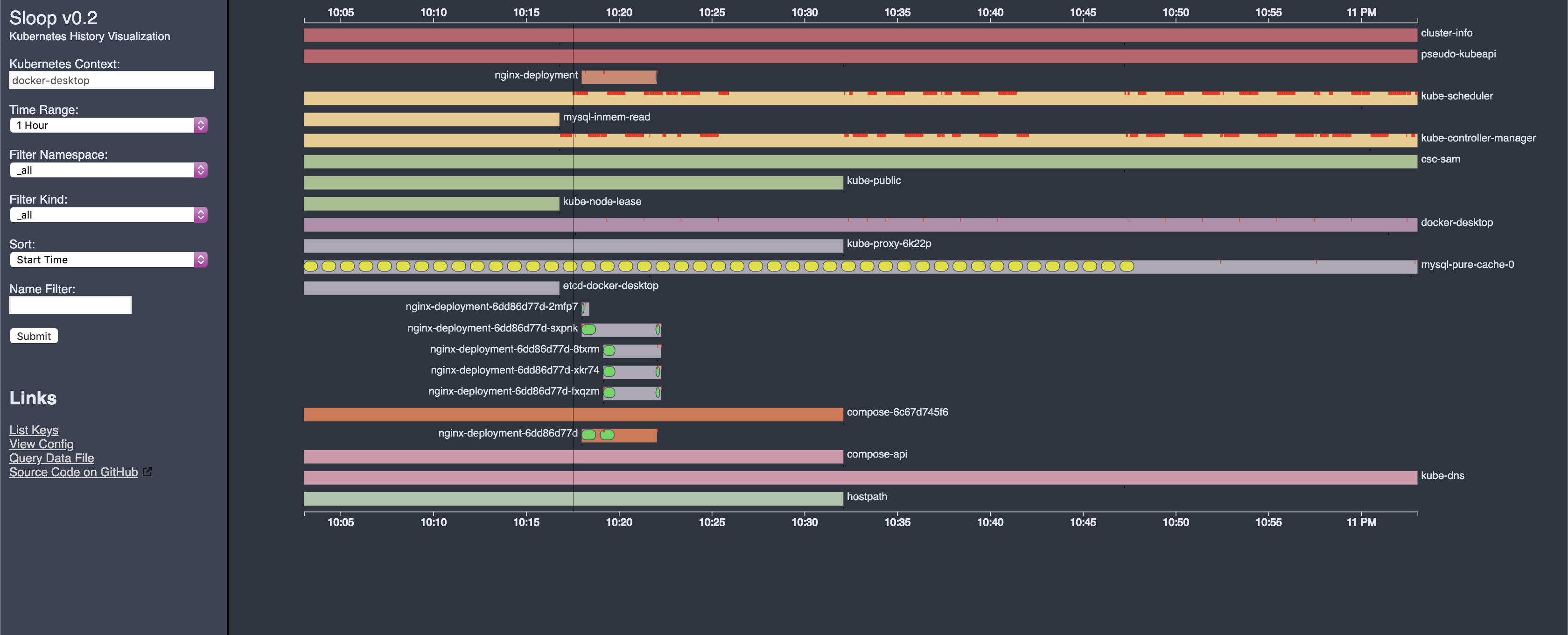
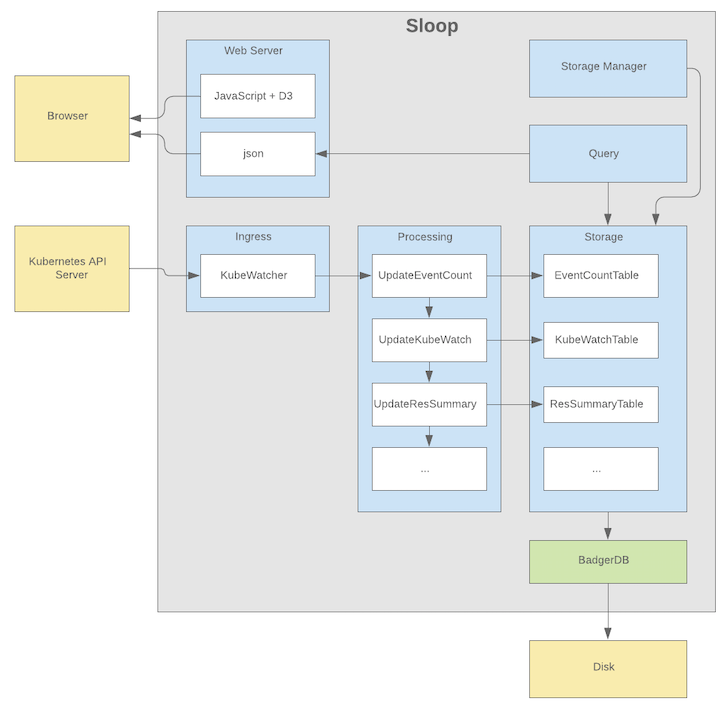
Sloop monitors Kubernetes, recording histories of events and resource state changes and providing visualizations to aid in debugging past events.
Key features:
- Allows you to find and inspect resources that no longer exist (example: discover what host the pod from the previous deployment was using).
- Provides timeline displays that show rollouts of related resources in updates to Deployments, ReplicaSets, and StatefulSets.
- Helps debug transient and intermittent errors.
- Allows you to see changes over time in a Kubernetes application.
- Is a self-contained service with no dependencies on distributed storage.
Sloop can be installed using any of these options:
Users can install sloop by using helm chart now, for instructions refer helm readme
- Docker:
sloopimage/sloop
Building Sloop from source needs a working Go environment with version 1.13 or greater installed.
Clone the sloop repository and build using make:
mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/salesforce
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/salesforce
git clone https://github.com/salesforce/sloop.git
cd sloop
make
$GOPATH/bin/sloopWhen complete, you should have a running Sloop version accessing the current context from your kubeConfig. Just point your browser at http://localhost:8080/
Other makefile targets:
- docker: Builds a Docker image.
- cover: Runs unit tests with code coverage.
- generate: Updates genny templates for typed table classes.
- protobuf: Generates protobuf code-gen.
To run from Docker you need to host mount your kubeconfig:
make docker
docker run --rm -it -p 8080:8080 -v ~/.kube/:/kube/ -e KUBECONFIG=/kube/config sloopIn this mode, data is written to a memory-backed volume and is discarded after each run. To preserve the data, you can host-mount /data with something like -v /data/:/some_path_on_host/
This is very similar to above but abstracts running docker with AWS credentials for connecting to EKS
make docker
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<access_key_id> AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<secret_access_key> AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=<session_token>
./providers/aws/sloop_to_eks.sh <cluster name>Data retention policy stated above still applies in this case.
This is an advanced feature. Use with caution.
To download a backup of the database, navigate to http://localhost:8080/data/backup
To restore from a backup, start sloop with the -restore-database-file flag set to the backup file downloaded in the previous step. When restoring, you may also wish to set the -disable-kube-watch=true flag to stop new writes from occurring and/or the -context flag to restore the database into a different context.
Refer to CONTRIBUTING.md
BSD 3-Clause