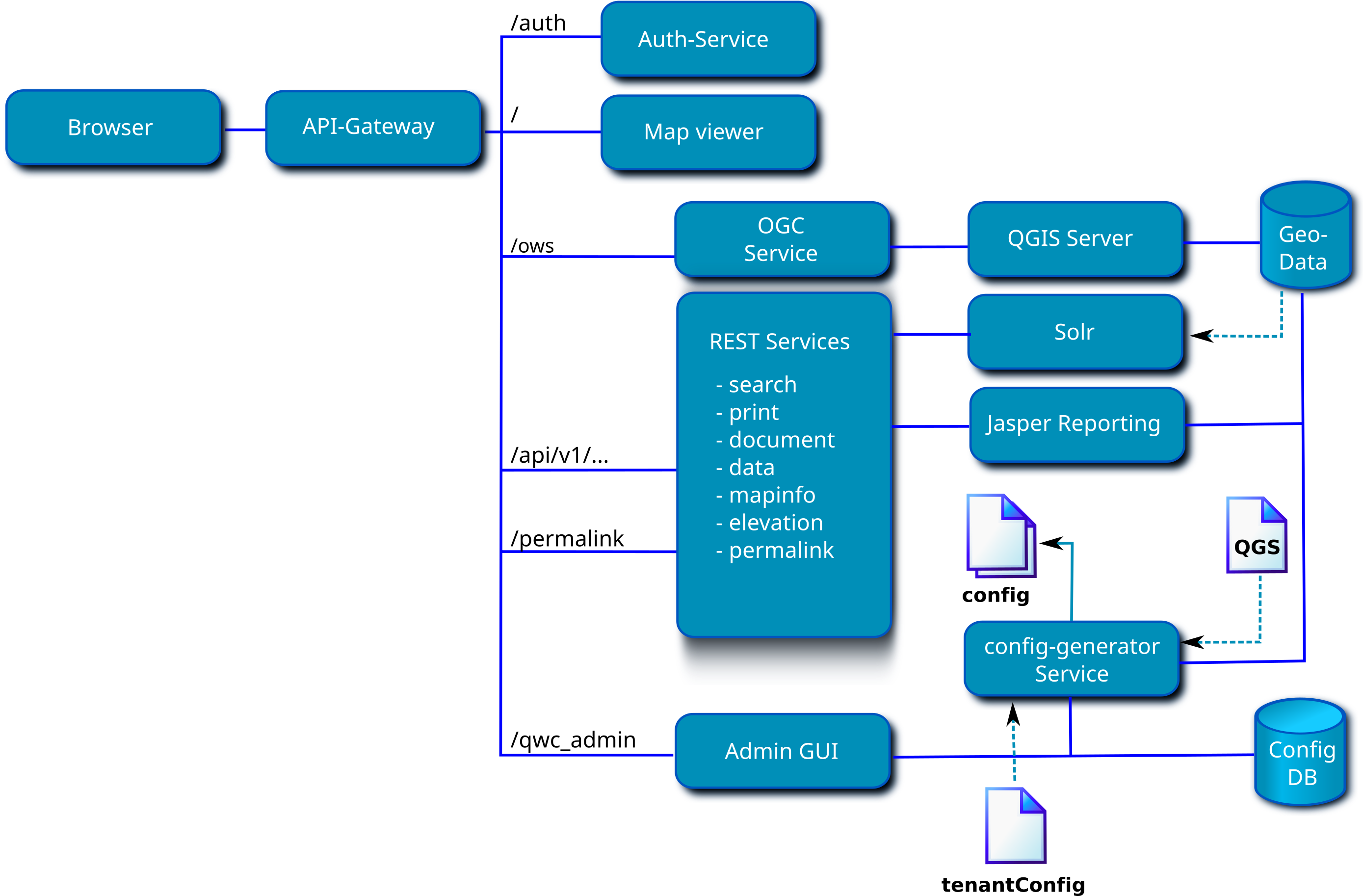
The QWC Services are a collection of microservices providing configurations for and authorized access to different QWC2 Map Viewer components.
This repository contains a sample setup for running QWC services with docker.
Please consult the upgrade notes when updating the docker images.
