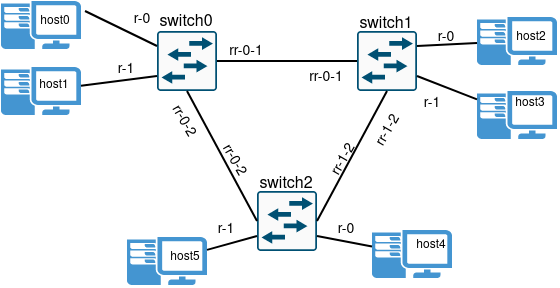
Ethernet Switch that uses VLAN segmentation for network efficiency, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) for loop prevention, and MAC address learning for fast frame forwarding. By managing VLAN membership, preventing loops, and learning MAC addresses, the implementation ensures reliable communication and facilitates network segmentation for enhanced performance.
- Frame Arrival: An Ethernet frame arrives at a switch through one of its ports.
- Destination MAC Address: The switch examines the destination MAC address in the header frame.
- MAC Address Table Lookup: The switch checks its MAC address table to find the port associated with the destination MAC address. If found, the frame is forwarded out of the corresponding port.
- Unknown Destination MAC Address: If the MAC address is unknown, the switch floods the frame to all ports except the incoming one to ensure connectivity.
- Broadcast and Multicast:
Broadcastframes are forwarded to all ports except the receiving one, all devices receive the broadcast.Multicastframes are forwarded only to ports interested in the multicast group.
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) segment a single physical LAN into multiple broadcast domains. The VLANs introduce the concept of VLAN tagging and forwards frames based on VLAN membership, facilitating efficient network segmentation and traffic management.
- Frame Reception: When a switch receives a frame with an unknown destination or broadcast, it forwards it to all ports within the same VLAN, including trunks.
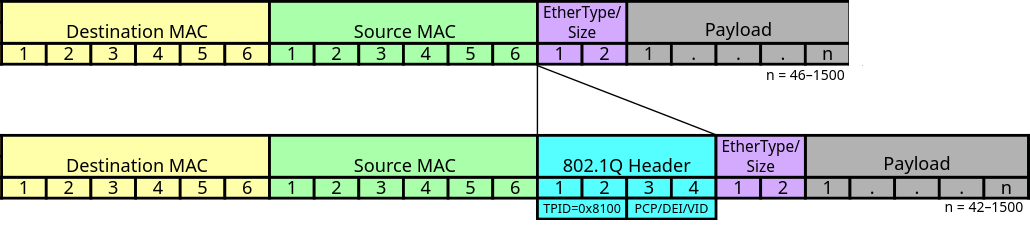
- IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Tagging: VLAN tagging is introduced using
IEEE 802.1Q, adding 4 bytes to the frame. TheVID field(12 bits) represents the VLAN identifier.
Switch Behavior:
- If on an access port:
- Forwards with
802.1Qheader on trunk interfaces. - Forwards without header if VLAN ID matches that of the incoming interface.
- Forwards with
- If on a trunk port:
- Removes VLAN tag and forwards:
- With
802.1Q header(including tag) on trunk interfaces. - Without header if VLAN ID matches that of the received frame on access interfaces.
- With
- Removes VLAN tag and forwards:
- Linux VLAN Filtering:
TPIDvalue of0x8200is used instead of0x8100.PCPandDEIare set to0. - Trunk Links: Links between switches operate in trunk mode, allowing passage of all VLANs.
- Configuration: VLANs and trunk configurations are set via a
configuration filespecified in the API section.
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is a protocol used to prevent loops in network topologies by creating a loop-free logical topology. This implementation provides a simplified version of STP to avoid LAN loops.
- Each switch initially considers itself as the
root bridgeand starts with all ports in theListening state. BPDUsare exchanged between switches to elect theroot bridgeand determine thedesignated ports.Trunkports are crucial for loop prevention, andSTPoperates only on these ports to avoid potential loops.
BPDU frames utilize encapsulation with the 802.2 Logical Link Control (LLC) header. The Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) utilize the encapsulation of the 802.2 Logical Link Control (LLC) header. The structure of a BPDU is as follows:
- Destination MAC (
DST_MAC):6bytes - Source MAC (
SRC_MAC):6bytes - LLC Length (
LLC_LENGTH):2bytes, indicating the total size of the frame including the BPDU. - LLC Header (
LLC_HEADER):3bytes, comprising the DSAP (Destination Service Access Point), SSAP (Source Service Access Point), and Control fields.DSAP:1byte, typically set to0x42to identify the STP protocol.SSAP:1byte, also set to0x42to identify the STP protocol.Control:1byte, often set to0x03for control purposes.
- BPDU Header (
BPDU_HEADER):4bytes, containing control information specific to STP. - BPDU Configuration (
BPDU_CONFIG):31bytes, encompassing various parameters such as flags, root bridge ID, root path cost, sender bridge ID, port ID, message age, max age, hello time, and forward delay.
- Initialization:
Trunk portsstart in theBlocking stateto prevent loops. Switches consider themselves asroot bridges, with all ports in theListening state. If a switch it's theroot bridge, all ports areDesignated. - BPDU Exchange: Switches exchange
BPDUsto elect theroot bridgeand determine designated ports.BPDUscontain root bridge ID, sender bridge ID, and root path cost, sent regularly on trunk ports. - Root Bridge Election: Upon receiving a
BPDU, switches compareroot bridge IDs. If received ID is lower, the switch updates its information and forwards the BPDU.- Switches continuously update root bridge information.
- Port States: Ports can be
Blocking,Listening,Learning, orForwarding.Blockingprevents loops,Listeningprepares for Learning state,Learning populatesMAC address tables, andForwardingfully operates.
- Loop Prevention: STP operates on trunk ports to prevent loops.
BPDUsdetermine best paths to:- root bridge
- block redundant links
- Frame Forwarding: Forward frames based on established spanning tree topology, ensuring a loop-free network.
To simulate a virtual network use Mininet. Mininet is a network simulator that utilizes real kernel, switch, and application code implementations. Mininet can be used on both Linux and WSL2.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install mininet openvswitch-testcontroller tshark python3-click python3-scapy xterm python3-pip
sudo pip3 install mininetAfter installing Mininet use the following command to increase the font size in the terminals we open.
echo "xterm*font: *-fixed-*-*-*-18-*" >> ~/.Xresources
xrdb -merge ~/.XresourcesWhen running the simulation, you may encounter the following error: Exception: Please shut down the controller which is running on port 6653:. To resolve the issue, you will need to run pkill ovs-test.