The react-arcgis repository is now archived (July 2022)
This project provided a library with a few ready to use React components (<Map />, <Scene />, <WebMap />, and <WebScene />) to get you started using the ArcGIS API for JavaScript in your React application. These components used esri-loader under the hood to lazy-load the ArcGIS API modules.
However, for a few years you have NOT needed react-arcgis to use the ArcGIS API in your React application. Instead it is best to use either @arcgis/core or esri-loader directly in your React application.
Please take a look at these modern alternatives to using react-arcgis:
- ArcGIS API for JavaScript: Build with ES Modules - how to use @arcgis/core with modern build tools (example uses React)
- ArcGIS API for JavaScript with create-react-app – An example of how to use @arcgis/core in Create React App.
- esri-loader React examples
Do you have a question related to JavaScript that isn’t specific to React? Post these questions in the GeoNET forum for the ArcGIS API for JavaScript.
IMPORTANT: This repository is now archived (July 2022) - please see above for how to use either @arcgis/core or esri-loader directly in your React application.
- Run
npm i --save esri-loader @esri/react-arcgisin your React application
If you need to support browsers lacking a native promise implementation, you will have to add a global Promise constructor polyfill to your project, as react-arcgis does not include one. See the esri-loader documentation for more details.
IMPORTANT: You must load ArcGIS API styles before using the components in this library. The snippets below assume you've already used one of the ways that esri-loader provides you with to load the ArcGIS API CSS.
Render a simple map in React:
import React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Map } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
ReactDOM.render(
<Map />,
document.getElementById('container')
);Or, render a 3D web-scene:
import React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Scene } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
ReactDOM.render(
<Scene />,
document.getElementById('container')
);You can also add webmaps and webscenes from ArcGIS Online:
import React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { WebMap, WebScene } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
ReactDOM.render(
<div style={{ width: '100vw', height: '100vh' }}>
<WebMap id="6627e1dd5f594160ac60f9dfc411673f" />
<WebScene id="f8aa0c25485a40a1ada1e4b600522681" />
</div>,
document.getElementById('container')
);If you want to change the style of the Map or Scene, just give it a class:
import React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Scene } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
ReactDOM.render(
<Scene className="full-screen-map" />,
document.getElementById('container')
);You can also pass properties into the Map, MapView, or SceneView via the viewProperties or mapProperties props:
import React from 'react';
import { Map } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
export default (props) => (
<Map
class="full-screen-map"
mapProperties={{ basemap: 'satellite' }}
/>
)These properties are passed directly to the available properties on the corresponding ArcGIS API classes:
import React from 'react';
import { Scene } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
export default (props) => (
<Scene
style={{ width: '100vw', height: '100vh' }}
mapProperties={{ basemap: 'satellite' }}
viewProperties={{
center: [-122.4443, 47.2529],
zoom: 6
}}
/>
)If you want to access the map and view instances directly after they are loaded, pass in an onLoad handler:
import React from 'react';
import { Map } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
export default class MakeAMap extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
map: null,
view: null
};
this.handleMapLoad = this.handleMapLoad.bind(this)
}
render() {
return <Map className="full-screen-map" onLoad={this.handleMapLoad} />;
}
handleMapLoad(map, view) {
this.setState({ map, view });
}
}Don't forget an onFail handler in case something goes wrong:
import React from 'react';
import { WebScene } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
export default class MakeAScene extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
status: 'loading'
};
this.handleFail = this.handleFail.bind(this);
}
render() {
return <WebScene className="full-screen-map" id="foobar" onFail={this.handleFail} />;
}
handleFail(e) {
console.error(e);
this.setState({ status: 'failed' });
}
}By default, the components in this library will use esri-loader's default options, which means they will lazy-load the modules from the CDN version of the ArcGIS API for JavaScript used by the version of esri-loader you have installed. See the esri-loader configuration documentation for information on how you can customize esri-loader's behavior.
The easiest way to do this is by calling esri-loader's setDefaultOptions() once at application startup before any of the components in this library are rendered.
import React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { setDefaultOptions } from 'esri-loader';
// app contains react-arcgis components
import { App } from './components/App.js';
// configure esri-loader to lazy load the CSS
// the fisrt time any react-arcgis components are rendered
setDefaultOptions({ css: true });
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('app')
);This requires esri-loader@^2.12.0. If you are using an older version of esri-loader you should probably upgrade.