- Quick start
- Architecture overview
- Service overview
- Selected configuration topics
- Resources and Permissions
- Group registration
- Health checks for Kubernetes
- Development
Install docker and docker compose:
- Docker: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/
- docker-compose: (https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/)
Clone qwc-docker and copy docker-compose and api-gateway configuration template:
git clone https://github.com/qwc-services/qwc-docker.git
cd qwc-docker
cp docker-compose-example.yml docker-compose.yml
cp api-gateway/nginx-example.conf api-gateway/nginx.conf
Create a secret key:
python3 -c 'import secrets; print("JWT_SECRET_KEY=\"%s\"" % secrets.token_hex(48))' >.env
Permissions for writable volumes: by default, all QWC services run as UID=33, GID=33. You can either:
-
Change the ownership of the writeable volumes accordingly:
sudo chown -R 33:33 volumes/attachments sudo chown -R 33:33 volumes/config sudo chown -R 33:33 volumes/qgs-resources sudo chown -R 33:33 volumes/qwc2/assets -
Or change the UID/GID which runs the QWC services to match the user/group which owns the shared volumes on the host by setting
SERVICE_GIDandSERVICE_GIDindocker-compose.ymlunderx-qwc-service-variables.
Set permissions for the shared solr data volume:
sudo chown 8983:8983 volumes/solr/data
Start all containers:
docker-compose up -d
Follow log output:
docker-compose logs -f
Open map viewer:
http://localhost:8088/
Open Admin GUI (Default admin credentials: username admin, password admin, requires password change on first login):
http://localhost:8088/qwc_admin
Conntect to DB:
psql "service=qwc_configdb" # Config DB
psql "service=qwc_geodb" # Demo data DB
- See pg_service.conf
Demo DB superuser password (please change for production use!):
- See
POSTGRES_PASSWORDin https://github.com/qwc-services/qwc-base-db/blob/main/Dockerfile
Stop all containers:
docker-compose down
Update containers:
- Change image tag for desired container in
docker-compose.yml - Run
docker-compose-pull <container name>
API-Gateway: API Gateway, forwards requests to individual services (http://localhost:8088)Auth-Service: Authentication service with local user database (default users:admin:admin,demo:demo) (http://localhost:8088/auth/login)Map viewer: QWC2 map viewer (http://localhost:8088)OGC Service: Proxy for WMS/WFS requests filtered by permissions, calls QGIS Server (http://localhost:8088/ows/api)Admin GUI: Admin GUI (http://localhost:8088/qwc_admin/)
Applications:
- QWC2 Map Viewer: The map viewer application
- QWC admin GUI: Configuration backend for managing users and permissions
- Registration GUI: GUI for registration of new users
REST services:
- DB auth service: Authentication service with local user database
- LDAP auth service: LDAP Authentication service
- Data service: Data edit service, required for QWC2 editing functionality
- Document service: Service for generating Jasper reports
- Elevation service: Service for providing elevation data, required for QWC2 elevation profile
- Feature info service: Service for providing enhanced GetFeatureInfo responses to QWC2
- Fulltext search service: Fulltext search service for the QWC2 search functionality
- Legend service: Service for providing enhanced legend graphics to QWC2
- Mapinfo service: Service for providing additional information to the QWC2 right-click map context popup
- OGC service: Proxy for WMS/WFS requests filtered by permissions, calls QGIS Server
- Permalink service: Service for storing compat permalinks and bookmarks generated by QWC2
- Print service: Service for enhancing the QWC2 GetPrint requests
Configuration database:
Configuration generator:
An overview of how each container accesses which volume can be found here.
-
If necessary, setup new PG service connections:
-
Locally:
cat >>~/.pg_service.conf <<EOF [qwc_example_conn] host=localhost port=5439 dbname=qwc_example_db user=qwc_service password=qwc_service sslmode=disable EOF -
For the QWC Docker:
cat >>~/.pg_service.conf <<EOF [qwc_example_conn] host=qwc-postgis port=5432 dbname=qwc_example_db user=qwc_service password=qwc_service sslmode=disable EOF
-
-
Configure project for QWC2
- Automatically generated theme configuration: Save project as
<project>.qgsinvolumes/qgs-resources/scan/(see config generator configuration) - Manual theme configuration: Save project as
<project>.qgsinvolumes/qgs-resources/and editvolumes/config-in/default/tenantConfig.json(see themesConfig documentation).
