This repository contains a Vagrantfile and an accompanying Ansible playbook that sets up a VirtualBox virtual machine that installs DevStack.
Ansible generates a local.conf file that defaults to:
- Use Neutron for networking
- Install Swift for object storage
- Install Solum for Application development
- Install Tempest for functional testing
By default, the VM uses 8GB of RAM. If you want to change this, edit the following line in Vagrantfile:
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--memory", 8192]
Install the following applications on your local machine first:
git clone https://github.com/julienvey/devstack-vagrant
cd devstack-vagrant
vagrant up
The vagrant up command will:
- Download an Ubuntu 13.10 (saucy) vagrant box if it hasn't previously been downloaded to your machine.
- Boot the virtual machine (VM).
- Clone the DevStack git repository inside of the VM.
- Run DevStack inside of the VM.
- Add eth2 to the br-ex bridge inside of the VM to enable floating IP access from the host machine.
It will take at least ten minutes for this to run, and possibly much longer depending on your internet connection and whether it needs to download the Ubuntu vagrant box.
By default, VMs started by OpenStack will not be able to connect to the internet. If you want your VMs to connect out, and you are running Linux as your host operating system, you must configure your host machine to do network address translation (NAT).
To enable NAT, issue the following commands in your host, as root:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADEIf you see an error like this:
devstack | FAILED => Authentication or permission failure. In some cases, you may have been able to authenticate and did not have permissions on the remote directory
Then you may have incorrect file permissions in the id_vagrant file. Make sure it is only readable by the owner, by doing:
chmod 0600 id_vagrant
You may ocassionally see the following error message:
[default] Waiting for VM to boot. This can take a few minutes.
[default] Failed to connect to VM!
Failed to connect to VM via SSH. Please verify the VM successfully booted
by looking at the VirtualBox GUI.
If you see this, retry by doing:
vagrant destroy --force && vagrant up
The VM is accessible at 192.168.27.100
The easiest way to log in the VM, is to type vagrant ssh
You can also use access it using vagrant as username and password, or use the provided id_vagrant private key to avoid typing a password.
Note that you do not need to be logged in to the VM to run commands against the OpenStack endpoint.
From your local machine, to run as the demo user:
source credentials/demo.openrc
To run as the admin user:
source credentials/admin.openrc
- URL: http://192.168.27.100
- Username: admin or demo
- Password: password
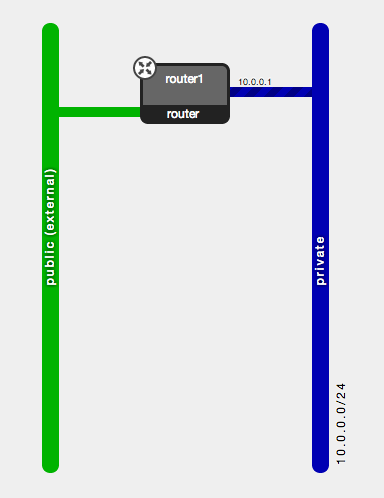
DevStack configures an internal network ("private") and an external network ("public"), with a router ("router1") connecting the two together. The router is configured to use its interface on the "public" network as the gateway.