openshift-aws-setup
Overview
This is an Ansible auotmation playbook that provisions a small OpenShift environment (1 master, x app nodes) that is suitable for demos, POCs and small workshops. The playbook can deploy either Origin or Container Platform.
AWS related configuration can be customised by modifying vars/aws-config.yaml. Note that the number of application nodes is configurable, the default is 3.
Prerequisites
- Ansible 2.4,1 or later is required
- AWS credentials: access key & secret --> http://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/managing-aws-access-keys.html
- Ansible installed --> http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/intro_installation.html
- Route 53 Public Hosted Zone. The playbook use Route53 for private and public DNS and routes. While the playbook automatically creates everything for the private DNS hosted zone and routes, it is expected that you have a public hosted zone in Route 53 that matches whatever you are using for the public DNS.
- By default a single admin user is created called
adminthat can be used to login into the web console. The password for the user is in thevars/aws-config.ymlvars file. PLEASE CHANGE THE PASSWORD TO SOMETHING UNIQUE!. Other users can be added to this file as well. - An AWS keypair must be generated and the reference in
vars/aws-config.ymlmust be updated to reference it (Currently referencing mykeypair). - You must update the
~/.ssh/configfile to include your keypair so the playbook can access the VMs in AWS. To do this, include the following line in you config file:
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/mykeypair.pem
Where my keypair is the name of your keypair. Obviously you need to have a copy of mykeypair.pem in the .ssh directory as well in order for it to be used.
Container Native Storage (CNS) Gluster
The playbook can optionally install CNS storage (gluster) as the default persistent storage provider for application storage. This will provision an additional three nodes dedicated to CNS. To use this feature, set the install_gluster to true and configure other parameters as needed. Note this is only used for application storage, the registry remains on AWS storage.
Note: You may wish to disable install_node_selector when installing gluster, see the section further below with regards to details.
Metrics, Logging and Prometheus (3.7)
The playbook can optionally install metrics, logging or prometheus (on 3.7 only). To do so, change install_metrics, install_logging and install_prometheus to true.
OpenShift Inventory
The OpenShift inventory can be customized by modifying roles/openshift-install/files/openshift_inventory.cfg if you want to have more advanced control over certain features.
Master and User Pods
By default, the master will not host user pods, just infra pods. If you want the master to host user pods, change install_node_selector to false in vars/aws-config.yml. Note that if you also install gluster, this will cause the gluster nodes to host user pods as well.
Note: You may want to set install_node_selector to false when you install gluster as there was an existing bug with the gluster install that causes the gluster pods to fail to be scheduled when this is enabled. This could also be corrected by updating the roles/openshift-install/files/openshift_inventory.cfg file to add the primary region to gluster.
SSL
This playbook can optionally use letsencrypt to create and install SSL certificates for the master and router. To use this
feature, change the use_lets_encrypt flag in the variables from false to true. Also make sure to set your email address as this is what lets encrypt will use to communicate with you.
Note that lets encrypt as a rate limit for creating certificates of 20 requests a week. To minimize requests to lets encrypt, the playbook will download the certifications locally to where it is running to back them up. You can then set use_lets_encrypt to false and set the various SSL certificate variables to re-use the cached certificates.
The steps the playbook uses was taken from this article, well worth reviewing if you want to understand the process. The one difference is that the playbook uses certbot in standalone mode rather then HAProxy to generate the certificate.
Run
You need to export your AWS credentials prior to running:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID>
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>
For OpenShift Origin, the command ./openshift-playbook-run.sh will execute the Ansible playbook
with a set of roles which will provision AWS infrastructure and install Openshift on top of that.
Installing OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) requires a Red Hat subscription and you must either provide your Red Hat credentials and the name of the pool to use to the script or a Red Hat organization and activation id.
./openshift-playbook-run.sh -e rhsm_username=me@something.com -e rhsm_password=mypassword -e rhsm_pool="sas876sa8sa76sjk..."
or
./openshift-playbook-run.sh -e rhsm_key_id=xxxxx -e rhsm_org_id=xxxxx"
Note the above is just an example, please update all variables including the pool name which is correct for your situation.
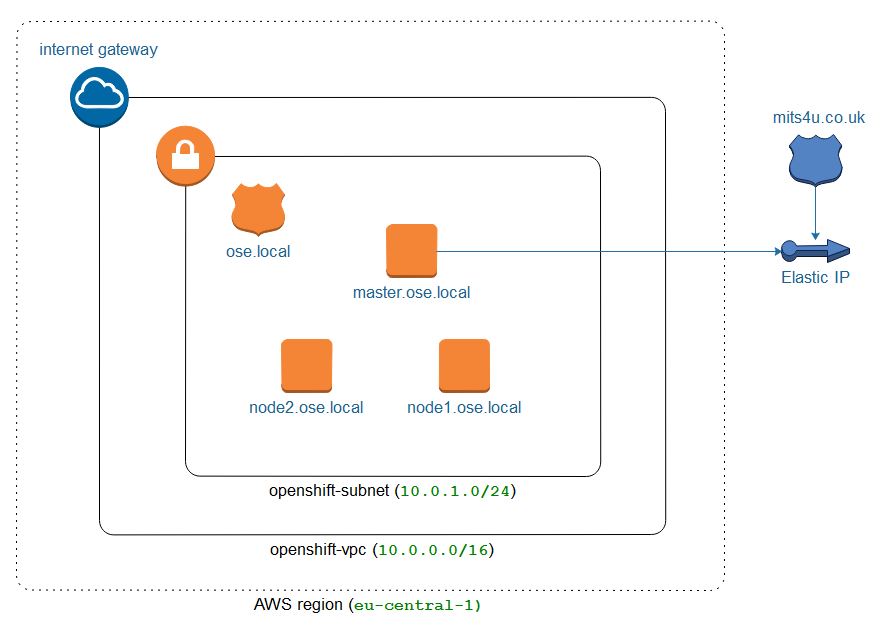
Network Topology
A private VPC and DNS is used, OpenShift is installed using the private IP addresses. This means the IP addresses never change, unlike EC2 public addresses, and the environment can be stopped and started as needed. install_node_selector A bastion is created as part of the installation, however once the installation is complete it is no longer needed and may be stopped or terminated. Note that it can be handy to keep the bastion around in a stopped state in case you want to manually re-run the installation again.
Troubleshooting
If the OpenShift installation fails at task run openshift installation script, you can ssh to the bastion and review the openshift-install.log file to see what issue occurred.
Cockpit is available on port 9090 so you can access it using the same URL as the master but change 8443 to 9090. If you set an OpenShift admin user Cockpit will be configured to use the same username/password.