- Automatically generated theme configuration: Save project as
-
Launch Admin GUI and generate configuration
- Preconfigured example:
volumes/qgs-resources/qwc_demo.qgs, with layersedit_points,edit_linesandedit_polygonsconfigured as editable layers in the Admin GUI - Changed the edit form type in the Attributes Form section of the QGIS layer properties dialog:
- Autogenerate: A flat edit form will be generated for QWC2
- Drag and Drop Designer: A grouped edit form will be generated for QWC2, the generated edit form is stored in
volumes/qwc2/assets/forms/autogen/<dataset>.ui - Provide ui-file: The specified UI form (must lie next to the project in or below
volumes/qgs-resources) will be copied tovolumes/qwc2/assets/forms/autogen/<dataset>.uiand used by QWC2 - See data service documentation
- Update configuration in Admin GUI
Make solr owner of solr data sudo chown 8983:8983 volumes/solr/data
# Cleanup
sudo rm -rf volumes/solr/data/*
docker-compose restart qwc-solr
curl 'http://localhost:8983/solr/gdi/dih_geodata?command=full-import'
curl 'http://localhost:8983/solr/gdi/dih_geodata?command=status'
curl 'http://localhost:8983/solr/gdi/select?q=search_1_stem:austr*'
curl 'http://localhost:8983/solr/gdi/dih_metadata?command=full-import&clean=false'
curl 'http://localhost:8983/solr/gdi/dih_metadata?command=status'
curl 'http://localhost:8983/solr/gdi/select?q=search_1_stem:qwc_demo'
Test query for fulltext search:
curl 'http://localhost:8983/solr/gdi/select?q=search_1_stem:austr*'
Use the sourcepole/qwc-map-viewer-base image rather than sourcepole/qwc-map-viewer-demo for qwc-map-viewer in docker-compose.yml.
Clone and build QWC2 Demo App (see Quick start) (or use your custom QWC2 build):
git clone --recursive https://github.com/qgis/qwc2-demo-app.git
cd qwc2-demo-app/
yarn install
yarn run build
Copy QWC2 files from a build:
SRCDIR=./qwc2-demo-app/ DSTDIR=./qwc-docker/volumes
cp -a SRCDIR/prod/ $DSTDIR/volumes/qwc2/
Note: The viewer config.json and index.html are by default loaded from volumes/config-in/default/, look for qwc2_config_file and qwc2_index_file in volumes/config-in/default/tenantConfig.json.
Note: The config generator will automatically adjust known service URLs in config.json (such as editServiceUrl) according to the URLs specified in the mapViewer section of tenantConfig.json, i.e. data_service_url
The Configuration database (ConfigDB) contains the database schema qwc_config for configurations and permissions of QWC services.
This database uses the PostgreSQL connection service qwc_configdb by default, which can be setup for the corresponding database in the PostgreSQL connection service file pg_service.conf. This default can be overridden by setting the environment variable CONFIGDB_URL to a custom DB connection string (see below).
Additional user fields are saved in the table qwc_config.user_infos with a a one-to-one relation to qwc_config.users via the user_id foreign key.
To add custom user fields, add new columns to your qwc_config.user_infos table and set your USER_INFO_FIELDS accordingly (see below).
An existing ConfigDB can be updated to the latest schema by running the database migrations from the qwc-config-db directory:
git clone https://github.com/qwc-services/qwc-config-db.git
cd qwc-config-db/
# Install alembic, either globally or activate python virtualenv and run `pip install -r requirements.txt`)
alembic upgrade head
Note: local PG service definition for qwc_configdb must exist:
cat >>~/.pg_service.conf <<EOF
[qwc_configdb]
host=localhost
port=5439
dbname=qwc_demo
user=qwc_admin
password=qwc_admin
sslmode=disable
EOF
QWC services can be configured according to the configuration schema described in the respective service READMEs in tenantConfig.json.
