An interface to subnational and national level COVID-19 data. For all countries supported, this includes a daily time-series of cases. Wherever available we also provide data on deaths, hospitalisations, and tests. National level data is also supported using a range of data sources as well as line list data and links to intervention data sets.
Install from CRAN:
install.packages("covidregionaldata")Install the stable development version of the package with:
install.packages("drat")
drat:::add("epiforecasts")
install.packages("covidregionaldata")Install the unstable development version of the package with:
remotes::install_github("epiforecasts/covidregionaldata")Load covidregionaldata, dplyr, scales, and ggplot2 (all used in
this quick start),
library(covidregionaldata)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(scales)This package can optionally use a data cache from memoise to locally
cache downloads. This can be enabled using the following (this will use
the temporary directory by default),
start_using_memoise()
#> Using a cache at: /var/folders/ss/817x_f3x2gnfr2gn2jrv_m3c0000gn/T//RtmpBAYQeNTo stop using memoise use,
stop_using_memoise()and to reset the cache (required to download new data),
reset_cache()To get worldwide time-series data by country (sourced from the World Health Organisation (WHO) by default by also optionally from the European Centre for Disease Control (ECDC), John Hopkins University, or the Google COVID-19 open data project), use:
nots <- get_national_data()
#> Downloading data from https://covid19.who.int/WHO-COVID-19-global-data.csv
#> Rows: 118,263
#> Columns: 8
#> Delimiter: ","
#> chr [3]: Country_code, Country, WHO_region
#> dbl [4]: New_cases, Cumulative_cases, New_deaths, Cumulative_deaths
#> date [1]: Date_reported
#>
#> Use `spec()` to retrieve the guessed column specification
#> Pass a specification to the `col_types` argument to quiet this message
#> Cleaning data
#> Processing data
nots
#> # A tibble: 118,263 x 15
#> date un_region who_region country iso_code cases_new cases_total
#> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2020-01-03 Asia EMRO Afghanistan AF 0 0
#> 2 2020-01-03 Europe EURO Albania AL 0 0
#> 3 2020-01-03 Africa AFRO Algeria DZ 0 0
#> 4 2020-01-03 Oceania WPRO American Samoa AS 0 0
#> 5 2020-01-03 Europe EURO Andorra AD 0 0
#> 6 2020-01-03 Africa AFRO Angola AO 0 0
#> 7 2020-01-03 Americas AMRO Anguilla AI 0 0
#> 8 2020-01-03 Americas AMRO Antigua & Bar… AG 0 0
#> 9 2020-01-03 Americas AMRO Argentina AR 0 0
#> 10 2020-01-03 Asia EURO Armenia AM 0 0
#> # … with 118,253 more rows, and 8 more variables: deaths_new <dbl>,
#> # deaths_total <dbl>, recovered_new <dbl>, recovered_total <dbl>,
#> # hosp_new <dbl>, hosp_total <dbl>, tested_new <dbl>, tested_total <dbl>This can also be filtered for a country of interest,
g7 <- c(
"United States", "United Kingdom", "France", "Germany",
"Italy", "Canada", "Japan"
)
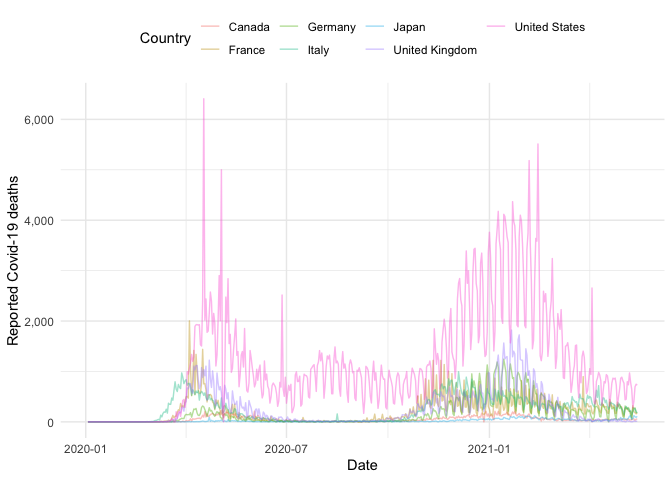
g7_nots <- get_national_data(countries = g7, verbose = FALSE)Using this data we can compare case information between countries, for example here is the number of deaths over time for each country in the G7:
g7_nots %>%
ggplot() +
aes(x = date, y = deaths_new, col = country) +
geom_line(alpha = 0.4) +
labs(x = "Date", y = "Reported Covid-19 deaths") +
scale_y_continuous(labels = comma) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "top") +
guides(col = guide_legend(title = "Country"))To get time-series data for subnational regions of a specific country, for example by level 1 region in the UK, use:
