 501 732 780 570 600
#> [58] 580 70 432 435 590 553 820 436 475 93 210 385 790 920 95 135 840 150 360
#> [77] 517 433 830 451 92 380 652 483 461 800 52 616 640 713 510 500 165 2 101
#> [96] 560 490 551 552
#> [1] All of your Countries are Matched.
#> [1] 1980
#> [1] 540 160 900 305 516 211 434 439 771 145 140 571 482 20 225 155 710 437
#> [19] 471 484 100 581 94 352 390 42 615 130 651 530 375 950 220 481 200 452
#> [37] 438 420 404 411 350 90 110 41 310 850 750 205 395 666 325 51 663 740
#> [55] 501 732 780 570 600 580 70 432 541 435 590 553 820 436 475 210 385 790
#> [73] 920 770 95 135 840 910 150 360 517 433 830 451 380 652 461 800 52 616
#> [91] 640 713 510 500 165 2 101 560 490 551 552
#> [1] All of your Countries are Matched.
#> [1] 1985
#> [1] 540 160 900 305 516 211 434 439 771 145 140 571 482 20 225 155 710 437
#> [19] 471 484 100 581 94 352 390 42 615 130 651 230 530 375 950 220 481 200
#> [37] 452 438 420 404 411 350 110 41 310 850 750 205 395 666 325 51 663 740
#> [55] 501 732 780 570 600 580 70 432 541 435 590 553 820 436 475 210 385 790
#> [73] 920 770 95 135 840 910 290 235 150 360 517 433 830 451 380 652 461 800
#> [91] 52 616 640 713 510 165 2 101 560 490 551 552
#> [1] All of your Countries are Matched.
#> [1] 1990
#> [1] 540 160 900 305 516 211 439 771 145 140 571 482 20 225 155 710 437 471
#> [19] 484 100 581 94 40 352 390 42 615 130 651 230 530 375 950 220 200 452
#> [37] 438 420 404 411 350 110 91 41 310 850 750 205 630 395 666 325 51 663
#> [55] 740 501 732 780 570 600 580 70 432 541 435 590 553 820 436 475 93 210
#> [73] 385 790 920 770 95 135 840 910 290 235 150 360 517 433 830 451 92 380
#> [91] 652 483 461 800 52 616 640 713 510 165 2 101 560 490 551 552
#> [1] All of your Countries are Matched.
#> [1] 1995
#> [1] 160 900 305 211 439 771 145 140 571 482 20 225 155 710 437 471 484 100
#> [19] 94 40 352 255 390 42 615 130 651 230 375 950 220 200 452 438 420 404
#> [37] 411 350 90 110 91 41 310 850 750 205 630 395 666 325 51 663 740 501
#> [55] 732 780 570 600 580 70 432 541 435 590 553 820 565 436 475 93 210 385
#> [73] 790 920 770 95 135 840 910 290 235 150 360 517 433 830 451 92 380 652
#> [91] 483 461 800 52 616 640 713 510 500 165 2 101 816 560 551 552
#> [1] All of your Countries are Matched.
#> [1] 2000
#> [1] 339 160 371 900 305 373 211 434 439 771 355 370 145 140 571 482 20 225
#> [19] 155 710 437 471 484 100 94 40 352 316 255 390 42 615 130 651 230 366
#> [37] 530 375 220 481 200 452 438 420 404 411 350 90 110 91 344 41 310 850
#> [55] 750 205 630 395 666 325 51 663 740 705 501 703 811 732 780 368 367 600
#> [73] 359 580 70 343 432 541 435 590 553 820 565 436 475 93 210 385 790 920
#> [91] 770 95 840 910 290 235 150 360 365 517 433 830 92 317 349 380 652 483
#> [109] 461 800 52 616 640 713 510 500 369 165 2 704 101 816 679 560 551 552
#> [1] All of your Countries are Matched.
In this model, ρ is the coeffcient for the spatially lagged outcome variable.
