- Based off project by Julio Casal https://dotnetmicroservices.com/
- Docker
- MongoDB
- Postman
-
to create new web api from terminal
dotnet new webapi -n Catalog
-
set up certificates to run on localhost
- This will allow Swagger to display in browser window for the API
dotnet dev-certs https --trust
- This will allow Swagger to display in browser window for the API
-
Install MongoDB Client Driver (NuGet)
dotnet add package MongoDB.Driver
-
Run local Docker Container
docker run -d --rm --name mongo -p 27017:27017 -v mongodbdata:/data/db mongo-d- dont attach to the process, just run it and let it go-rm- destroy the container after you are done, dont keep it running--name- name of the Image / Container you are creating-p- the port-v- the MongoDB volume, so you dont destroy the data when you stop the Docker Containermongodbdata:/data/db mongo- store your DB data at this file path in Mongo to persist the data after the Container has closed
-
View running Docker processes
docker ps
-
Stop running Docker process
docker stop {name}
-
View Docker Volumes
docker volume ls
-
Remove Docker Volume
docker volume rm {volume name}
-
Run local Docker Container with environment variables (DB username, password, etc.)
docker run -d --rm --name mongo -p 27017:27017 -v mongodbdata:/data/db -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=mongoadmin -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=password1 mongo-d- dont attach to the process, just run it and let it go-rm- destroy the container after you are done, dont keep it running--name- name of the Image / Container you are creating-p- the port-v- the MongoDB volume, so you dont destroy the data when you stop the Docker Containermongodbdata:/data/db mongo- store your DB data at this file path in Mongo to persist the data after the Container has closed- So at this point, our DB knows about requiring user authentication we have set, but our Services do not know about it
- Set these in
appsettings.jsonand the.NET Secret Manager
- Set these in
- So at this point, our DB knows about requiring user authentication we have set, but our Services do not know about it
-
dotnet user-secrets initSet UserSecretsId to '7ee7c261-9b12-4f9e-9fc0-de16f4fd7384' for MSBuild project '/Users/j/Desktop/Catalog/Catalog.csproj'.
- to add a secret
dotnet user-secrets set MongoDbSettings:Password password1Successfully saved MongoDbSettings:Password = password1 to the secret store.
- Finally
- Set the username and password in the MongoDB Connection string in
settings/mongodbsettings.csreturn $"mongodb://{User}:{Password}@{Host}:{Port}";
- Set the username and password in the MongoDB Connection string in
-
- A health check is an endpoint like
https://localhost:5001/healththat will tell if an API is able to receive requests and able to communicate with the DB or other services it depends on - Install Open Source MongoDB library to check MongoDB connection status as part of Health Check
dotnet add package AspNetCore.HealthChecks.MongoDb
- This can be configured in
startup.csservices.AddHealthChecks().AddMongoDb(mongoDbSettings.ConnectionString, name: "mongodb", timeout: TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3));app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllers(); endpoints.MapHealthChecks("/health"); });
- Testing Health Check can be done by sending a GET request to https://localhost:5001/health
- it should return
200Healthy - Now stop the docker instance of the Mongo container
docker stop mongo - Send another GET request to https://localhost:5001/health
- Verify it returns
503Unhealthy
- it should return
-
dotnet add package Microsoft.Bcl.AsyncInterfaces-
Health Checks can be customized and configured to return more detailed information as a JSON object like this:
{ "status": "Healthy", "checks": [ { "name": "mongodb", "status": "Healthy", "exception": "none", "duration": "00:00:00.0923151" } ] }- More customization options can be seen here https://github.com/Xabaril/AspNetCore.Diagnostics.HealthChecks for all kinds or BackEnd stuff including AWS, Kafka, RabbitMQ, SendGrid, Kubernetes, Azure, etc.
-
-
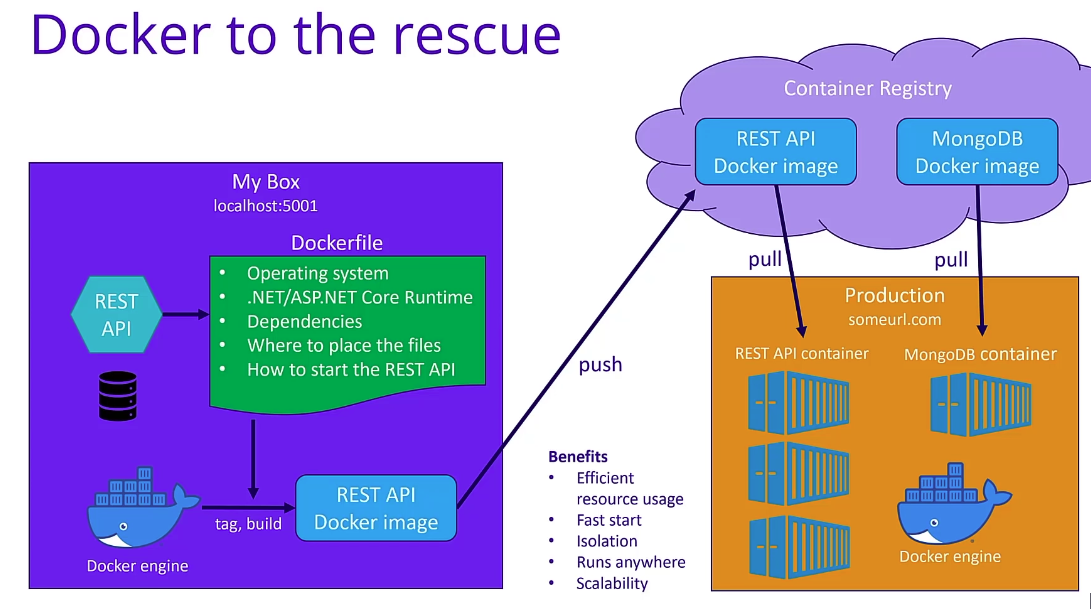
Problems Docker helps solve / simplify
- What kind of machine is my server going to run on?
