This repository contains implementations of four fast adversarial attacks on no-reference image- and video-quality metrics.
- Cumulative UAP [training code] [inference code]
- Generative UAP [training code] [inference code]
- Optimized UAP [training code] [inference code]
- CNN-based [training code] [inference code] [pre-trained models]
In this code, we attacked PaQ-2-PiQ NR image quality metric. To attack any other NR metric, you need to change the target model.
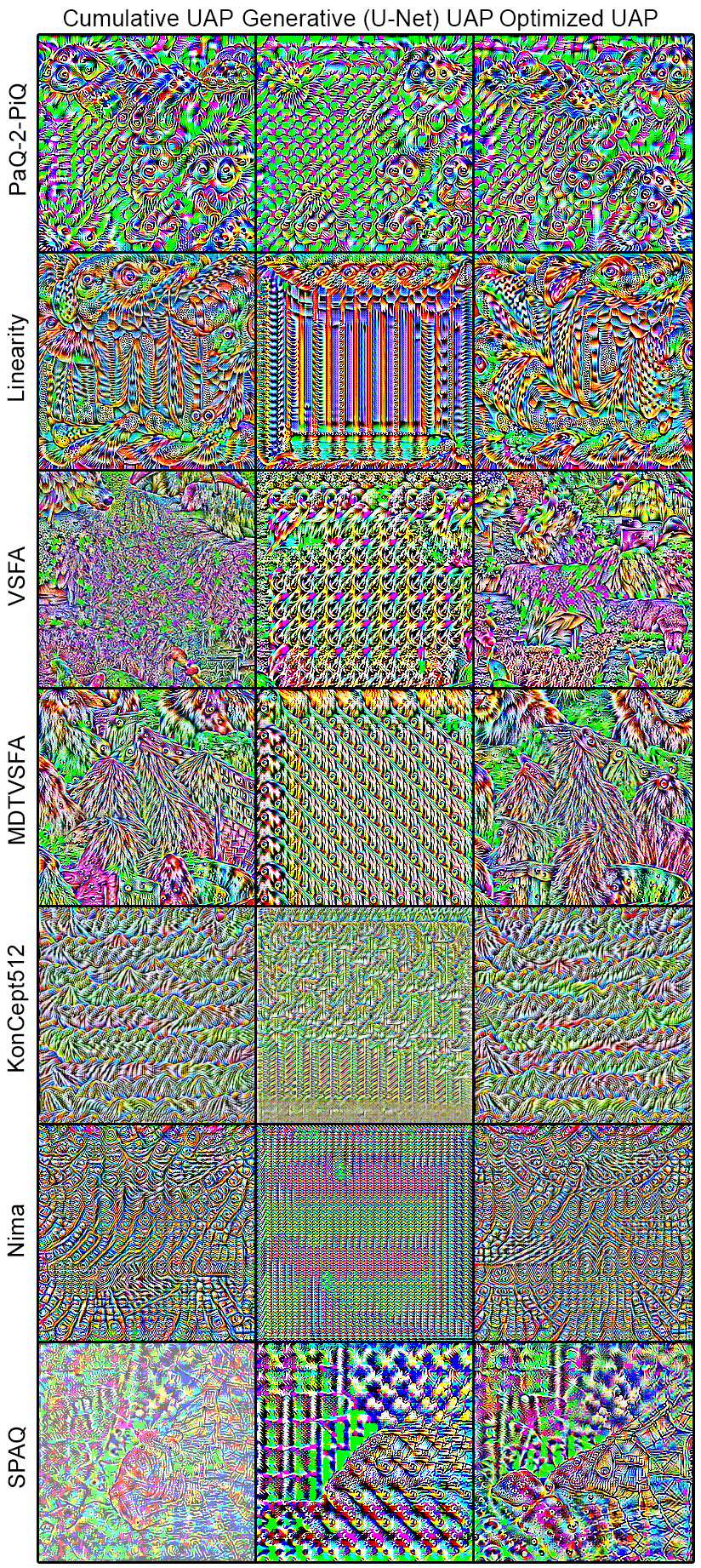
Visualizations of UAPs generated using different methods when attacking PaQ-2-PiQ, Linearity, VSFA, MDTVSFA, KonCept512, Nima, and SPAQ.
If you use this code for your research, please cite our paper.
@article{SHUMITSKAYA2024103913,
title = {Towards adversarial robustness verification of no-reference image- and video-quality metrics},
journal = {Computer Vision and Image Understanding},
volume = {240},
pages = {103913},
year = {2024},
issn = {1077-3142},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2023.103913},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S107731422300293X},
author = {Ekaterina Shumitskaya and Anastasia Antsiferova and Dmitriy Vatolin},
keywords = {Image Quality Assessment, Blind Image Quality Assessment, Attacks on Image-Quality Metrics},
abstract = {In this paper, we propose a new method of analysing the stability of modern deep image- and video-quality metrics to different adversarial attacks. The stability analysis of quality metrics is becoming important because nowadays the majority of metrics employ neural networks. Unlike traditional quality metrics based on nature scene statistics or other hand-crafter features, learning-based methods are more vulnerable to adversarial attacks. The usage of such unstable metrics in benchmarks may lead to being exploited by the developers of image and video processing algorithms to achieve higher positions in leaderboards. The majority of known adversarial attacks on images designed for computer vision tasks are not fast enough to be used within real-time video processing algorithms. We propose four fast attacks on metrics suitable for real-life scenarios. The proposed methods are based on creating perturbations that increase metrics scores and can be applied frame-by-frame to attack videos. We analyse the stability of seven widely used no-reference image- and video-quality metrics to proposed attacks. The results showed that only three metrics are stable against our real-life attacks. This research yields insights to further aid in designing stable neural-network-based no-reference quality metrics. Proposed attacks can serve as an additional verification of metrics’ reliability.}
}