Advanced Lane Finding Project
Note: this is Udacity Nano Degree project, please refer to Udacity Repository for the project information and requirements.
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Compute the camera calibration matrix and distortion coefficients given a set of chessboard images.
- Apply a distortion correction to raw images.
- Use color transforms, gradients, etc., to create a thresholded binary image.
- Apply a perspective transform to rectify binary image ("birds-eye view").
- Detect lane pixels and fit to find the lane boundary.
- Determine the curvature of the lane and vehicle position with respect to center.
- Warp the detected lane boundaries back onto the original image.
- Output visual display of the lane boundaries and numerical estimation of lane curvature and vehicle position.
1. use the opencv findChessboardCorners() and calibrateCamera() funtion to implement the camera calibration.
The code for this step in the camera_calibration.py which located in camera_cal folder.
run the camera_calibration.py to process the calibration.
In the function calibriate(), the process as below:
- prepare the
objp[], which is same matrix as chessboard X6 - create list
objepiont[]andimgpionts[]to hold the 3D and 2D pioints. - go through all the calibration image to search for conerner. use opencv
findChessboardCornersfunction. - use opencv
calibratteCamera()to getmtxanddist - write the calibration paramter to a pickle file camera_cal.p
To test if the pickle file which contain the 'mtx' and 'dist' work. use the test() function to test and visualize the result.
- read the pickle and load the
mtxanddist - read test image
- use
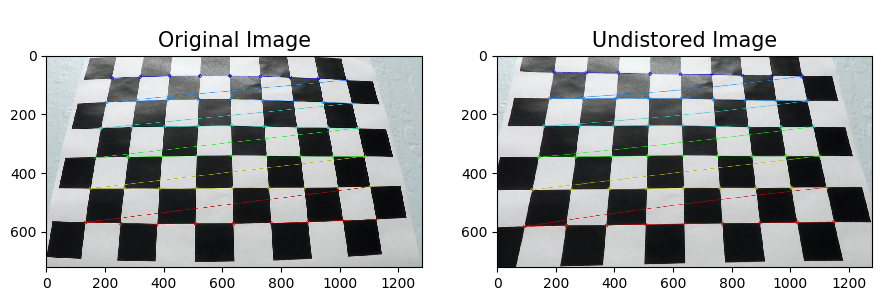
cv2.undistort()to undistort the test image. the result as below
pipeline.py include the class Pipeline, the function pipeline() which used to handle the image. You could run "pipeline.py" to see the pipeline effect.
The process described below:
use the paremeter from pickle file camera_cal.p (this is done by the function: get_camera_cal()) use the cv2.undistort to get the undistort image,the image showed below(resized to 640X360 to fit the file.):

All the image process code is in the image_process.py
in the pipeline it use the funtion import from image_process.py
s_thresh=(170,255)
sx_thresh=(20, 100)
image_threshed = color_grid_thresh(image_undist, s_thresh=s_thresh, sx_thresh=sx_thresh)
This is a combination of color and gradient thresholds to generate a binary image.
in color: it use a HLS's s channel, for gradient, use x direction gradient.
the detialed code is in the image_process.py, function color_grid_thresh, after apply the threshold, the image as below.
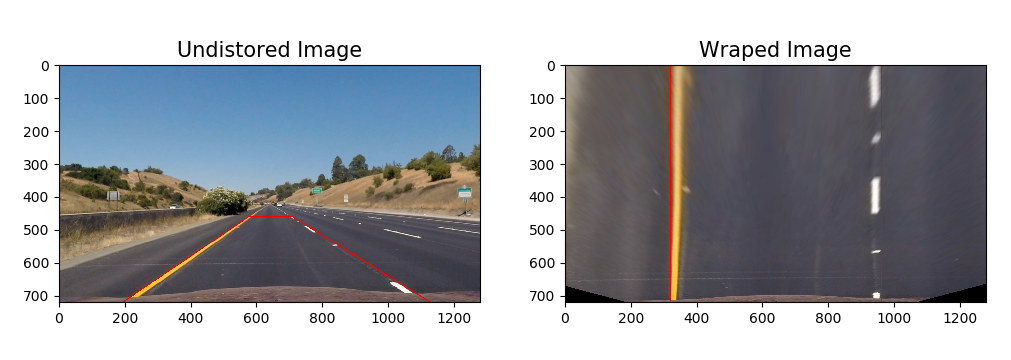
To implement perspective tranform, first need get the tranform parameter M and Minv.
This is done by the view_perspective.py, just like camera_cal, get the parameter then write into a pickle file for further use.
You could run "view_perspective.py" to see the transform.
