A Jupyter extension to make, download and extract archive files.
Features:
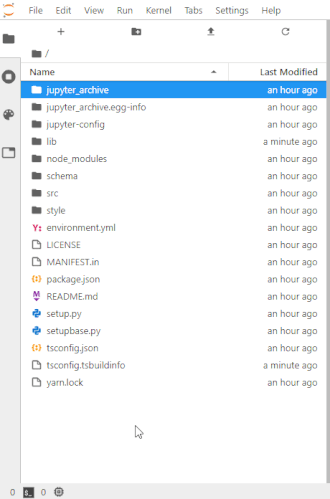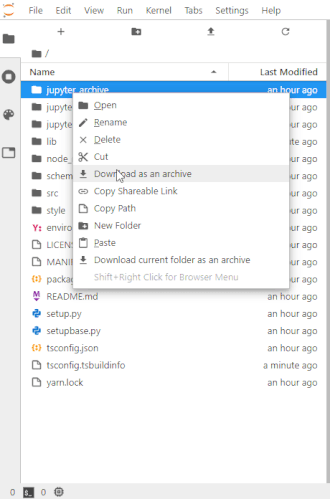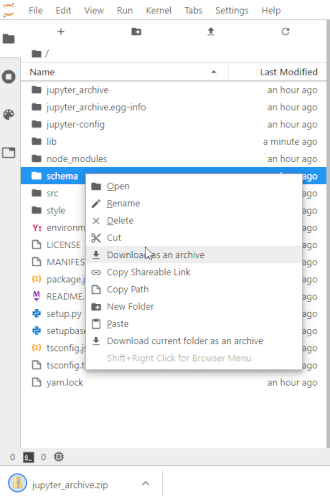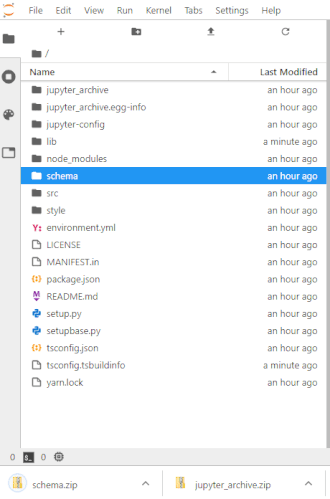
- Download selected or current folder as an archive.
- Supported formats: 'zip', 'tar.gz', 'tar.bz2' and 'tar.xz'.
- Archiving and downloading are non-blocking for Jupyter. UI can still be used.
- Archive format can be set in the JLab settings.
- Alternatively, you can choose the format in the file browser menu (the format setting needs to be set to
null). - Decompress an archive directly in file browser.
- Notebok client extension not available. Contributions are welcome.
The server extension has some configuration settings -- the values below are the default one:
{
JupyterArchive: {
stream_max_buffer_size: 104857600, // The max size of tornado IOStream buffer
handler_max_buffer_length: 10240, // The max length of chunks in tornado RequestHandler
archive_download_flush_delay: 100 // The delay in ms at which we send the chunk of data to the client.
}
}You can also set new values with the following environment variables:
JA_IOSTREAM_MAX_BUFFER_SIZEJA_HANDLER_MAX_BUFFER_LENGTHJA_ARCHIVE_DOWNLOAD_FLUSH_DELAY
- JupyterLab >= 3.0 or Notebook >= 7.0
For JupyterLab 2.x, have look there.
To install the extension, execute:
pip install jupyter-archiveOr
conda install -c conda-forge jupyter-archiveTo remove the extension, execute:
pip uninstall jupyter-archiveOr
conda remove jupyter-archiveIf you are seeing the frontend extension, but it is not working, check that the server extension is enabled:
jupyter server extension listIf the server extension is installed and enabled, but you are not seeing the frontend extension, check the frontend extension is installed:
jupyter labextension listNote: You will need NodeJS to build the extension package.
The jlpm command is JupyterLab's pinned version of
yarn that is installed with JupyterLab. You may use
yarn or npm in lieu of jlpm below.
# Clone the repo to your local environment
# Change directory to the jupyter-archive directory
# Install package in development mode
pip install -e ".[test]"
# Link your development version of the extension with JupyterLab
jupyter labextension develop . --overwrite
# Server extension must be manually installed in develop mode
jupyter server extension enable jupyter_archive
# Rebuild extension Typescript source after making changes
jlpm buildYou can watch the source directory and run JupyterLab at the same time in different terminals to watch for changes in the extension's source and automatically rebuild the extension.
# Watch the source directory in one terminal, automatically rebuilding when needed
jlpm watch
# Run JupyterLab in another terminal
jupyter labWith the watch command running, every saved change will immediately be built locally and available in your running JupyterLab. Refresh JupyterLab to load the change in your browser (you may need to wait several seconds for the extension to be rebuilt).
By default, the jlpm build command generates the source maps for this extension to make it easier to debug using the browser dev tools. To also generate source maps for the JupyterLab core extensions, you can run the following command:
jupyter lab build --minimize=FalseUnder BSD license. See LICENSE.
- Hadrien Mary: @hadim
- Frédéric Collonval: @fcollonval
# Server extension must be manually disabled in develop mode
jupyter server extension disable jupyter_archive
pip uninstall jupyter-archiveIn development mode, you will also need to remove the symlink created by jupyter labextension develop
command. To find its location, you can run jupyter labextension list to figure out where the labextensions
folder is located. Then you can remove the symlink named @hadim/jupyter-archive within that folder.
This extension is using Pytest for Python code testing.
Install test dependencies (needed only once):
pip install -e ".[test]"
# Each time you install the Python package, you need to restore the front-end extension link
jupyter labextension develop . --overwriteTo execute them, run:
pytest -vv -r ap --cov jupyter_archiveThis extension uses Playwright for the integration tests (aka user level tests). More precisely, the JupyterLab helper Galata is used to handle testing the extension in JupyterLab.
More information are provided within the ui-tests README.
See RELEASE