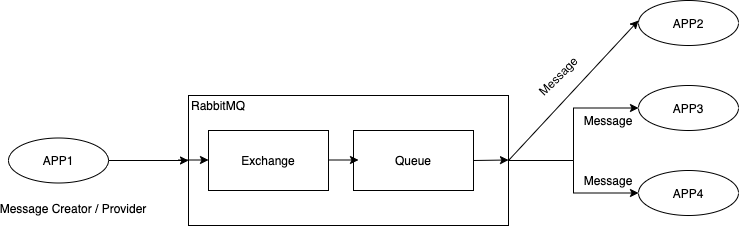
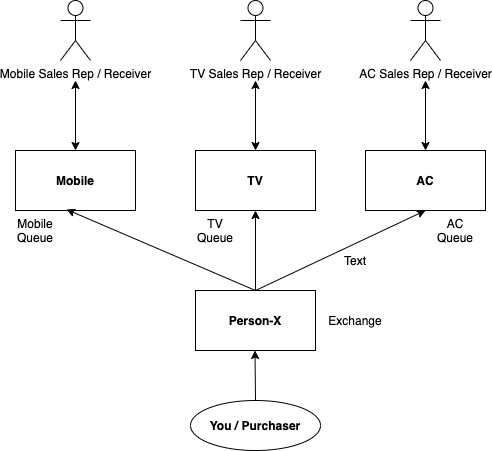
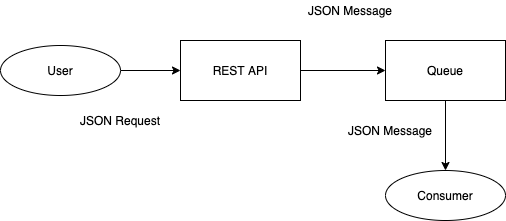
Java Messaging System (JMS)
Here is the typical example of JMS architecture overview.
Here is the type JMS example:
There are FOUR different types of exchanges available in JMS
- Direct
- Fanout
- Headers
- Topic
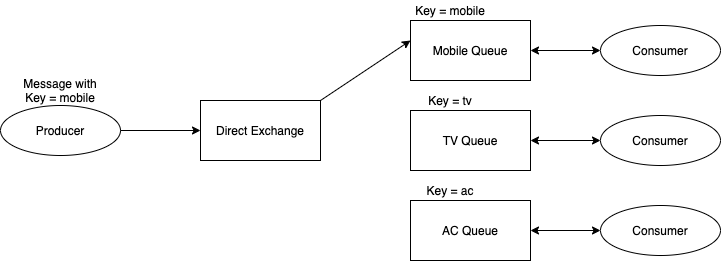
##Direct Exchange
- This type of messages will first goto the Exchanges.
- Through Exchange, message will pass to Queue using binding key
- From Queue to consumer
- In order to bind a Queue in Exchange we have to provide a "Key"
Steps to follow to create Direct Exchange and Queue:
- First: Create a Exchange with type as Direct (ex: direct-exchange)
- Second: Create three different Queues namely "Mobile", "TV" and "AC"
- Third: Attach the created Queue in Exchange under
BindingsusingAdd binding from this exchangewithQueue NameandRouting Key.
TIP: By using this
Direct ExchangeMessage Producerwill talk toExchangewhereasMessage Consumerwill talk toQueueto get the message.
For Source code refer
com.techstack.queue.directpackage
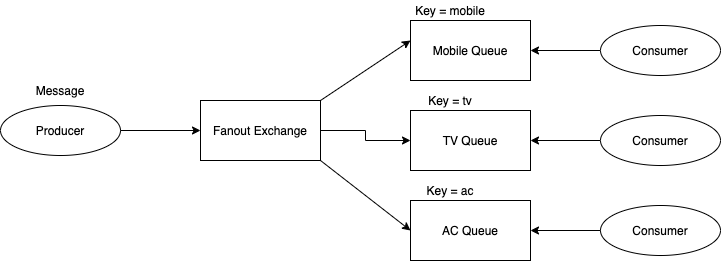
##Fanout Exchange
- This type of messages will first goto the Exchanges.
- Through Exchange, message will pass to EACH Queue which is associated with this Exchange
- From Queue to consumer
- In order to bind a Queue in Exchange we have to provide a "Key"
Typical example for Fanout Exchange is Publish-Subscribe model like Group Message or Bulk Email or other form of Group Messages.
Steps to follow to create Fanout Exchange and Queue:
- First: Create a FanoutExchange with type as Fanout (ex: fanout-exchange)
- Second: Create two different Queues namely "Mobile" and "AC"
- Third: Attach the created Queue in FanoutExchange under
BindingsusingAdd binding from this exchangewithQueue Name.
