This is the repository for NeuralProphet project for Theoretical Foundations of DataScience course. Contributors are Alexey Voskoboinikov and Polina Pilyugina. The main aim of this project is to improve NeuralProphet Library.
Second status report is contained in the repository.
- Refactor the code with PyTorch Lightning in accordance with existing API
- Adapt and include existing implementations of SOTA models for time series forecasting under the NeuralProphet API
- Add hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune as additional module
- Recreate LIBRA framework for benchmarking in Python and run it on NeuralProphet and our additionally included models
- Add neccessary tests and documentation for introduced functional
The main source of the code of this work is original NeuralProphet library. Firstly, we will refactor the code to support PyTorch Lightning. This includes refactoring the model itself and all additional parts. The main goal of refactoring is to structure the code in a reusable way and separate research modules from engineering parts. Additionally, we seek to introduce functional for distributed training from PyTorch Lightning.
For model implementations we will use modules from PyTorch Forecasting. They are already built in PyTorch Lightning. We will add data preprocessing steps for these models. Additionally, we will add wrappers so that these models will rely on the same API and produce results in the same format as NeuralProphet.
For hyperparameter tuning we will introduce a new module using Ray Tune functional.
Additionally, we will add LIBRA framework functional for benchmarking. Currently, this framework is available only in R, so we will implement it in python and include in NeuralProphet. This will allow future users to add datasets and compare results.
We refactor existing code of TimeNet and NeuralProphet itself in Pytorch Lightning framework. We preserved the full original structure and functionality. We have added a new parameter to NeuralProphet which is number of GPUs used for train. It is supported by Pytorch Lightning Trainer module by default and allows for distributed training on GPUs, which was not originally possible.
We introduced LSTM model, as a part of additional models modules.
It is based on refactored into Pytorch Lightning LSTM model from pure Pytorch.
For LSTM, the main class has the same functionality as the NeuralProphet and supports all main methods.
An example of LSTM usage can be foung in example_notebooks/LSTM_example.ipynb notebook.
Here is the example of using LSTM module:
m = LSTM(n_lags = 10,
n_forecasts=7,
num_hidden_layers=1,
d_hidden=64,
learning_rate=0.1,
epochs=20)
metrics_df = m.fit(df, freq = '5min')
future = m.make_future_dataframe(df, preiods = 7, n_historic_predictions=True)
forecast = m.predict(future)
We also introduced NBeats model.
It is based on the Pytorch Forecasting model implementation.
We refactored existing model code to support NeuralProphet Metric class.
We also created a new wrapper class, which has the same main modules as NeuralProphet and can be used with the same API.
An example of NBeats usage can be foung in example_notebooks/NBeats_example.ipynb notebook.
Here is the example of using NBeats module:
m = NBeatsNP(
max_encoder_length = 150,
epochs = 100,
num_gpus = 0,
auto_lr_find=True)
m.fit(df, freq = '5min')
future = m.make_future_dataframe(df, preiods = 7, n_historic_predictions=10)
forecast = m.predict(future)
We also introduced DeepAR model in the same way as NBeats, as it also was based on Pytorch Forecasting library.
We also refactored existing model code to support NeuralProphet Metric class, in particular training and validation steps.
An example of DeepAR usage can be foung in example_notebooks/DeepAR_example.ipynb notebook.
Here is the example of using DeepAR module:
deepar = DeepAR(
context_length=60,
prediction_length=20,
epochs = 100,
num_gpus = 0,
patience_early_stopping = 10,
early_stop = True,
auto_lr_find=True)
m.fit(df, freq = '5min')
future = m.make_future_dataframe(df, preiods = 7, n_historic_predictions=10)
forecast = m.predict(future)
We introduced a new module for hyperparameter tuning.
It relies on Ray Tune library, as it has an easy integration with Pytorch Lightning models and allows distributed training.
This module is located in neuralprophet/hyperparameter_tuner.py file.
It has two modes: auto and manual.
The automated mode runs hyperparameter tuning on predefined by us sets of hyperparameters.
It is useful as a first step for new users and fast tuning.
The manual mode allows users to define their own hyperparameter spaces to tune over.
In example_notebooks/hyperparameter_example.ipynb we provide users with a basic example of how to use this module.
Here is an example of hyperparameter optimization usage:
best_params, results_df = tune_hyperparameters('NP', df, freq)
An example output of this function looks as follows:
{'growth': 'off',
'n_changepoints': 100,
'changepoints_range': 0.8,
'trend_reg': 0.0,
'yearly_seasonality': False,
'weekly_seasonality': False,
'daily_seasonality': False,
'seasonality_mode': 'additive',
'seasonality_reg': 0.5,
'n_lags': 100,
'd_hidden': 8,
'num_hidden_layers': 2,
'ar_sparsity': 0.8,
'learning_rate': 0.010444235692186717,
'loss_func': 'Huber',
'normalize': 'minmax'}
It can be used further directly into NeuralProphet configuration initialization.