- Physical machine? Virtual Machine?
- Linux? Windows? Be sure to pick the right OS version for your needs
- Physical machine? Virtual Machine?
- How are we getting files to and from our server?
- What if DB requires different version of OS or dependencies?
- What if we want to move to a new version of .NET?
- How do we quickly start the REST API on the machine?
- What if one instance of the API or service is not enough to handle the load?
- What kind of machine is my server going to run on?
-
- The Dockerfile can set configurations for:
- OS
- .NET / ASP.NET Core Runtime
- Dependencies
- Where to place the files in the file system
- How to star the REST API
- The Dockerfile can set configurations for:
-
-
-
Multi-stage builds
-
https://blog.jetbrains.com/dotnet/2021/03/15/generate-dockerfile-for-net-applications-with-rider/
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:5.0 AS base WORKDIR /app EXPOSE 80 FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk:5.0 AS build WORKDIR /src COPY ["Catalog.csproj", "./"] RUN dotnet restore "Catalog.csproj" COPY . . WORKDIR "/src/." RUN dotnet build "Catalog.csproj" -c Release -o /app/build FROM build AS publish RUN dotnet publish "Catalog.csproj" -c Release -o /app/publish FROM base AS final WORKDIR /app COPY --from=publish /app/publish . ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "Catalog.dll"]
-
-
-
- A health check is an endpoint like
-
- Build a Docker Image
docker build -t catalog:v1 .-t- tag.- current directory
- View summary of image vulnerabilities and recommendations
docker scout quickview- SBOM of image already cached, 190 packages indexed
- Build a Docker Image
Your image catalog:v1 │ 7C 14H 15M 31L Base image debian:10-slim │ 5C 7H 5M 30L Refreshed base image debian:10-slim │ 0C 1H 0M 29L │ -5 -6 -5 -1 Updated base image debian:stable-slim │ 0C 0H 0M 17L │ -5 -7 -5 -13
- Create a Docker Network so our API Container can talk to our MongoDB Container
docker network create net5tutorial
- To view Docker Network
docker network ls
-
- First make sure there are no containers running locally
docker ps- close any that are running -docker stop mongo
- Run the Container you want with the configurations you want
docker run -d --rm --name mongo -p 27017:27017 -v mongodbdata:/data/db -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=mongoadmin -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=password1 --network=net5tutorial mongo-d- dont attach to the process, just run it and let it go-rm- destroy the container after you are done, dont keep it running--name- name of the Image / Container you are creating-p- the port-v- the MongoDB volume, so you dont destroy the data when you stop the Docker Containermongodbdata:/data/db mongo- store your DB data at this file path in Mongo to persist the data after the Container has closed- So at this point, our DB knows about requiring user authentication we have set, but our Services do not know about it
- Set these in
appsettings.jsonand the.NET Secret Manager
- Set these in
- So at this point, our DB knows about requiring user authentication we have set, but our Services do not know about it
--network- the docker network the container should run in
- View Docker Images to verify the image was created
docker images- should see
catalog v1 ...
- should see
- Run the Container in Prod with interactive tag
-itto see the logsdocker run -it --rm -p 8080:80 -e MongoDbSettings:Host=mongo -e MongoDbSettings:Password=password1 --network=net5tutorial catalog:v1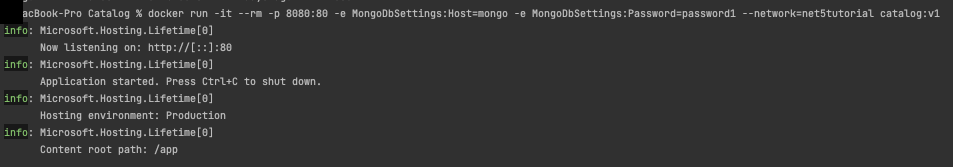
- notice
Hosting environment: Production - to test in production send GET request to http://localhost:8080/items
- verify a
200response, verify in console, no307redirect --> means we're in Prod and not Dev environment
- verify a
- notice
- First make sure there are no containers running locally
- How to share our Docker Image
- We can share our Docker Image publicly on https://hub.docker.com
docker loginin terminal with docker credentials- View images
docker images
- Tag our image
docker tag catalog:v1 {docker-username}/catalog:v1
- Verify new image created
docker images
- Push new image to Docker Hub
docker push {docker-username}/catalog:v1
- To test locally, remove the local images and pull down from Docker Hub
docker imagesdocker rmi {docker-username}/catalog:v1docker rmi catalog:v1- Logout of Docker to verify it is a public image
docker logout
- Verify your public image can be run publicly (not logged into Docker)
- Pull down to local
docker pull {docker-username}/catalog:v1
- Verify
docker images- Should see the pulled down image
- View images