TIP: By using this
Fanout ExchangeMessage Producerwill talk toExchangewhereasMessage Consumerwill talk toQueueto get the message.
For Source code refer
com.techstack.queue.fanoutpackage
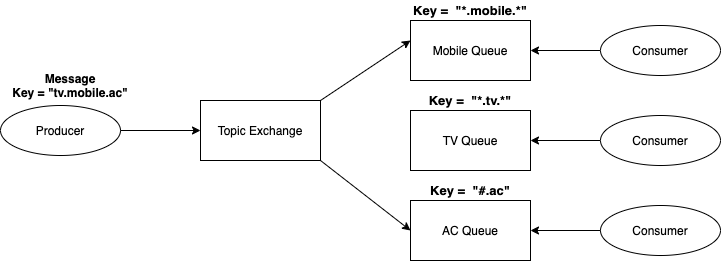
##Topic Exchange
- This type of messages will first goto the Topic Exchanges.
Steps to follow to create Topic Exchange and Queue:
- First: Create a FanoutExchange with type as Fanout (ex: fanout-exchange)
- Second: Create two different Queues namely "Mobile" and "AC"
- Third: Attach the created Queue in FanoutExchange under
BindingsusingAdd binding from this exchangewithQueue Name.
Key points:
- Producer side, message created with
keyseparated by.(dot). For example:tv.mobile.ac - Topic Exchange would identify those keys
*.mobile.*. Which means*meanseactly one wordbefore and after the mobile. #.achere#meansany number of wordsbeforeac- Here in the above diagram, TV expresion
*.tv.*doesn't satisfy the TOPIC Exchange key format. Hence, message will not moved to it's Queue. Expected istv.*.*
Some Examples about Topic Key:
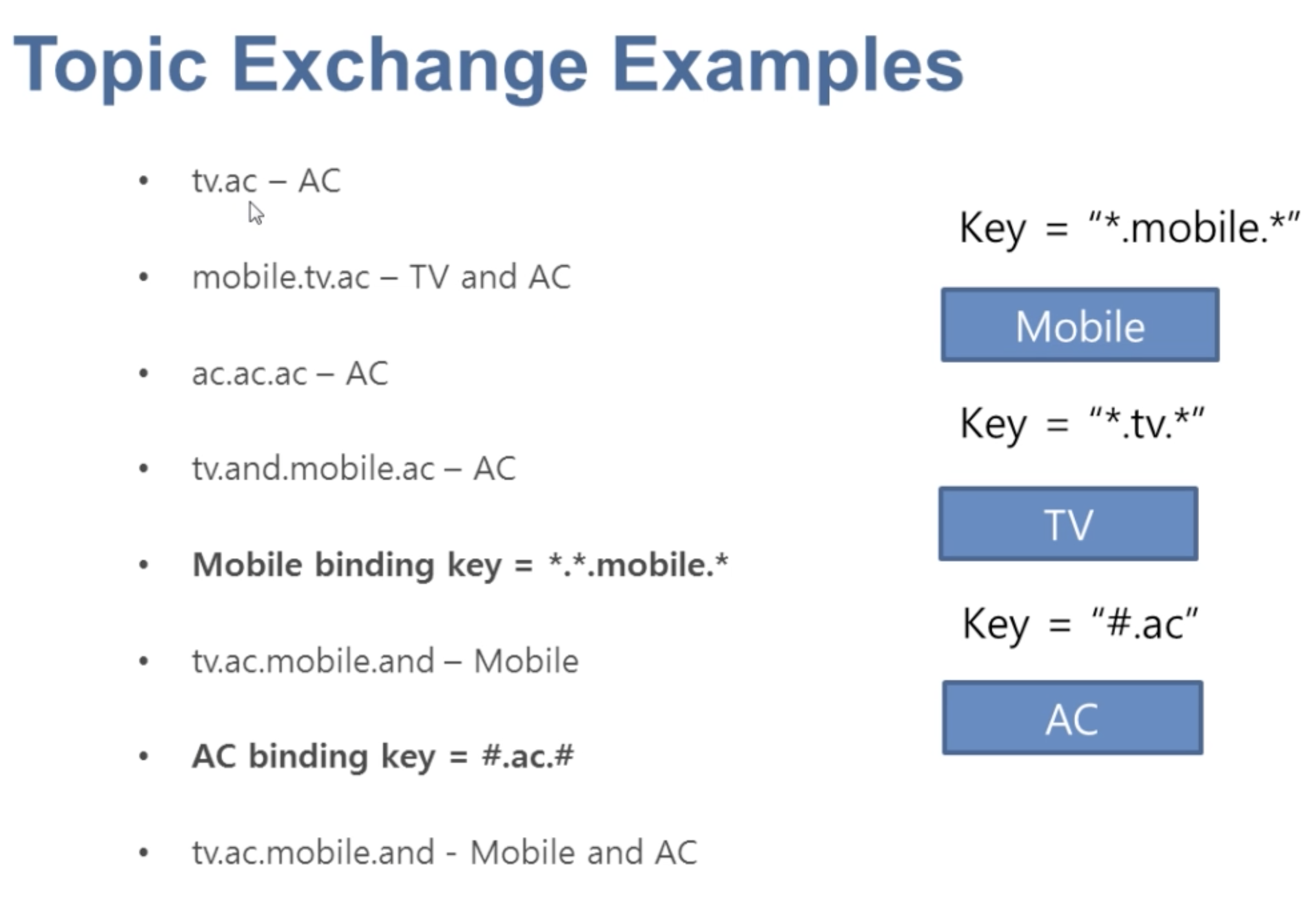
TIP: By using this
Topic ExchangeMessage Producerwill talk toExchangewhereasMessage Consumerwill talk toQueueto get the message.