Variables can also be set as environment variables in capitalized form in docker-compose.yml.
Some variables must be set as environment variables in docker-compose.yml:
| ENV | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
INPUT_CONFIG_PATH |
config-in |
Base path for service configuration files |
OUTPUT_CONFIG_PATH |
/tmp |
Base path for service configuration files |
JWT_SECRET_KEY |
******** |
secret key for JWT token |
TENANT_URL_RE |
None | Regex for tenant extraction from base URL. Example: ^https?://.+?/(.+?)/ |
TENANT_HEADER |
None | Tenant Header name. Example: Tenant |
See READMEs of services for details.
-
Add container entry in
docker-compose.yml, ensuring the following two environment variables are set:- SERVICE_MOUNTPOINT=/<mountpoint> - JWT_SECRET_KEY=$JWT_SECRET_KEYExample:
qwc-print-service: image: sourcepole/qwc-print-service:v2022.01.26 environment: <<: *qwc-service-variables SERVICE_MOUNTPOINT: '/api/v1/print' volumes: - ./volumes/config:/srv/qwc_service/config:ro ports: - "127.0.0.1:5020:9090" -
Add corresponding entry in
api-gateway/nginx.conf, example:location /api/v1/print { proxy_pass http://qwc-print-service:9090; } -
If necessary, uncomment/add the respective service url in the
mapViewerconfig block ofvolumes/config-in/default/tenantConfig.json, i.e.{ "name": "mapViewer", "generator_config": { # ... }, "config": { "print_service_url": "/api/v1/print/", # ... } } -
Add the service configuration block below
servicesinvolumes/config-in/default/tenantConfig.json, according to the service config schema, i.e.{ "name": "print", "config": { "ogc_service_url": "http://qwc-ogc-service:9090/", "qgis_server_version": "3.16" } }
Permissions and configurations are based on different resources with assigned permissions in the configuration database. These can be managed in the QWC configuration backend.
The following resource types are available:
map: WMS corresponding to a QGIS Projectlayer: layer of a mapattribute: attribute of a map layer
print_template: print composer template of a QGIS Projectdata: Data layer for editingattribute: attribute of a data layer
data_create: Data layer for creating featuresdata_read: Data layer for reading featuresdata_update: Data layer for updating featuresdata_delete: Data layer for deleting features
viewer: custom map viewer configurationviewer_task: permittable viewer tasks
The resource name corresponds to the technical name of its resource (e.g. WMS layer name).
The resource types can be extended by inserting new types into the qwc_config.resource_types table.
These can be queried, e.g. in a custom service, by using PermissionClient::resource_permissions() or
PermissionClient::resource_restrictions() from QWC Services Core.
Available map, layer, attribute and print_template resources are collected from WMS GetProjectSettings and the QGIS projects.
data and their attribute resources define a data layer for the Data service.
Database connections and attribute metadata are collected from the QGIS projects.
For more detailed CRUD permissions data_create, data_read, data_update and data_delete can be used instead of data
(data and write=False is equivalent to data_read; data and write=True is equivalent to all CRUD resources combined).
The viewer resource defines a custom viewer configuration for the map viewer (see Custom viewer configurations).
The viewer_task resource defines viewer functionalities (e.g. printing or raster export) that can be restricted or permitted.
Their name (e.g. RasterExport) corresponds to the key in menuItems and toolbarItems in the QWC2 config.json. Restricted viewer task items are then removed from the menu and toolbar in the map viewer. Viewer tasks not explicitly added as resources are kept unchanged from the config.json.
Permissions are based on roles. Roles can be assigned to groups or users, and users can be members of groups.
A special role is public, which is always included, whether a user is signed in or not.
Each role can be assigned a permission for a resource.
The write flag is only used for data resources and sets whether a data layer is read-only.
Based on the user's identity (user name and/or group name), all corresponding roles and their permissions and restrictions are collected. The service configurations are then modified according to these permissions and restrictions.