lag <- ntspreg(reg,W)
summary(lag)#>
#> Call:spatialreg::lagsarlm(formula = formula, data = df, listw = listw,
#> method = "eigen", zero.policy = TRUE, tol.solve = 1e-10)
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
#> -0.7549372 -0.0809244 -0.0095003 0.0670258 0.6844804
#>
#> Type: lag
#> Coefficients: (asymptotic standard errors)
#> Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
#> (Intercept) -0.3079667 0.0656794 -4.6889 2.746e-06
#> polity4L 0.7457442 0.0214521 34.7633 < 2.2e-16
#> lrgdpchL 0.0531095 0.0079384 6.6902 2.229e-11
#> as.factor(year)1965 -0.0589817 0.0330236 -1.7860 0.07409
#> as.factor(year)1970 -0.0751453 0.0319103 -2.3549 0.01853
#> as.factor(year)1975 -0.0758992 0.0313635 -2.4200 0.01552
#> as.factor(year)1980 -0.0436485 0.0313208 -1.3936 0.16344
#> as.factor(year)1985 -0.0306376 0.0313216 -0.9782 0.32799
#> as.factor(year)1990 0.0407703 0.0310648 1.3124 0.18938
#> as.factor(year)1995 0.0733024 0.0309442 2.3689 0.01784
#> as.factor(year)2000 0.0157911 0.0301255 0.5242 0.60016
#>
#> Rho: 0.092467, LR test value: 4.488, p-value: 0.034134
#> Asymptotic standard error: 0.042432
#> z-value: 2.1792, p-value: 0.02932
#> Wald statistic: 4.7487, p-value: 0.02932
#>
#> Log likelihood: 247.2436 for lag model
#> ML residual variance (sigma squared): 0.032792, (sigma: 0.18109)
#> Number of observations: 854
#> Number of parameters estimated: 13
#> AIC: -468.49, (AIC for lm: -466)
#> LM test for residual autocorrelation
#> test value: 0.33204, p-value: 0.56446
In this model, λ is the coefficient on the spatially lagged disturbance term.
lag_err <- ntsperr(reg,W)
summary(lag_err)#>
#> Call:spatialreg::errorsarlm(formula = formula, data = df, listw = listw,
#> method = "eigen", zero.policy = TRUE, tol.solve = 1e-11)
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
#> -0.736974 -0.083456 -0.011526 0.068874 0.698778
#>
#> Type: error
#> Coefficients: (asymptotic standard errors)
#> Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
#> (Intercept) -0.2589496 0.0621459 -4.1668 3.089e-05
#> polity4L 0.7475215 0.0214992 34.7698 < 2.2e-16
#> lrgdpchL 0.0534045 0.0079733 6.6979 2.114e-11
#> as.factor(year)1965 -0.0560378 0.0330115 -1.6975 0.08960
#> as.factor(year)1970 -0.0723244 0.0318947 -2.2676 0.02335
#> as.factor(year)1975 -0.0746763 0.0313722 -2.3803 0.01730
#> as.factor(year)1980 -0.0432951 0.0313410 -1.3814 0.16715
#> as.factor(year)1985 -0.0299043 0.0313366 -0.9543 0.33993
#> as.factor(year)1990 0.0405267 0.0310994 1.3031 0.19253
#> as.factor(year)1995 0.0728451 0.0309618 2.3527 0.01864
#> as.factor(year)2000 0.0138366 0.0301252 0.4593 0.64602
#>
#> Lambda: 0.062942, LR test value: 0.65125, p-value: 0.41966
#> Asymptotic standard error: 0.078322
#> z-value: 0.80363, p-value: 0.42161
#> Wald statistic: 0.64583, p-value: 0.42161
#>
#> Log likelihood: 245.3253 for error model
#> ML residual variance (sigma squared): 0.032952, (sigma: 0.18153)
#> Number of observations: 854
#> Number of parameters estimated: 13
#> AIC: -464.65, (AIC for lm: -466)
In this model, ρ is the coefficient on the spatially lagged outcome variable, and λ is the coefficient on the spatially lagged disturbance term.