The view transform use manully adjust the 4 source piont. after serveral times adjust, the 4 poinst as below.
src = np.float32(
[[(img_size[0] / 2) - 63, img_size[1] / 2 + 100],
[((img_size[0] / 6) - 20), img_size[1]],
[(img_size[0] * 5 / 6) + 60, img_size[1]],
[(img_size[0] / 2 + 65), img_size[1] / 2 + 100]])
dst = np.float32(
[[(img_size[0] / 4), 0],
[(img_size[0] / 4), img_size[1]],
[(img_size[0] * 3 / 4), img_size[1]],
[(img_size[0] * 3 / 4), 0]]) The wraped binary image as below
the lane_detection.py implement the lane-line pixels detection.
the function find_lane_pixels() use a slide window to find the lane-line pixels.
after get the lane_pixels, use np.polyfit() to get polynomial paratmeters, this is done in get_polynomial in the example, it like below. [A B C]
[ 1.42425935e-04 -3.09709625e-01 5.13026355e+02]
[ 1.96100345e-04 -2.96906479e-01 1.12235500e+03]To visualize the search result and fit polynomial, use fit_polynomial() function. the visualized result as below. show the search window/lane pixels/fit polynimial.
5. Calculate the radius of curvature of the lane and the position of the vehicle with respect to center.
The cacualtion is done in the cal_curv.py, the function measure_curv() used to calculate radius.
Firstly, transform the lane piont from pixels to meters,
# Transform pixel to meters
leftx = leftx * xm_per_pix
lefty = lefty * ym_per_pix
rightx = rightx * xm_per_pix
righty = righty * ym_per_pixthen fit these data use np.polyfit()
After get the polynomial parameter, use the function R = (1+(2Ay+B)^2)^3/2 / (|2A|)
For the offset, it is similar, tranfer pixel to meter, compare the lane center with picture center to get offse. these are in the function measure_offset()
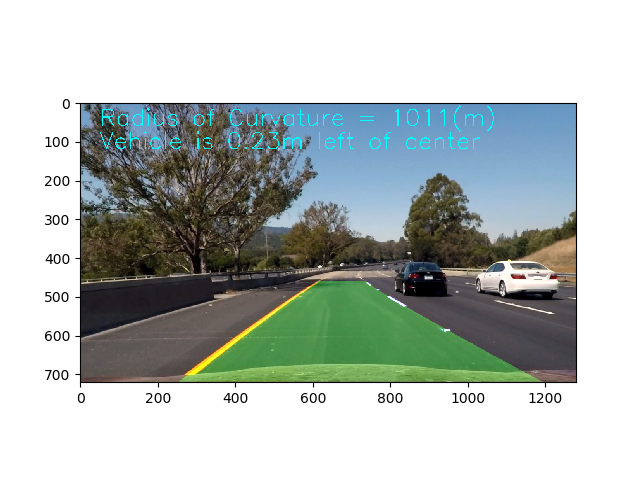
In the Pipeline class, use below code to visualzie the lane and caculation. to avoid number quick jump in the screen, display the 15 frames average.
def project_fit_lane_info(self, image, color=(0,255,255)):
"""
project the fited lane information to the image
use last 15 frame average data to avoid the number quick jump on screen.
"""
offset = np.mean(self.offset[-15:-1]) if len(self.offset) > self.smooth_number else np.mean(self.offset)
curverad = np.mean(self.radius[-15:-1]) if len(self.radius) > self.smooth_number else np.mean(self.radius)
direction = "right" if offset < 0 else "left"
str_cur = "Radius of Curvature = {}(m)".format(int(curverad))
str_offset = "Vehicle is {0:.2f}m ".format(abs(offset)) + "{} of center".format(direction)
cv2.putText(image, str_cur, (50,60), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,2,color,2)
cv2.putText(image, str_offset, (50,120), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,2,color,2)The result as below picture.
In the pipeline.py, you could go to line 487 to 498, choice test on one image or a batch of image to see how the pipeline work.
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""
image_test_tracker(), test pipeline on one image and show the image on screen
images_test_tracker(), test pipeline on images and write the result to related folder
"""
image_test_tracker("./test_images/test6.jpg", "project", debug_window=False)
# image_test_tracker("test_images/challenge/1.jpg", "challenge", debug_window=True)
# image_test_tracker("test_images/harder/1.jpg", "harder", debug_window=True)
# images_test_tracker("test_images/", "output_images/", "project", debug_window=True)
# images_test_tracker("test_images/challenge/", "output_images/challenge/", "challenge", debug_window=True)
# images_test_tracker("test_images/harder/", "output_images/harder/", "harder", debug_window=True)To apply the pipeline on the video, you could run the gen_video.py. to generate video. the option is explained in the document description. the code is in line 66-84
if __name__ == "__main__":
"""
choise one line to uncoment and run the file, gen the video.