Using the DEFAULT_ALLOW environment variable, some resources can be set to be permitted or restricted by default if no permissions are set (default: False). Affected resources are map, layer, print_template and viewer_task.
e.g. DEFAULT_ALLOW=True: all maps and layers are permitted by default
e.g. DEFAULT_ALLOW=False: maps and layers are only available if their resources and permissions are explicitly configured
The QWC Config Generator generates a JSON file for all permissions (JSON schema) from the QWC ConfigDB. See READMEs of QWC services for service specific contents in permissions.json.
Alternatively, a simplified permissions format is also supported, see unified permissions.
Using the optional Registration GUI allows users to request membership or unsubscribe from registrable groups. These requests can then be accepted or rejected in the Admin GUI.
Workflow:
- Admin GUI
- admin user creates new groups with assigned roles and permissions on resources
- admin user configures registrable groups
- Registration GUI
- user select desired groups from registrable groups and submits application form
- admin users are notified of new registration requests
- Admin GUI
- admin user selects entry from list of pending registration requests
- admin user accepts or rejects registration requests for a user
- user is added to or removed from accepted groups
- user is notified of registration request updates
- Map Viewer
- user permissions are updated for new groups
Health checks are a simple way to let the system know if an instance of the app is working or not working. If an instance of the app is not working, then other services should not access it or send a request to it. Instead, requests should be sent to another instance of the app that is ready, or retried at a later time. The system should also bring the app back to a healthy state.
Readiness probes are designed to let Kubernetes know when the app is ready to serve traffic. Kubernetes makes sure the readiness probe passes before allowing a service to send traffic to the pod. If a readiness probe starts to fail, Kubernetes stops sending traffic to the pod until it passes.
Check is available at: /ready
Example check:
- Return ok, if web service is initialized and running
Check is available at: /healthz
Liveness probes let Kubernetes know if the app is alive or dead. If the app is alive, then Kubernetes leaves it alone. If the app is dead, Kubernetes removes the Pod and starts a new one to replace it.
Example checks:
- Check database connection (Example service: qwc-admin-gui)
- Check if all data files are available and readable (Example service: qwc-elevation-service)
Create a QWC services dir:
mkdir qwc-services
cd qwc-services/
Clone QWC Config DB:
git clone https://github.com/qwc-services/qwc-config-db.git
Clone QWC Config service:
git clone https://github.com/qwc-services/qwc-config-service.git
Clone QWC OGC service:
git clone https://github.com/qwc-services/qwc-ogc-service.git
Clone QWC Data service:
git clone https://github.com/qwc-services/qwc-data-service.git
Clone QWC Map Viewer:
git clone https://github.com/qwc-services/qwc-map-viewer.git
Clone QWC Admin GUI:
git clone https://github.com/qwc-services/qwc-admin-gui.git
See READMEs of each service for their setup.
Setup your ConfigDB and run migrations (see QWC Config DB).
Run local services (set $QGIS_SERVER_URL to your QGIS server and $QWC2_PATH to your QWC2 files):
cd qwc-config-service/
QGIS_SERVER_URL=http://localhost:8001/ows/ QWC2_PATH=qwc2/ python server.py
cd qwc-ogc-service/
QGIS_SERVER_URL=http://localhost:8001/ows/ CONFIG_SERVICE_URL=http://localhost:5010/ python server.py
cd qwc-data-service/
CONFIG_SERVICE_URL=http://localhost:5010/ python server.py
cd qwc-map-viewer/
OGC_SERVICE_URL=http://localhost:5013/ CONFIG_SERVICE_URL=http://localhost:5010/ QWC2_PATH=qwc2/ python server.py
cd qwc-admin-gui/
python server.py
Sample requests:
curl 'http://localhost:5010/ogc?ows_type=WMS&ows_name=qwc_demo'
curl 'http://localhost:5010/qwc'
curl 'http://localhost:5013/qwc_demo?VERSION=1.1.1&SERVICE=WMS&REQUEST=GetCapabilities'
curl 'http://localhost:5012/qwc_demo.edit_points/'
curl 'http://localhost:5030/themes.json'
curl 'http://localhost:5031'
To build containers for local services, in use build: rather than image: in docker-compose.yml:
qwc-print-service:
# image: sourcepole/qwc-print-service:v2022.01.13
build:
context: ./qwc-services/qwc-print-service
# [...]