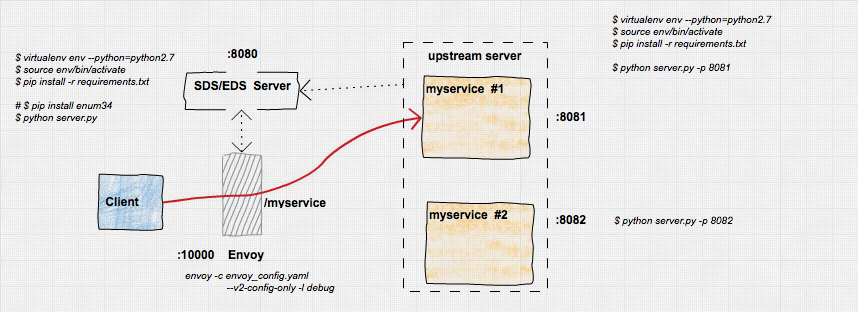
A simple app demonstrating a small part of Envoy's Endpoint Discovery Service. THis is a sample walkthough of a trivial envoy config that sets up:
- Envoy with SDS bootstrap (both envoy
v1andv2APIs) - SDS Server to provide service discovery info for upstream back to Envoy
- N upstream instances envoy will proxy back.
Some of the configurations are hardcoded in the envoy_config.yaml file just as a demonstration. Specifically, the service, cluster and bootstrap endpoint
to get discovery information.
- Endpoint Discovery Service
- Endpoing Overview
- SDS at Lyft
- Envoy Dynamic Configuration
- Envoy v2 API
- EDS v2 API Reference_
- Envoy API for developers
- envoy binary
- python (and virtualenv)
Bootstraping SDS within Envoy is relatively simple:
- name: listener_0
address:
socket_address: { address: 0.0.0.0, port_value: 10000 }
filter_chains:
- filters:
- name: envoy.http_connection_manager
config:
stat_prefix: ingress_http
...
...
- match: { prefix: "/" }
route: { cluster: service_backend }
http_filters:
- name: envoy.router
clusters:
- name: service_backend
type: EDS
connect_timeout: 0.25s
eds_cluster_config:
service_name: myservice
eds_config:
api_config_source:
#api_type: REST_LEGACY # GET /v1/registration/myservice
#api_type: REST # POST /v2/discovery:endpoints
api_type: REST
cluster_names: [eds_cluster]
refresh_delay: 5s
- name: eds_cluster
type: STATIC
connect_timeout: 0.25s
hosts: [{ socket_address: { address: 127.0.0.1, port_value: 8080 }}]Note the api_type: is set to v2 REST endpoint. If you want to swtich to v1 simply use api_type: REST_LEGACY
You can basically 'copy out an envoy binary from docker if you're using a linux flavor
$ mkdir /tmp/envoybin
$ docker run -v /tmp/envoybin/:/tmp/envoybin -ti envoyproxy/envoy /bin/bash
copy the envoy binary out and exit container
root@45e96404eb8a:/# cp /usr/local/bin/envoy /tmp/envoybin/
root@45e96404eb8a:/# exit
exit
find envoy outside now
$ ls /tmp/envoybin/envoy
/tmp/envoybin/envoy
So start envoy with debug enabled:
envoy -c envoy_config.yaml -l debugAt this point, envoy attempts to connect to the upstream EDS cluster at 127.0.0.1:8080 but since your SDS isn't running yet, nothing additional config takes place.
