-
- null
- undefined
- string
- number
- boolean
- symbol (ES6)
-
- object
- Array
- Function
在 js 中我们有一个通用的判断类型的函数: typeof()。 typeof 的结果值有以下六种:
- "undefined"
- "string"
- "number"
- "boolean"
- "object"
- "function"
对于对象类型,不管什么样的对象类型,使用typeof得到的结果都是 object;因此, js借用了java语言中 instanceof 去判断对象实例属于什么类型。
console.log(Object instanceof Object);//true
console.log(Function instanceof Function);//true
console.log(Number instanceof Number);//false
console.log(String instanceof String);//false
console.log(Function instanceof Object);//true
console.log(Foo instanceof Function);//true
console.log(Foo instanceof Foo);//false
let a;
if (typeof(a) === "undefined") {
console.log('This value is undefined');
}
- Solution 1:
let a = null; if (a === null) { console.log('This value is null'); } - Solution 2:
let a = null; if ( !a && typeof(a) !=="undefined" && a != 0) { console.log('This value is null'); }- 注意: 这里的 == 和 === 需要严格使用,否则就不会达到想要的效果。 比如, a != 0 包含了 a !== false 和 a !== 0的情况;但是 a !== 0 只包含了 a !== 0 的情况。
-
把NAN不等于任何一个值(包含其自身)
let a = 'str'; if (isNaN(a)) { console.log('This value is NaN'); }
-
const a = [1,2,3,4];
-
Solution 1: concat
const a = [1,2,3,4]; const b = [].concat(a); b[0] = 9; console.log(a); console.log(b); -
Solution 2: slice()
const a = [1,2,3,4]; const b = a.slice(); b[0] = 9; console.log(a); console.log(b); -
Solution 3: ES6中的拓展运算符 ...
const a = [1,2,3,4]; const b = [...a]; //或者 const [...b] = a; b[0] = 9; console.log(a); console.log(b); -
Solution 4: JSON.parse(JSON.stringify())
const a = [1,2,3,4]; const b = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(a)); b[0] = 9; console.log(a); console.log(b); -
const a = {name: 'Tom', age: 18};
-
Solution 1: ES6中的拓展运算符 ... (只适用于单层非嵌套对象)
const a = {name: 'Tom', age: 18}; const b = {...a}; b.name = 'Jerry'; console.log(a) console.log(b); -
Solution 2: ES6中的 Object.assign({},param) (只适用于单层非嵌套对象)
const a = {name: 'Tom', age: 18}; const b = Object.assign({}, a); b.name = 'Jerry'; console.log(a) console.log(b); -
Solution 3: JSON.parse(JSON.stringify()) (可适用于嵌套对象,但如果对象中有undefined , Symbol, function的情况会被忽略)
const a = {name: 'Tom', age: 18}; const b = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(a)); b.name = 'Jerry'; console.log(a); console.log(b)
注意: 上面所有的方法都是针对基本的数组或者对象。对于特殊的情况:比如嵌套数组或对象;对象中值为值为 undefined, Symbol, function的情况。这些情况直接采用上面的方法就没法达到深复制的效果。
- JSON.parse(JSON.stringify()) 该方法会忽略值为 undefined, Symbol, function的情况,例如下面的例子:
var syb = Symbol('obj'); var person = { name :'tino', say: function(){ console.log('hi'); }, ok: syb, un: undefined }; var copy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(person)); console.log(copy); // {name: "tino"}
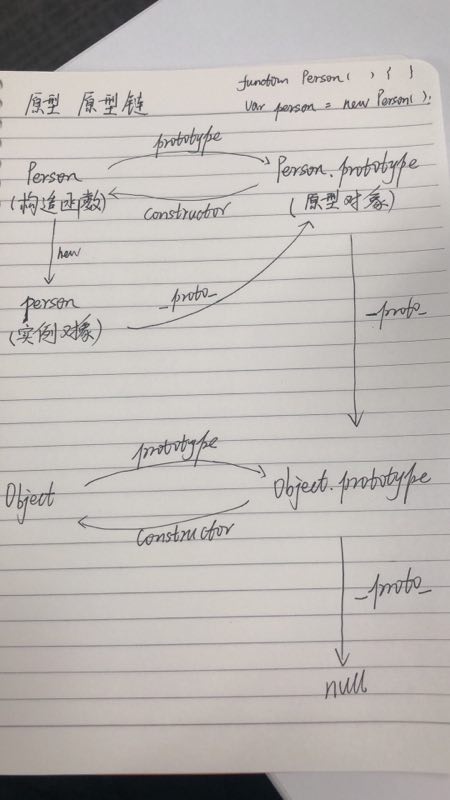
- 实例是对象的构造函数创建出来的
- 实例的原型对象指向类/对象的原型
- 原型的原型对象指向继承类/对象的原型
-
实现继承的几种方式 该内容参考其他博客,紧供参考,转载请注明出处
-
Solution 1:
console.time('1'); let str = 'qwertwergggg1115gtttt66890jjjkk550llllnnnfhjfkg88876666'; const strArr = [...str]; const strObj = {}; let maxKey = strArr[0]; strArr.forEach((item) => { strObj[item] = strObj[item] === undefined ? 1 : strObj[item] + 1; if (strObj[item] > strObj[maxKey]) { maxKey = item; } }); console.log(maxKey); console.timeEnd('1'); // 1: 0.48876953125ms -
Solution 2:
console.time('1'); let str = 'qwertwergggg1115gtttt66890jjjkk550llllnnnfhjfkg88876666'; const strArr = [...str] const strSet = new Set(strArr); let maxKey = ''; let maxValue = 0; strSet.forEach(value => { const num = strArr.filter(item => item === value).length; if (num > maxValue) { maxValue = num; maxKey = value; } }); console.log(maxKey); console.log(maxValue); console.timeEnd('1'); // 0.877197265625ms
对比Solution 1 和 Solution 2, 对于一般的字符串, Solution 1效率更高。
-
:root指代html 元素;除非有特殊的更高级别的元素;通常用来定义全局的css-
:root { --my-customize-var: red; } .test { background-color: var(--my-customize-var) }
-
-
-
Note
/* Selects any paragraph inside a header, main or footer element that is being hovered */ :where(header, main, footer) p:hover { color: red; cursor: pointer; } /* The above is equivalent to the following */ header p:hover, main p:hover, footer p:hover { color: red; cursor: pointer; }The difference between :where() and :is() is that :where() always has 0 specificity, whereas :is() takes on the specificity of the most specific selector in its arguments.
specificity: 可以理解为我们通常讲的权重
-
@support 是css的一个规则,用来检测浏览器是否支持某个css @supports not(display: grid) { div { display: flex; } } // 通过js获取这个rule let myRules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules; console.log(myRules[0]); // a CSSSupportsRule representing the feature query. -
gap: row-gap column-gap // Usage example .container { display: flex; gap: 1rem; } -
/* Keyword values */ content-visibility: visible; content-visibility: hidden; content-visibility: auto; /* Global values */ content-visibility: initial; content-visibility: unset;
-
-
SPA是客户端渲染,通过加载执行JS来创建DOM元素构建页面,但是爬虫只是请求静态资源,不会执行JS文件,所以抓取不到DOM结构,也分析不出来有用的信息。
-
-
-
-
-
- 按需加载会优化首次渲染慢的问题 lazyload