dstack is an open-source platform to build and share data and ML applications within hours
Installing and running dstack is very easy:
pip install dstack==0.6.5
dstack goIf you run it for the first time, it may take a while. Once it's done, you'll see the following output:
To access the application, open this URL in the browser: http://localhost:8080/auth/verify?user=dstack&code=xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx&next=/
The default profile in "~/.dstack/config.yaml" is already configured. You are welcome to push your applications using Python package.To access dstack, click the URL provided in the output. If you try to access dstack without using this URL, it will
require you to sign up using a username and a password.
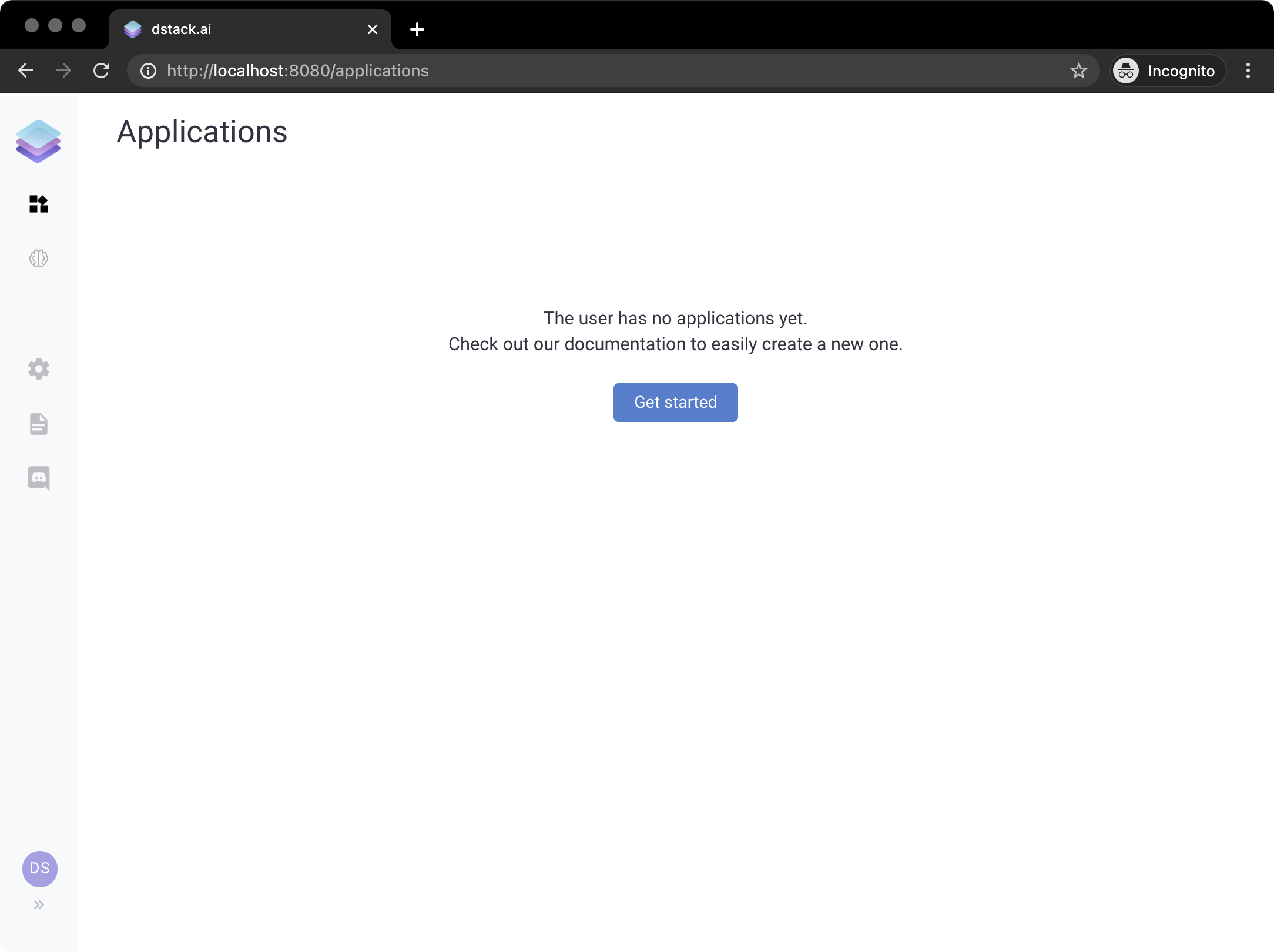
If you open the URL, you'll see the following interface:
You'll be logged as the dstack user. The page you'll see is Applications. It shows you all published applications
which you have access to. The sidebar on the left lets you open other pages: ML Models, Settings, Documentation,
and Chat.