If you can't use setDefaultOptions(), you can use the loaderOptions prop provided by each of the components in this library. That will be passed as options to loadModules(). Keep in mind that if you use loaderOptions, you must pass the same options to all react-arcgis components in your application, as well as any places where your application calls loadModules() directly.
The functionality available through the ArcGIS API for JavaScript goes well beyond just rendering maps, and if your application needs to do more with the map than simply show it, you will likely need to load and use additional classes from the ArcGIS API and provide the instances of those classes with references to the maps you've created with the components in this library.
Fortunately you've already installed esri-loader, which allows you to load any additional ArcGIS API modules your application might need. Also, react-arcgis provides the children of <Map />, <Scene />, <WebMap />, and <WebScene /> with access to their parent's map and view instances through props.
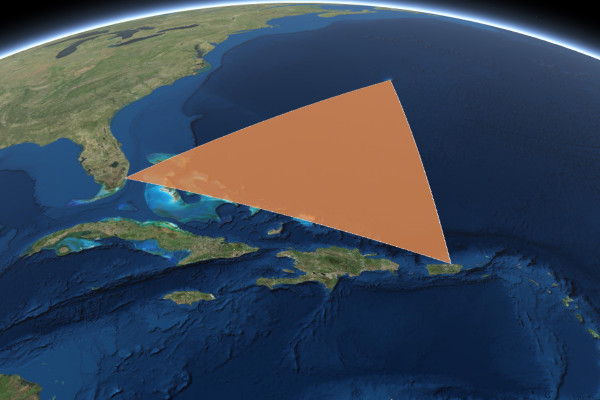
For example, let's convert a Bermuda Triangle graphic from this example into a react component:
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { loadModules } from 'esri-loader';
const BermudaTriangle = (props) => {
const [graphic, setGraphic] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
loadModules(['esri/Graphic']).then(([Graphic]) => {
// Create a polygon geometry
const polygon = {
type: "polygon", // autocasts as new Polygon()
rings: [
[-64.78, 32.3],
[-66.07, 18.45],
[-80.21, 25.78],
[-64.78, 32.3]
]
};
// Create a symbol for rendering the graphic
const fillSymbol = {
type: "simple-fill", // autocasts as new SimpleFillSymbol()
color: [227, 139, 79, 0.8],
outline: { // autocasts as new SimpleLineSymbol()
color: [255, 255, 255],
width: 1
}
};
// Add the geometry and symbol to a new graphic
const graphic = new Graphic({
geometry: polygon,
symbol: fillSymbol
});
setGraphic(graphic);
props.view.graphics.add(graphic);
}).catch((err) => console.error(err));
return function cleanup() {
props.view.graphics.remove(graphic);
};
}, []);
return null;
}
export default BermudaTriangle;Now we can use the <BermudaTriangle /> component within our <Map />, <Scene />, <WebMap />, or <WebScene />, and the map and view props will automatically be supplied by react-arcgis:
import * as React from 'react';
import { Scene } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
import BermudaTriangle from './BermudaTriangle'; // The Graphic component we just made
export default (props) => (
<Scene class="full-screen-map">
<BermudaTriangle />
</Scene>
)See the esri-loader documentation on working with ArcGIS types.
First, make sure esri-loader is installed as a dependency of your application:
npm install --save esri-loaderThen, update any import statements for loadModules():
// Replace old `loadModules` imports...
// import { Map, loadModules } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
// With a new, separate esri-loader import:
import { Map } from '@esri/react-arcgis';
import { loadModules } from 'esri-loader';Anyone is welcome to contribute to this package. However, we do not plan to add any more components to this library. If you have created a component that you'd like to share, we encourage you to share it via CodeSandbox or a gist. Once you've done that feel free to open an issue and we'll help spread the word.
We gladly welcome bug fixes or improvements to documentation.
Here are some commands that may be helpful for development:
npm test: Runs the unit testsnpm run build: Builds the application
To run the demo application against the code you are developing, you'll need to run these commands:
npm link
npm run build
cd demo
npm i
npm link @esri/react-arcgis
npm startKeep in mind that the start script only watches for changes to code in the demo app. You'll have to re-run npm run build each time you make changes in to the library and want to verify them in the demo app.
Copyright © 2017-2019 Esri
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
A copy of the license is available in the repository's LICENSE file.