Now in a new window, start the upstream service on a given the default port for the script (:8081)
cd upstream/
virtualenv env --python=python2.7
source env/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
$ python server.py -p 8081Right now envoy doens't know aboutt his endpoint:
Now start SDS without any bootstrapped config:
cd eds_server/
virtualenv env --python=python2.7
source env/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
# ImportError: No module named enum
# pip install enum34
python main.pyYou should see the following output on SDS stdout indicating an inbound Envoy discovery request:
Inbound v2 request for discovery. POST payload: {u'node': {u'build_version': u'fd44fd6051f5d1de3b020d0e03685c24075ba388/1.6.0-dev/Clean/RELEASE', u'cluster': u'mycluster', u'id': u'test-id'}, u'resource_names': [u'myservice']}
127.0.0.1 - - [29/Apr/2018 22:59:04] "POST /v2/discovery:endpoints HTTP/1.1" 200 -
then on the envoy proxy stdout, something like:
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.323][157796][debug][config] bazel-out/k8-opt/bin/source/common/config/_virtual_includes/http_subscription_lib/common/config/http_subscription_impl.h:67] Sending REST request for /v2/discovery:endpoints
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.323][157796][debug][router] source/common/router/router.cc:250] [C0][S636378528925215024] cluster 'eds_cluster' match for URL '/v2/discovery:endpoints'
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.323][157796][debug][router] source/common/router/router.cc:298] [C0][S636378528925215024] ':method':'POST'
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.323][157796][debug][router] source/common/router/router.cc:298] [C0][S636378528925215024] ':path':'/v2/discovery:endpoints'
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.323][157796][debug][router] source/common/router/router.cc:298] [C0][S636378528925215024] ':authority':'eds_cluster'
...
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.324][157796][debug][client] source/common/http/codec_client.cc:52] [C2] connected
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.324][157796][debug][pool] source/common/http/http1/conn_pool.cc:225] [C2] attaching to next request
...
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.330][157796][debug][client] source/common/http/codec_client.cc:81] [C2] response complete
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.330][157796][debug][pool] source/common/http/http1/conn_pool.cc:200] [C2] response complete
...
[2018-04-29 22:59:10.331][157796][debug][pool] source/common/http/http1/conn_pool.cc:115] [C2] client disconnectedBasically, this shows no updates were recieved from the endpoint
You can verify that envoy doesn't know anything about this endpoint by attempting to connect through to it:
curl -v http://localhost:10000/
$ curl -v http://localhost:10000/
...
< HTTP/1.1 503 Service Unavailable
< content-length: 19
< content-type: text/plain
< date: Mon, 30 Apr 2018 06:06:20 GMT
< server: envoy
<
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
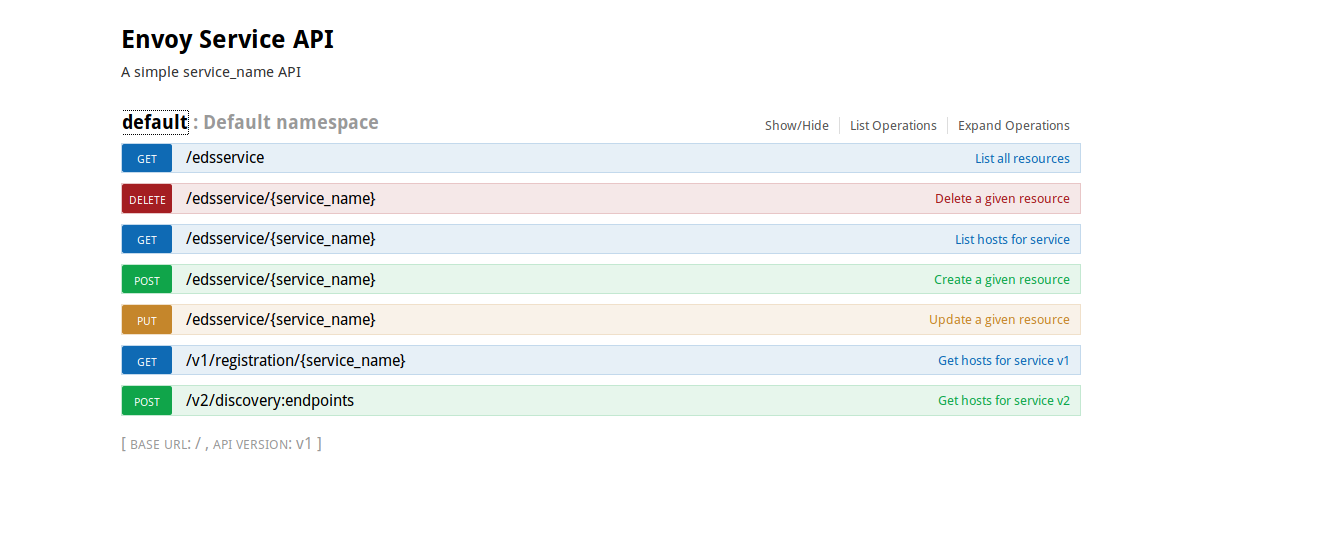
no healthy upstreamsNow we're ready to add an upstream service configuration to the SDS server. This sample uses Flask-RESTplus framework
which delivers a convenient API console (you can, ofcourse, use curl)
connect to SDS servers UI console at:
http://localhost:8080/
curl -X GET "http://localhost:8080/edsservice/myservice" -H "accept: application/json"
{
"hosts": [
{
"ip_address": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 8081,
"tags": {
"az": "us-central1-a",
"canary": false,
"load_balancing_weight": 50
}
}
]
}From there, you can register a service endpoint by selecting POST and the default payload.