the video will be output to ./outpu_videos/temp/
option: subclip = True, just use (0-5) second video, False, use total long video.
option: debug_window = True, project the debug window on the up-right corner of the screen to visualize the image handle process
and write the fit lane failure/search lane failure image to ./output_videos/temp/images
"""
# get_image("./test_video/challenge_video.mp4", "./test_images/challenge/", [i for i in range(1,16)])
# get_image("./test_video/harder_challenge_video.mp4", "./test_images/harder/", [i for i in range(1,47)])
gen_video_tracker("project_video.mp4", subclip=True, debug_window=True)
# gen_video_tracker("project_video.mp4", subclip=False, debug_window=False)
# gen_video_tracker("challenge_video.mp4", subclip=True, debug_window=True)
# gen_video_tracker("challenge_video.mp4", subclip=False, debug_window=True)
# gen_video_tracker("harder_challenge_video.mp4", subclip=True, debug_window=True)
# gen_video_tracker("harder_challenge_video.mp4", subclip=False, debug_window=False)With the image process established on single image. We couldn't get the left/right lane correctly in whole video. there is always noise which will affect the lane detection.
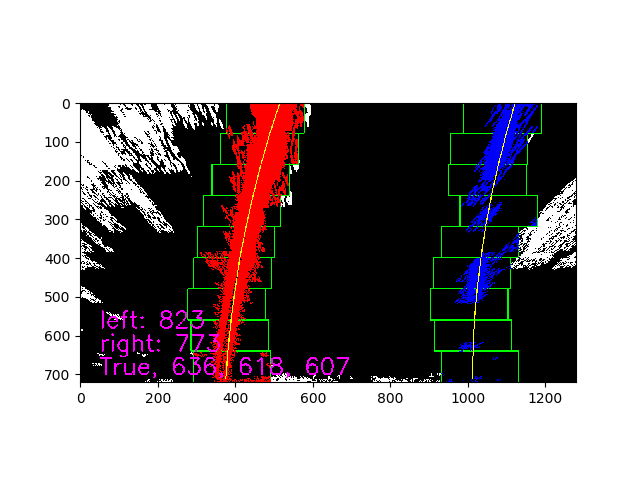
For example, in some frame, the lan detection failed, as below picuture shows

The full size picture is link to full size picture
To solve this problem, we need to know what happed when the process not work.
so I add a function project_debug_window() in the class, and we also need to check the fit lane(fitted polynomial) is OK or not.
To check the lane at y postion 720/bot, 360/mid, 0/top the lane pixel distence and project to the final result picture for debug.
build the function lane_sanity_check() in lane_detection.py
lane_distance_bot = right_fitx[720] - left_fitx[720]
lane_distance_mid = right_fitx[320] - left_fitx[320]
lane_distance_top = right_fitx[0] - left_fitx[0]The debug picture as below, the full size could find [here]
This is done by the class "Pipeline"'s function project_debug_window()
(./examples/project_detect_fail_with_debug.png)

When lane detect is False. use the recent data to project the lane area and culcualte the lane radius and car offset.
one detect failure and use recent data. As below picture show

Use the Pipeline.pipeline(), skip the noise frame, the pipeline work well on the project_video.mp4 well.
The project video is here project_video.mp4. The videos with debug window could find here project_video_with_debug_window.mp4.
To solve the challenge video problem. Improve the pipeline with image process.
The challenge vidoe could be find here challenge_video.mp4.
The challenge video with debug window could be found here challenge_video_with_debug_window.
The main change of pipeline for harder_challenge compare with challenge is the image process, the search method is also changed.
The harder challenge vidoe could be find here harder_challenge_video.mp4.
The harder challenge video with debug window could be found here harder_challenge_video_with_debug_window.mp4.
find_lane_pixels() (helpers/lane_detection.py) is used to search the whole warped image to find the lane pionts.
The pipeline handle the image off-line, so not consider the efficiency issue. In real application, the pipeline must hanle the image before the next image arrive. a quick search method should be applied.
The lane_sanity_check() (helpers/lane_detection.py) function is very simple. To check if the fitted polynomial lines, just compare the fitted lines three y postions x distence to check if the fitted lines is OK. this is not work very well when the lane curve change dramticlly just like the in the harder_challenge video.
-
camera_cal the code which calibration the camera
-
examples some example pictures
-
helper all the functions which used in pipeline.py and video.py
-
output_images the images which processed by diff function.
-
output_video the video has finished
-
test_images the images used to test the pipeline
-
test_video three video for testing the lane detection
-
pipeline.py the code which use to hande the images. the actual lane dection happend.
-
requirements.txt the python package list in local machine
-
gen_video.py the code with use "pipeline" to handle the vidoe and generate the output video.