This project aims to show how to build an end to end solution for complaints management, hosted in AWS. It will go through all the key stages of the delivery lifecycle.
Tools & Infrastructure:
Infrastructure Provisioning: Terraform
Orchestration : AWS Step Functions
Modelling: Transformers
Model Management: HuggingFace Hub
Front End: Budibase
TODO List:
- Write Requirements Framework for ML Projects 🚧
- Write Model Training Script ✅
- Make Dataset publicly available through HuggingFace Datasets - PR Open ✅
- Write Terraform based Serverless Model Inference Endpoints ✅
- Use HuggingFace Hub as Model Registry ✅
- Build ML Ops layer for model retraining, champion vs. challenger assessment, stretch-goal: canary deployment 🚧
- Build Step Function Orchestrations 🚧
- Build Model Explainability using Shap 🚧
- Build Complaints Data Store on DynamoDB ✅
- Set-up automated infrastructure updating - CI/CD build with github actions 🚧
- Set-up Pytest, code coverage, infrastructure test suite 🚧
- Build Front-end on Budibase 🚧
- Write Budibase deployment scripts in Terraform
- Write Blog posts for End to End 🚧
The complaints department in the fictional MegaBank recieves customer complaints and enquiries which need to be triaged to the right teams. In order to do this there is a triage team which screens the incoming complaints and routes them to the right product team. Each product team has it's own recurring issues it is aware of and has policies and procedures to resolve them in a systematic way, in addition to those, new issues may arise where a complaints analyst will need to use their best judgement to address the complaint. MegaBank also has a commitment to the regulator to ensure vulnerable customers (the elderly / ex-service people) follow a different customer journey to ensure they are seen to by qualified analysts.
The complaints department has collected a large amount of complaints which have labels to help route them appropriately to the right product team, highlighting the most probable issue and with corresponding labels for vulnerable customers where applicable.
The Business would like to explore re-deploying the triage team to the product teams and to use an ML Based Triage system in it's place.
By analysing the re-allocation rate from one product team to another, it has been inferred that the accuracy rate of the triage team when sending complaints to the product team is 80%. Similarly, when comparing the initial issue to the final issue stated on file, a accuracy rate of 71% has been recorded. Finally, the team is able to identify vulnerable customers with a 60% recall based on the first interaction.
Meeting the team's existing performance with a confidence interval ± 3% has been agreed with the business as model which meets the success criteria, which can be deployed to production.
- The implementation must not change the current ways of working of the operations team
- The implementation must be designed with a feedback loop in place so it can adapt to new issues
- All outputs should be aligned to a specific model version to ensure all outcomes are traceable
- Decision explainability is not required at the time of allocation but should be available if requested by the regulator
- The system should be able to extend if required, e.g. including an additional model 'task' in the pipeline
- The system should be able to handle different model deployment strategies when a new model becomes available
- System should be able to scale between 3k and 15k complaints to be processed per day
- System should cut the time of allocation by at least 50% - it currently takes the triage team 1-3 minutes to triage an incoming complaint
- A cost saving of at least 50% is expected on the price of the existing BAU team, even though they are being redeployed. This should include the cost the infrastructure, services, database usage etc.
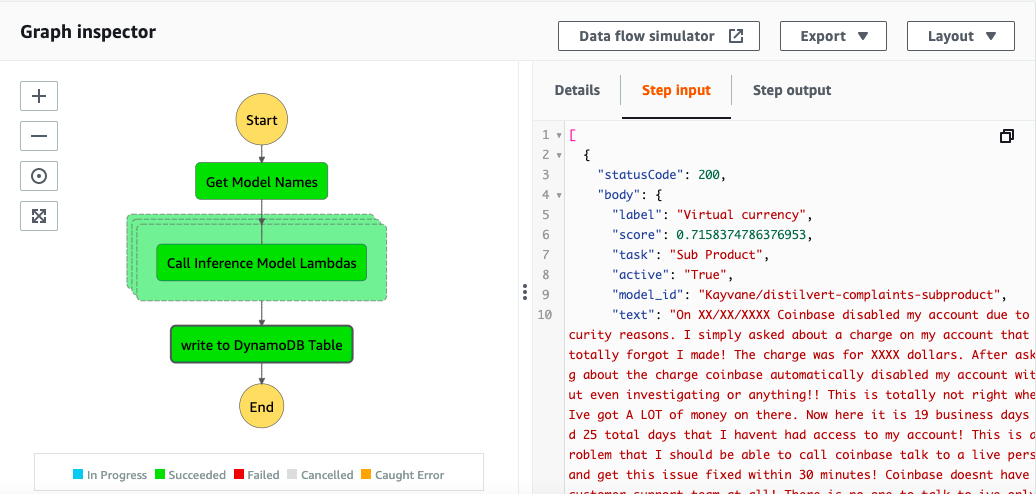
The system can handle new models being added to the model_info table and dynamically include them in the inference step as long as the model asset is hosted on HuggingFace Model Hub. The model is fetched from Model Hub if it has not yet been cached and is used as part of the inference step.
The step function generates one model_inference lambda per input model name.
This allows our system to scale efficiently without any additional intervention after adding our model to the model registry table and setting it to active.