Since we defined the service as myservice in the envoy_config.yaml, we can
need to register an endpoint against it:
curl -X POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --header 'Accept: application/json' -d '{
"hosts": [
{
"ip_address": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 8081,
"tags": {
"az": "us-central1-a",
"canary": false,
"load_balancing_weight": 50
}
}
]
}' http://localhost:8080/edsservice/myserviceWhat this will do is set some endpoints for myservice. Now, envoy will query SDS for membership so on the next poll, you'll see some lines like:
[2018-04-29 23:18:02.360][159226][debug][upstream] source/common/upstream/eds.cc:105] EDS hosts changed for cluster: service_backend (0) priority 0
[2018-04-29 23:18:02.360][159231][debug][upstream] source/common/upstream/cluster_manager_impl.cc:642] membership update for TLS cluster service_backend
[2018-04-29 23:18:02.360][159226][debug][upstream] source/common/upstream/cluster_manager_impl.cc:642] membership update for TLS cluster service_backend
[2018-04-29 23:18:02.360][159233][debug][upstream] source/common/upstream/cluster_manager_impl.cc:642] membership update for TLS cluster service_backend
[2018-04-29 23:18:02.360][159234][debug][upstream] source/common/upstream/cluster_manager_impl.cc:642] membership update for TLS cluster service_backend
[2018-04-29 23:18:02.360][159232][debug][upstream] source/common/upstream/cluster_manager_impl.cc:642] membership update for TLS cluster service_backend
[2018-04-29 23:18:02.360][159226][debug][pool] source/common/http/http1/conn_pool.cc:200] [C7] response complete
[2018-04-29 23:18:02.360][159226][debug][pool] source/common/http/http1/conn_pool.cc:220] [C7] moving to ready
Since we already started the upstream service above, you can connect to it via envoy:
$ curl -v http://localhost:10000/
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< content-type: text/html; charset=utf-8
< content-length: 36
< server: envoy
< date: Mon, 30 Apr 2018 06:21:43 GMT
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 3
<
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
40b9bc6f-77b8-49b7-b939-1871507b0fcc(note the server: envoy part in the header)
Ok, so now we've dynamically added in an endpoint...lets remove it by the SDS server's custom API and emptying out its hosts: []
curl -X PUT --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --header 'Accept: application/json' -d '{
"hosts": [ ]
}' http://localhost:8080/edsservice/myserviceNow try the endpoint, you should see no healthy upstream message from envoy
$ curl -v http://localhost:10000/
< HTTP/1.1 503 Service Unavailable
< content-length: 19
< content-type: text/plain
< date: Mon, 30 Apr 2018 06:23:40 GMT
< server: envoy
<
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
no healthy upstreamOk, you can continue to play with the endpoints by adding and removing new upstream services on differnet ports:
eg:
$ python server.py -p 8082
$ python server.py -p 8083
and then using the API to add hosts to the SDS server (use the PUT endpoint to do that)
curl -X PUT "http://localhost:8080/edsservice/myservice" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"hosts\": [ { \"ip_address\": \"127.0.0.1\", \"port\": 8081, \"tags\": { \"az\": \"us-central1-a\", \"canary\": false, \"load_balancing_weight\": 50 } }, { \"ip_address\": \"127.0.0.1\", \"port\": 8082, \"tags\": { \"az\": \"us-central1-a\", \"canary\": false, \"load_balancing_weight\": 50 } } ]}"I wrote this up just in an effort to play around with envoy i'm pretty much new to this so i likely have numerous
misunderstanding on what i just did here...if you see something amiss, please do let me know.