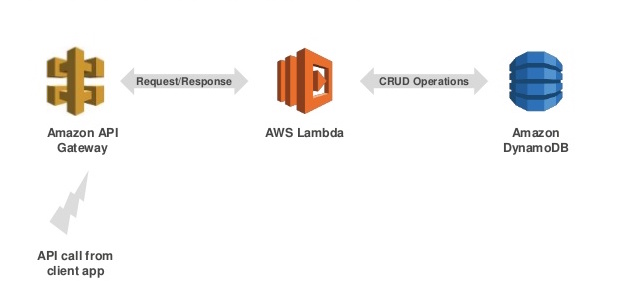
This code base is an example API built with the Java 8 runtime for AWS Lambda, in the context of a common use case: an API backed by Amazon DynamoDB as its data store. In a production deployment, you would use Amazon API Gateway to proxy RESTful API requests to the Lambda functions, each of which corresponds to a single API call. When API Gateway is added, the architecture is as follows:
By using Lambda together with DynamoDB and API Gateway, there is no need to deploy or manage servers for either the application tier or database tier. If the front end consists of mobile devices and a web app statically hosted on Amazon S3, the result is a completely serverless architecture with no need to deploy or manage servers anywhere in the system, in either the front end or back end. For further information, see the following blog post series:
- Serverless Architectures with Java 8, AWS Lambda, and Amazon DynamoDB — Part 1.
- Serverless Architectures with Java 8, AWS Lambda, and Amazon DynamoDB — Part 2.
The example use case is a company which maintains a catalog of sports events, and has decided to build an API for that catalog backed by DynamoDB. For each event, the company needs to have a record that includes the name of the home team, the event date, the name of the other (away) team, the sport involved (e.g. basketball, baseball etc.), city, country, etc. The home page of the company’s application must display all local events for a user’s favorite home team, as well as all other sports events in the user’s home city. Other queries regarding events must be supported, but queries to support the home page are the most important.
To keep this example simple, only a single Event table in DynamoDB is used to model the data, which essentially is a catalog of available events. Within this table, events are modeled using a composite key having the home team name as partition key, and event date as sort key, with the away team name as an ordinary attribute. This allows an event to be modeled as a single item in the table.
The primary prerequisite for running the code for this example is to create a table in DynamoDB. The following attributes are required, with types indicated and whether the attribute functions as a partition or sort key for the table or a Global Secondary Index (GSI):
homeTeam: String, Partition Key
eventDate: Number, Sort Key
awayTeam: String, GSI Partition Key
city: String, GSI Partition Key
eventId: Number
sport: String
country: String
Follow these steps to deploy the application:
-
Create a DynamoDB table with the keys and attributes mentioned above.
-
Create Lambda functions, one for each handler in the EventFunctions class.
-
Create a API Gateway API. Note that even if you don't do this step, you can still test the Lambda functions via the Lambda console "test function" tab.
To automate deployment of the Lambda functions and API Gateway, consider using AWS SAM (Serverless Application Model). Using SAM can simplify deploying an API, such as this one, built with a single code base that supports multiple Lambda functions. See http://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/deploying-lambda-apps.html.