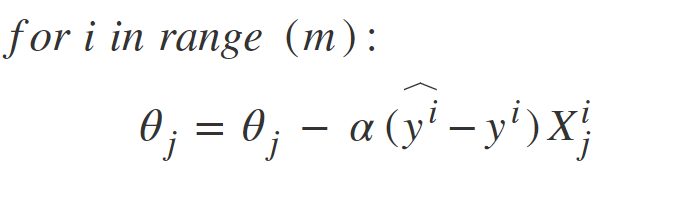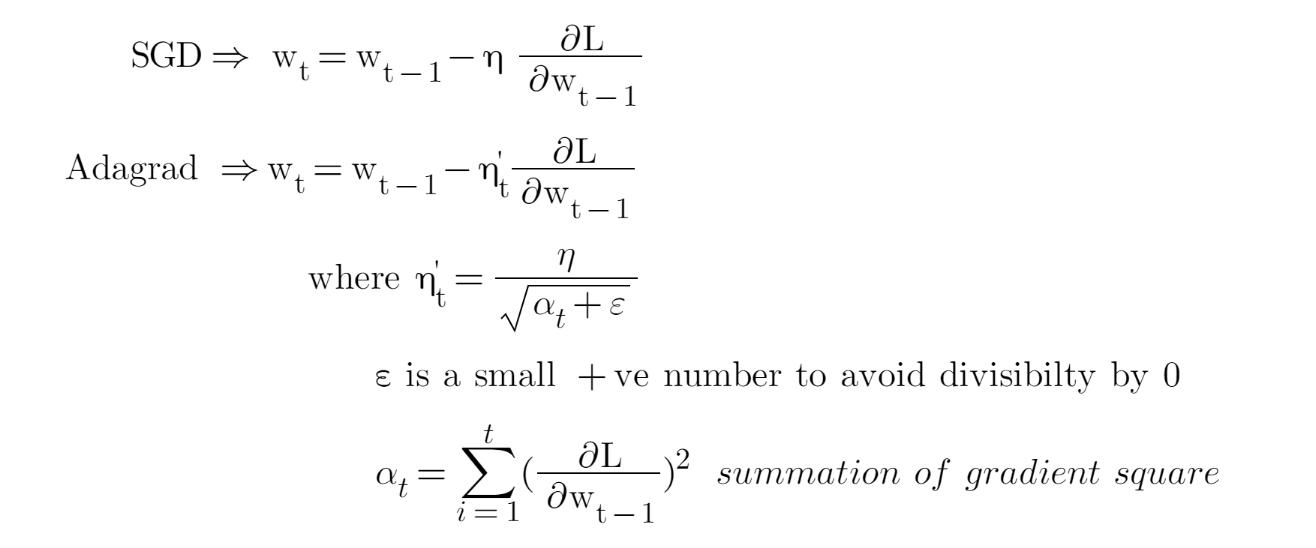Neural network baseline involves all these optimizations which can help to improve the model based on data variety, so understanding these algorithms lead us to get a better perspective of the neural network models and choose the correct one.
The picture below can help to understand expressions of this topic better!All of these algorithms are developed from each other or combined to perform better, covering weaknesses and strengthening powers.
lets see connections :

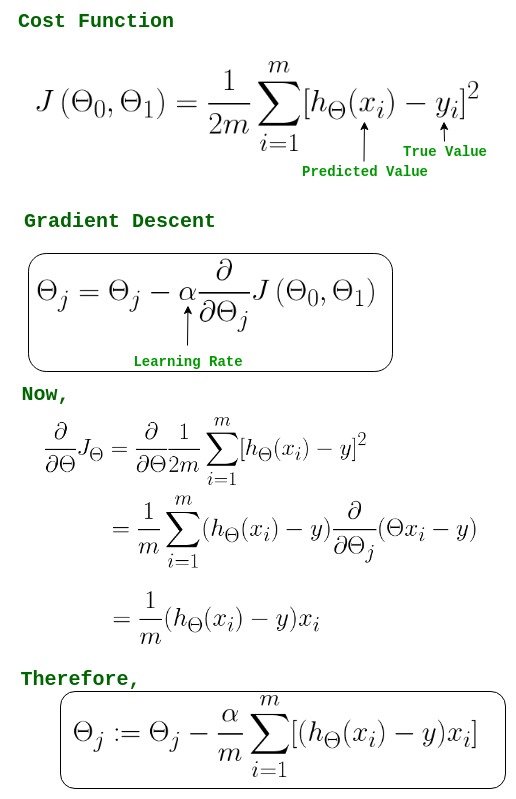
In mathematics gradient descent (also often called steepest descent) is a first-order iterative optimization algorithm for finding a local minimum of a differentiable function. The idea is to take repeated steps in the opposite direction of the gradient (or approximate gradient) of the function at the current point because this is the direction of the steepest descent.
the size of the below arrows depends on the learning rate variable:
Stochastic Gradient Descent, a few samples are selected randomly instead of the whole data set for each iteration.gradient descent compute operations on all dataset. Prblem comes up when data is so big(e.x 200milion data) .This problem is solved by Stochastic Gradient Descent. In SGD, it uses only a single sample, i.e., a batch size of one, to perform each iteration. in SGD, we find out the gradient of the cost function of a single example at each iteration instead of the sum of the gradient of the cost function of all the examples.
SGD is generally noisier than typical Gradient Descent
SGD with Momentum is a stochastic optimization method that adds a momentum term to regular stochastic gradient descent :
A typical value is 0.9. The momentum name comes from an analogy to physics, such as a ball accelerating down a slope. In the case of weight updates, we can think of the weights as a particle traveling through parameter space which incurs acceleration from the gradient of the loss. but why momentum? Actually, SGD with momentum is the method that helps accelerate gradients vectors in the right directions, thus leading to faster converging.
As we discussed, all the above algorithms have a const learning rate but imagine data contains high dimension, in this situation the high-dimensional non-convex nature of neural networks optimization could lead to different sensitivity on each dimension. The learning rate could be too small in some dimensions and could be too large in another dimension. One obvious way to mitigate that problem is to choose different learning rates for each dimension. This algorithm adaptively scaled the learning rate for each dimension.
Adagrad allows us to give more importance to updates in parameters that have associated features that are sparse, or more generally, to give more importance to parameter updates that have experimented with a record of relatively lower gradients.
There is a slight variation of AdaGrad called RMSProp(Root Mean Squared Propagation) that addresses the problem that AdaGrad has. With RMSProp we still keep the running sum of squared gradients but instead of letting that sum grow continuously throughout training, we let that sum decay. Optimization Algorithms in Deep Learning.
The update step in the case of RMSProp looks the same as in AdaGrad where we divide the current gradient by the sum of squared gradients to have this nice property of accelerating the movement along the one dimension and slowing down the movement along the other dimension. RMSprop Learning rate is still manual because the suggested value is not always appropriate for every task.
Adaptive Moment Estimation (Adam) is another method that computes adaptive learning rates for each parameter. In addition to storing an exponentially decaying average of past squared gradients vt like Adadelta and RMSprop, Adam also keeps an exponentially decaying average of past gradients mt, similar to momentum.
Adam is the most common optimizer in deep learning models because :
Adamax is a variant of Adam based on the infinity norm.
The purpose of this project is to learn and understand gradient descent algorithms better. you can run code and choose your algorithm and after execution, you will get a gif that shows how the algorithm converges to the data. (Do not change random seed) you can change parameters watch how parameters can change the process of convergence.
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1743/1/012002/pdf