In this work we follow the original repository structure of NeuralProphet in order to preserve the existing functionality. Here we present the structure of repository and the files which were changed or added in the process of out project.
└── neural_prophet
├── LICENSE
├── MANIFEST.in
├── README.md
├── docs
├── example_data
├── example_notebooks
│ ├── LSTM_example.ipynb
│ ├── NBeats_example.ipynb
│ ├── DeepAR_example.ipynb
│ ├── hyperparameter_example.ipynb
├── mkdocs.yml
├── neuralprophet
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── additional_models.py
│ ├── configure.py
│ ├── forecaster.py
│ ├── forecaster_additional_models.py
│ ├── hyperparameter_tuner.py
│ ├── time_net.py
├── notes
├── peer_reviews
├── pyproject.toml
├── requirements.txt
├── scripts
├── setup.py
└── tests
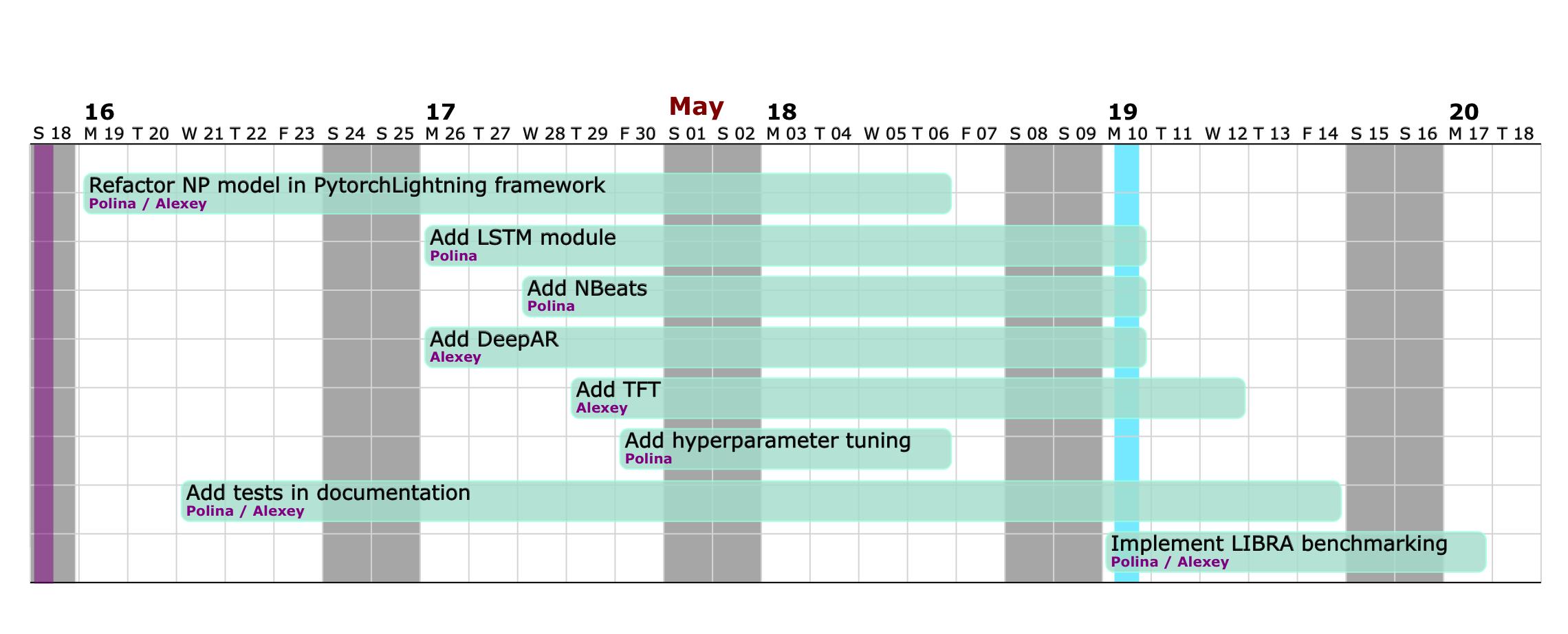
We distributed our main tasks and goals evenly, as described on the roadmap below. Both of us will work on refactoring into PyTorch Lightning. Alexey will focus on the main TimeNet model class, while Polina will work on the forecaster code. We also distributed models we aim to add. Polina will work on N-Beats and LSTM, while Alexey will work on Temporal Fusion Transformers and DeepAR. We will write corresponding tests and documentation of implemented modules. Further, Polina will focus on hyperparameter tuning addition, while Alexey will implement LIBRA framework in python. Afterwards, we will both work on the benchmarking using LIBRA framework and finalization of the project.
At a current stage, we are finished with code refactoring into Pytorch Lightning. We also added three models: LSTM, NBeats and DeepAR, and created a structure for TemporalFusionTransformer, which will be added further. We also implemented hyperparameter optimization module and will further work on adding support for other models. Currently, it supports LSTM and NeuralProphet.