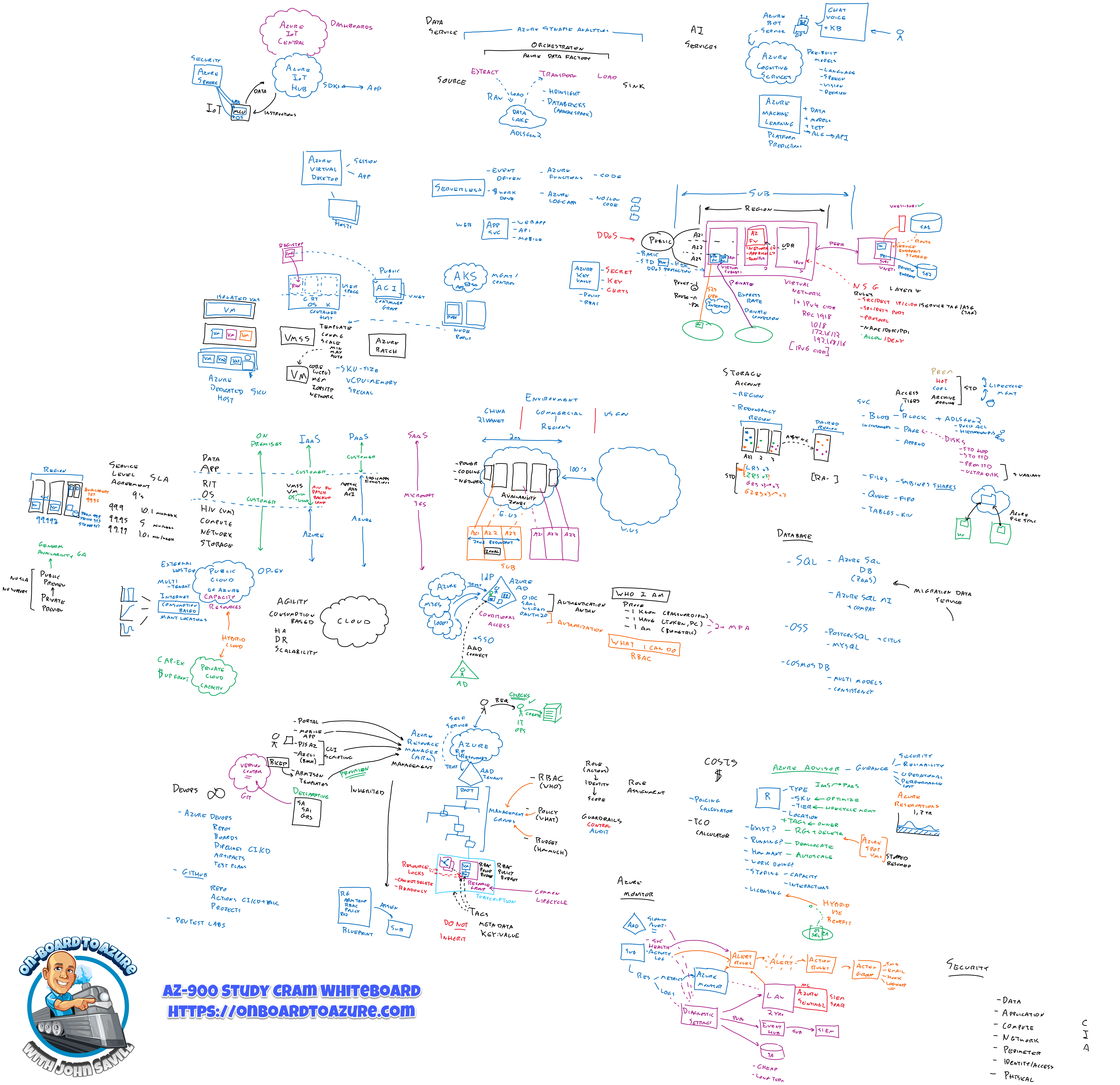
- AZ-900 Azure Fundamentals Certification Course (youtube playlist, 8.5 hours)
- AZ-900 Azure Fundamentals Study Cram (youtube, 3.5 hours)
- Microsoft Azure Master Class (youtube, 20 hours)
- Identify the Benefits of Cloud Computing: agility, high availability, disaster recovery, scalability, agility, consumption based
- High availability: Depending on the service-level agreement (SLA) that you choose, your cloud-based apps can provide a continuous user experience with no apparent downtime, even when things go wrong.
- Scalability: Apps in the cloud can scale vertically and horizontally:
- Scale vertically to increase compute capacity by adding RAM or CPUs to a virtual machine.
- Scaling horizontally increases compute capacity by adding instances of resources, such as adding VMs to the configuration.
- Elasticity: You can configure cloud-based apps to take advantage of autoscaling, so your apps always have the resources they need.
- Agility: Deploy and configure cloud-based resources quickly as your app requirements change.
- Geo-distribution: You can deploy apps and data to regional datacenters around the globe, thereby ensuring that your customers always have the best performance in their region.
- Disaster recovery: By taking advantage of cloud-based backup services, data replication, and geo-distribution, you can deploy your apps with the confidence that comes from knowing that your data is safe in the event of disaster.
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx) is the up-front spending of money on physical infrastructure, and then deducting that up-front expense over time. The up-front cost from CapEx has a value that reduces over time.
- Operational Expenditure (OpEx) is spending money on services or products now, and being billed for them now. You can deduct this expense in the same year you spend it. There is no up-front cost, as you pay for a service or product as you use it.
- Azure Regions
- abonnements, groupes d’administration et ressources Azure
- azure virtual machines
- Azure Dedicated Host
- Managed Disks
- Sample ARM template
- Defense in depth
- The physical security layer is the first line of defense to protect computing hardware in the datacenter.
- The identity and access layer controls access to infrastructure and change control.
- The perimeter layer uses distributed denial of service (DDoS) protection to filter large-scale attacks before they can cause a denial of service for users.
- The network layer limits communication between resources through segmentation and access controls.
- The compute layer secures access to virtual machines.
- The application layer helps ensure that applications are secure and free of security vulnerabilities.
- The data layer controls access to business and customer data that you need to protect.
- DDoS Overview
- express route fundamentals
- CloudExchange colocation
- Point-to-point Ethernet connection
- Any-to-any connection
- Directly from ExpressRoute sites
- Cloud Adoption Framework
- Describe Microsoft Privacy Statement, Online Services Terms (OST) and Data Protection
- Factors to Reduce Cost
- Functionality and Usage of Pricing and TCO Calculators
- Purpose of Service Level Agreements
- Azure Advisor, Monitor, Service Health