For Source code refer
com.techstack.queue.topicpackage
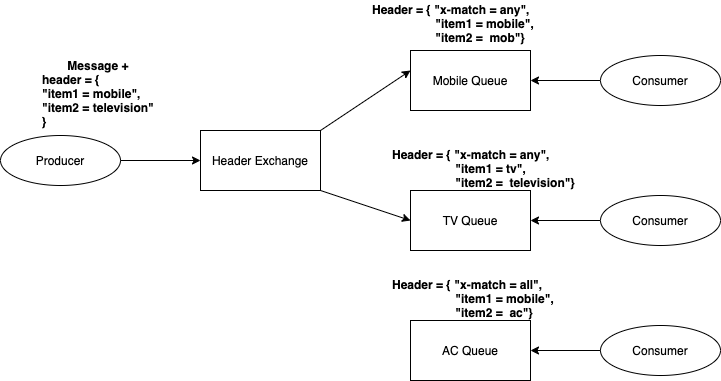
##Header Exchange
Messages with Header from Producer side will talk to HeaderExchange and based on the Exchange Header Configuration it would
route the message to specific Queue based on the Header "x-match = any | all". Here any is a OR condition and all means AND condition.
For example:
- It's a key value pair from producer side.
header = {
"item1 = mobile",
"item2 = television"
}- In the Header Exchange settings, it is configured as
x-match = anywhich means inside the incoming messageanyof thekey = valuematched attached with this Exchange Queue, the message would route to that Queue.
Header = { "x-match = any",
"item1 = mobile",
"item2 = mob"
}Once you created a Header Exchange in AMQP Server, you have to select the Bindings. Under the Bindings section, select Queue Name and use arguments key = value select
appropriate data type
TIP: By using this
Header ExchangeMessage Producerwill talk toExchangewhereasMessage Consumerwill talk toQueueto get the message.
For Source code refer
com.techstack.queue.headerspackage
Basically Default Exchange is type of Direct Exchange which doesn't have any name.
If you open RabbitMQ Exchanges tab you will see (AMQP fefault) which is of type direct.
Spring Boot and RabbitMQ provides
- RabbitMQ Template - To Produce Message
- RabbitMQ Listener - To Consume Message
For Producer Example: Refer com.techstack.rabbitmq.controller.RabbitMqController#processName
- Cloud Foundry is an open source cloud Platform As A Service (PaaS) on which developers can build, deploy, run and scale application.
- Setting Up Pivotal Cloud Foundry and Creating Organization and CLI installation
- Creating RabbitMQ service
- Spring Boot Deployment
- Spring Boot Deployment using Spring Cloud (Dependency)
- Login to your PCF Console
- Click on the Marketplace and search for "CloudAMQP" service
- Select Free Plan called "Little Lemur"
- Create a service with your "Service-Name"
- Once service instance up and running, click Manage button. It will open a Cloud AMQP.
- In the LHS you will find RabbitMQ Manager
- Alternatively you can use Hosts information
- It will ask you to enter username and password
Cloud AMQP is offering a service for RabbitMQ on Cloud. For more information refer CloudAMQP.
Integrating with Java: https://www.cloudamqp.com/docs/java.html
Someo of the usecases explained here: https://www.cloudamqp.com/docs/usecases.html