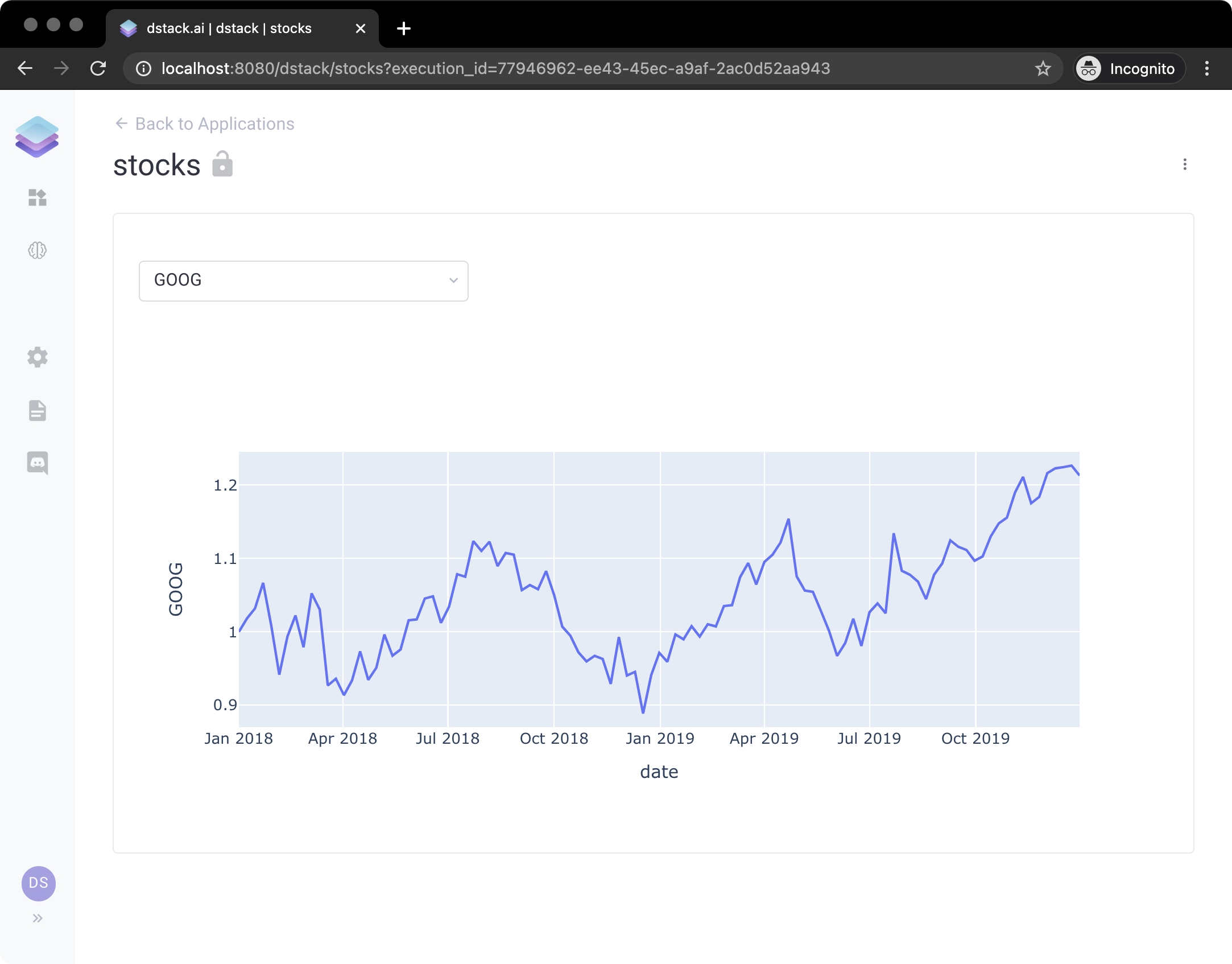
Here's an elementary example of using dstack. The application takes real-time stock exchange data from Yahoo Finance
for the FAANG companies and renders it for a selected symbol. Here's the Python code that you have to run to make such
an application:
import dstack as ds
import plotly.express as px
app = ds.app() # create an instance of the application
# an utility function that loads the data
def get_data():
return px.data.stocks()
# a drop-down control that shows stock symbols
stock = app.select(items=get_data().columns[1:].tolist())
# a handler that updates the plot based on the selected stock
def output_handler(self, stock):
# a plotly line chart where the X axis is date and Y is the stock's price
self.data = px.line(get_data(), x='date', y=stock.value())
# a plotly chart output
app.output(handler=output_handler, depends=[stock])
# deploy the application with the name "stocks" and print its URL
url = app.deploy("stocks")
print(url)If you run it and click the provided URL, you'll see the application:
To learn about how this application works and to see other examples, please check out the Tutorials documentation page.
To learn in more detail about what applications consist of and how to use all their features, check out the Concepts documentation page.
dstack decouples the development of applications from the development of ML models by offering an ML registry. This
way, one can develop ML models, push them to the registry, and then later pull these models from applications.
dstack's ML Registry supports Tensorflow, PyTorch, or Scikit-Learn models.