lag_sac <- ntspsac(reg,W)
summary(lag_sac)lag_sac <- ntspsac(reg,W)
summary(lag_sac)
#>
#> Call:spatialreg::sacsarlm(formula = formula, data = df, listw = listw,
#> method = "eigen", zero.policy = TRUE, tol.solve = 1e-10)
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
#> -0.757587 -0.080138 -0.010874 0.066737 0.680636
#>
#> Type: sac
#> Coefficients: (asymptotic standard errors)
#> Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
#> (Intercept) -0.313396 0.066420 -4.7184 2.377e-06
#> polity4L 0.745464 0.021458 34.7400 < 2.2e-16
#> lrgdpchL 0.052735 0.007919 6.6592 2.753e-11
#> as.factor(year)1965 -0.059242 0.033072 -1.7913 0.07324
#> as.factor(year)1970 -0.075151 0.031963 -2.3512 0.01871
#> as.factor(year)1975 -0.075805 0.031400 -2.4142 0.01577
#> as.factor(year)1980 -0.044000 0.031348 -1.4036 0.16043
#> as.factor(year)1985 -0.030298 0.031352 -0.9664 0.33385
#> as.factor(year)1990 0.041215 0.031080 1.3261 0.18480
#> as.factor(year)1995 0.073868 0.030974 2.3849 0.01709
#> as.factor(year)2000 0.016229 0.030163 0.5381 0.59054
#>
#> Rho: 0.10702
#> Asymptotic standard error: 0.048627
#> z-value: 2.2008, p-value: 0.027748
#> Lambda: -0.054986
#> Asymptotic standard error: 0.10084
#> z-value: -0.54527, p-value: 0.58557
#>
#> LR test value: 4.8089, p-value: 0.090316
#>
#> Log likelihood: 247.4041 for sac model
#> ML residual variance (sigma squared): 0.032765, (sigma: 0.18101)
#> Number of observations: 854
#> Number of parameters estimated: 14
#> AIC: -466.81, (AIC for lm: -466)
In this example, all of the specification tools select the SAR model. The Wald and Likelihood ratio tests reject the null hypothesis ρ = 0, but fail to reject λ = 0. The Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) also selects the SAR as the best fitting model. The Bayesian Information Criterion selects the SAR model as well.
BIC(lag)
BIC(lag_err)
BIC(lag_sac)BIC(lag)
#> [1] -406.7382
BIC(lag_err)
#> [1] -402.9015
BIC(lag_sac)
#> [1] -400.3092
Given the temporally lagged dependent variable in the SAR specification, this model is the first-order spatio-temporal autoregressive distributed lag (STADL) model discussed in Cook, Hays and Franzese (2021).
To cite tscsdep in publications, please use:
citation("tscsdep")
#>
#> To cite 'tscsdep' in publications, please use:
#>
#> Hays, Jude C., Valentina González-Rostani, Scott Cook, Robert
#> Franzese, and Wooseok Kim. (2021). {tscsdep}: {T}ools for analyzing
#> country-year time-series-cross-sectional data with spatial and
#> temporal dependence. version 0.1.0.
#> https://github.com/judechays/STADL
#>
#> A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
#>
#> @Manual{,
#> title = {{tscsdep}: {T}ools for analyzing country-year time-series-cross-sectional data with spatial and temporal dependence},
#> author = {Jude Hays and Valentina González-Rostani and Scott Cook and Robert Franzese and Wooseok Kim},
#> note = {version 0.1.0},
#> year = {2021},
#> url = {https://github.com/judechays/STADL},
#> }Jude Hays (jch61@pitt.edu), Valentina González-Rostani (mag384@pitt.edu), Scott Cook (sjcook@tamu.edu), Robert Franzese (franzese@umich.edu), and Wooseok Kim (wskr@umich.edu)
Jude Hays (jch61@pitt.edu)
Acemoglu, Daron, Simon Johnson, James A Robinson, and Pierre Yared. 2008. “Income and Democracy.” American Economic Review 98 (3): 808–42.
Bivand, Roger S., Edzer Pebesma, and Virgilio Gomez-Rubio. 2013. Applied Spatial Data Analysis with R, Second Edition. Springer, NY. https://asdar-book.org/.
Bivand, Roger, Jan Hauke, and Tomasz Kossowski. 2013. “Computing the Jacobian in Gaussian Spatial Autoregressive Models: An Illustrated Comparison of Available Methods.” Geographical Analysis 45 (2): 150–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/gean.12008.
Bivand, Roger, and Gianfranco Piras. 2015. “Comparing Implementations of Estimation Methods for Spatial Econometrics.” Journal of Statistical Software 63 (18): 1–36. https://www.jstatsoft.org/v63/i18/.
Cook, Scott J., Jude C. Hays, and Robert J. Franzese. 2020. “Model Specification and Spatial Interdependence.” In The SAGE Handbook of Research Methods in Political Science and International Relations, edited by Luigi Curini and Robert Franzese, 730–47.
———. Forthcoming. “STADL Up! The Spatio-Temporal Autoregressive Distributed Lag Model for TSCS Data Analysis.” American Political Science Review.
Weidmann, Nils B., Guy Schvitz, and Luc Girardin. 2021. Cshapes: The CShapes 2.0 Dataset and Utilities. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=cshapes.
Wickham, Hadley, Jim Hester, and Winston Chang. 2021. Devtools: Tools to Make Developing r Packages Easier. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=devtools.
Wickham, Hadley, and Evan Miller. 2021. Haven: Import and Export ’SPSS’, ’Stata’ and ’SAS’ Files. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=haven.