uk_nots <- get_regional_data(country = "UK", verbose = FALSE)
uk_nots
#> # A tibble: 6,136 x 26
#> date region region_code cases_new cases_total deaths_new deaths_total
#> <date> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2020-01-30 East Mi… E12000004 NA NA NA NA
#> 2 2020-01-30 East of… E12000006 NA NA NA NA
#> 3 2020-01-30 England E92000001 2 2 NA NA
#> 4 2020-01-30 London E12000007 NA NA NA NA
#> 5 2020-01-30 North E… E12000001 NA NA NA NA
#> 6 2020-01-30 North W… E12000002 NA NA NA NA
#> 7 2020-01-30 Norther… N92000002 NA NA NA NA
#> 8 2020-01-30 Scotland S92000003 NA NA NA NA
#> 9 2020-01-30 South E… E12000008 NA NA NA NA
#> 10 2020-01-30 South W… E12000009 NA NA NA NA
#> # … with 6,126 more rows, and 19 more variables: recovered_new <dbl>,
#> # recovered_total <dbl>, hosp_new <dbl>, hosp_total <dbl>, tested_new <dbl>,
#> # tested_total <dbl>, areaType <chr>, cumCasesByPublishDate <dbl>,
#> # cumCasesBySpecimenDate <dbl>, newCasesByPublishDate <dbl>,
#> # newCasesBySpecimenDate <dbl>, cumDeaths28DaysByDeathDate <dbl>,
#> # cumDeaths28DaysByPublishDate <dbl>, newDeaths28DaysByDeathDate <dbl>,
#> # newDeaths28DaysByPublishDate <dbl>, newPillarFourTestsByPublishDate <lgl>,
#> # newPillarOneTestsByPublishDate <dbl>,
#> # newPillarThreeTestsByPublishDate <dbl>,
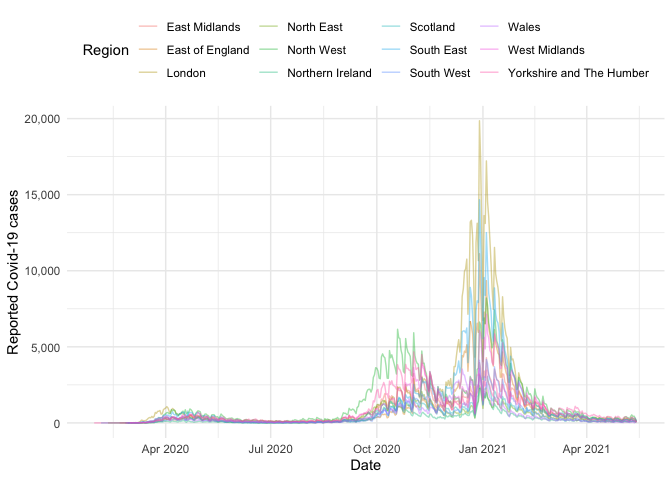
#> # newPillarTwoTestsByPublishDate <dbl>Now we have the data we can create plots, for example the time-series of the number of cases for each region:
uk_nots %>%
filter(!(region %in% "England")) %>%
ggplot() +
aes(x = date, y = cases_new, col = region) +
geom_line(alpha = 0.4) +
labs(x = "Date", y = "Reported Covid-19 cases") +
scale_y_continuous(labels = comma) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "top") +
guides(col = guide_legend(title = "Region"))See get_available_datasets() for supported regions and subregional
levels. For an updated view of dataset status check the hosted
page
or build the dataset status vignette.
For further examples see the quick start
vignette.
Additional subnational data are supported via the JHU() and Google()
classes. Use the available_regions() method once these data have been
downloaded and cleaned (see their examples) for subnational data they
internally support.
If using covidregionaldata in your work please consider citing it
using the following,
#>
#> To cite covidregionaldata in publications use:
#>
#> Sam Abbott, Katharine Sherratt, Joe Palmer, Richard Martin-Nielsen,
#> Jonnie Bevan, Hamish Gibbs, and Sebastian Funk (2020).
#> covidregionaldata: Subnational Data for the COVID-19 Outbreak, DOI:
#> 10.5281/zenodo.3957539
#>
#> A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
#>
#> @Article{,
#> title = {covidregionaldata: Subnational Data for the COVID-19 Outbreak},
#> author = {Sam Abbott and Katharine Sherratt and Joe Palmer and Richard Martin-Nielsen and Jonnie Bevan and Hamish Gibbs and Sebastian Funk},
#> journal = {-},
#> year = {2020},
#> volume = {-},
#> number = {-},
#> pages = {-},
#> doi = {10.5281/zenodo.3957539},
#> }
We welcome contributions and new contributors! We particularly appreciate help adding new data sources for countries at sub-national level, or work on priority problems in the issues. Please check and add to the issues, and/or add a pull request. For more details, start with the contributing guide. For details of the steps required to add support for a dataset see the adding data guide.