Here's a very simple example of how to push a model to dstack:
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.multiclass import OneVsRestClassifier
import dstack as ds
X = [[1, 2], [2, 4], [4, 5], [3, 2], [3, 1]]
y = [0, 0, 1, 1, 2]
classif = OneVsRestClassifier(estimator=SVC(random_state=0))
classif.fit(X, y)
url = ds.push("classif", classif)
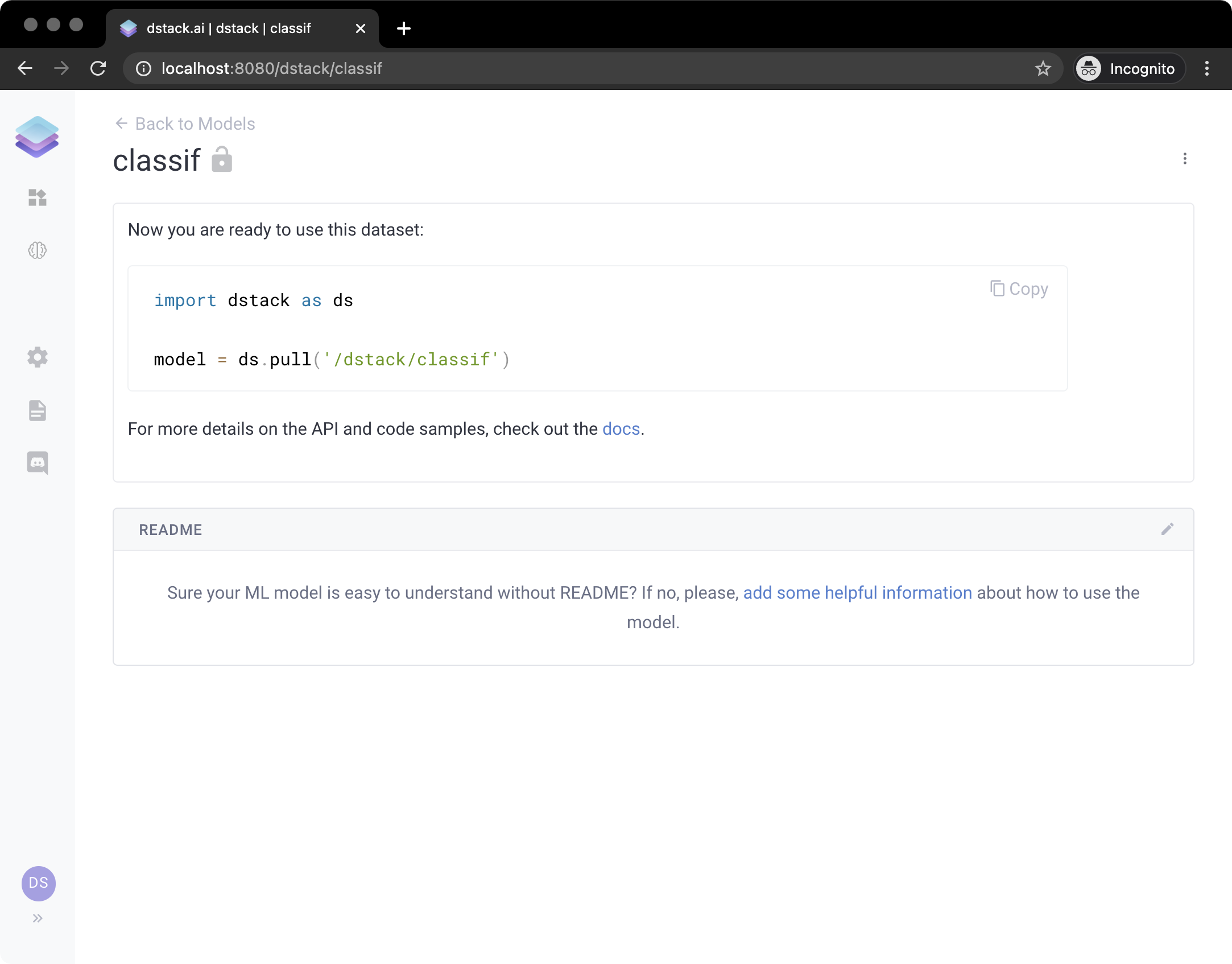
print(url)Now, if you click the URL, it will open the following page:
Here you can see the snippet of how to pull the model from an application or from anywhere else:
import dstack as ds
X = [[1, 2], [2, 4], [4, 5], [3, 2], [3, 1]]
classif = ds.pull('/dstack/classif')
classif.predict(X)To learn how to build an application that uses a simple ML model, check out the corresponding tutorial.
Do you have any feedback either minor or critical? Please, file an issue in our GitHub repo or write to us on our Discord Channel.
Have you tried dstack? Please share your feedback with us using this form!
For more details on the API and code samples, check out the docs.
The instructions on how to build dstack from sources can be found here.
dstack is an open-source library licensed under the Apache 2.0 license