Note: This is a preliminary version of the Wild-Time benchmark. We are working on code refactoring and will release the final version in October
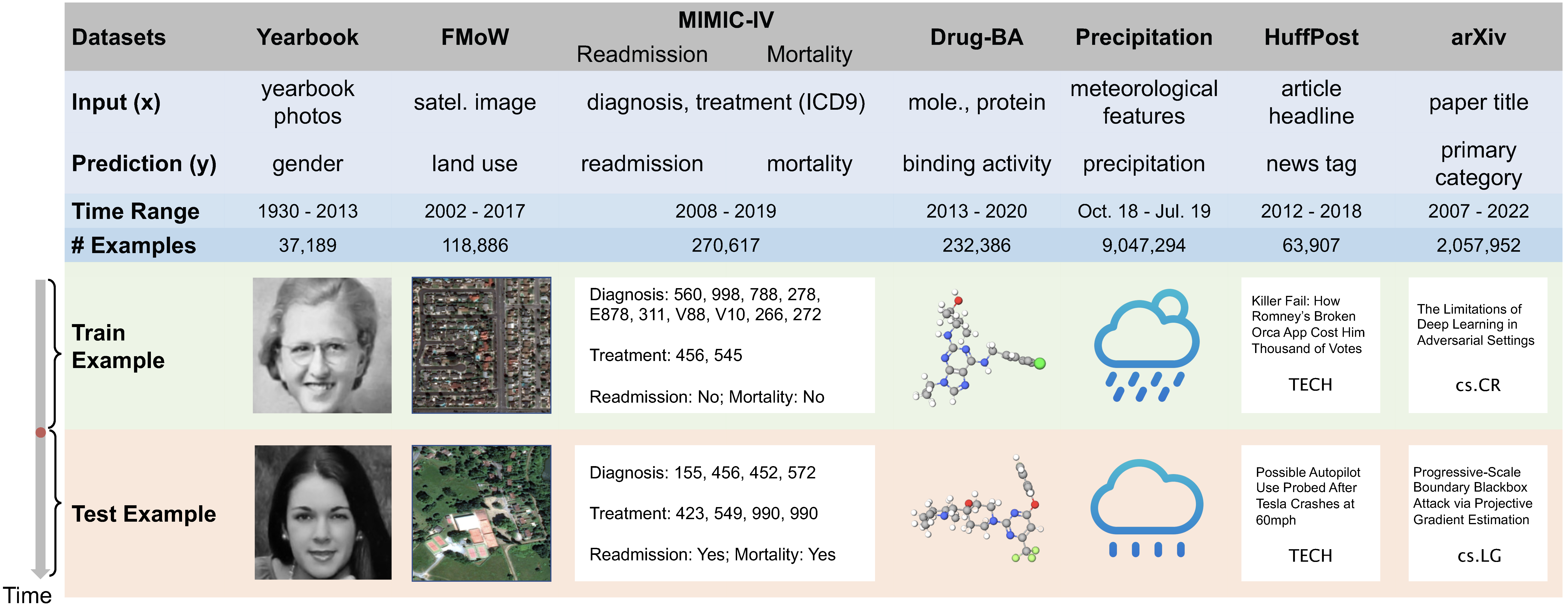
Distribution shifts occur when the test distribution differs from the training distribution, and can considerably degrade performance of machine learning models deployed in the real world. While recent works have studied robustness to distribution shifts, distribution shifts arising from the passage of time have the additional structure of timestamp metadata. Real-world examples of such shifts are underexplored, and it is unclear whether existing models can leverage trends in past distribution shifts to reliably extrapolate into the future. To address this gap, we curate Wild-Time, a benchmark of 7 datasets that reflect temporal distribution shifts arising in a variety of real-world applications, including drug discovery, patient prognosis, and news classification.
This repo includes scripts to download all Wild-Time datasets, code for all baselines, and scripts for training and evaluating these baselines on Wild-Time datasets.
If you find this repository useful in your research, please cite the following paper:
@inproceedings{yao2022wildtime,
title={Wild-Time: A Benchmark of in-the-Wild Distribution Shift over Time},
author={Huaxiu Yao and Caroline Choi and Yoonho Lee and Pang Wei Koh and Chelsea Finn},
booktitle={Proceedings of the Thirty-sixth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Datasets and Benchmarks Track},
year={2022},
}
We will release the arXiv version of our paper, along with the final code repository, in 1-2 months.
To download the Wild-Time datasets and run baselines, clone this repo to your local machine.
git clone git@github.com:huaxiuyao/Wild-Time.git
cd Wild-Time
pip install -r requirements.txt
In the directory Wild-Time, create the folders Data, checkpoints, and results.
- gdown==4.5.1
- lightly==1.2.27
- matplotlib==3.5.0
- numpy==1.19.5
- omegaconf==2.0.6
- pandas==1.1.3
- Pillow==9.2.0
- pytorch_lightning==1.2.7
- pytorch_tabular==0.7.0
- scikit_learn==1.1.2
- tdc==0.1
- torch==1.7.0
- torchcontrib==0.0.2
- torchvision==0.8.1
- transformers==4.21.1
- wilds==2.0.0
Create the folder Wild-Time/Data.
To download the MIMIC-WildT dataset, users must be credentialed on PhysioNet and sign the Data Use Agreement due to data use resstrictions. Please refer to the next section for instructions.
If you do not need to download the MIMIC-WildT dataset, you can skip the next section and simply run the command python download_datasets.py --datasets=arxiv, drug, fmow, huffpost, precipitation, yearbook.
- Become a credentialed user on PhysioNet. This means that you must formally submit your personal details for review, so that PhysioNet can confirm your identity.
- If you do not have a PhysioNet account, register for one here.
- Follow these instructions for credentialing on PhysioNet.
- Complete the "Data or Specimens Only Research" training course.
- Sign the data use agreement.
- Log in to your PhysioNet account.
- Go to the MIMIC-IV dataset project page.
- Locate the "Files" section in the project description.
- Click through, read, and sign the Data Use Agreement (DUA).
- Go to https://physionet.org/content/mimiciv/1.0/ and download the following CSV files from the "core" and "hosp" modules to
./Data:- patients.csv
- admissions.csv
- diagnoses_icd.csv
- procedures_icd.csv
Decompress the files and put them under
./Data.
- Run the command
python download_datasets.py --datasets=arxiv, drug, fmow, huffpost, precipitation, yearbook, mimic.
To train a baseline on a Wild-Time dataset and evaluate under Eval-Fix (default evaluation), use the command
python main.py --dataset=[DATASET] --method=[BASELINE] --lr=[LEARNING RATE] --train_update_iters=[TRAIN ITERS] --num_workers=[WORKERS] --random_seed=[SEED] --offline --split_time=[TIME STEP] [BASELINE-SPECIFIC HYPERPARAMETERS]
- Specify the dataset with
--dataset.- [arxiv, drug, fmow, huffpost, mimic, precipitation, yearbook]
- For MIMIC, specify one of two prediction tasks (mortality and readmission) using
--prediction_type=mortalityor--prediction_type=readmission.
- Specify the baseline with
--method. - To run Eval-Fix, add the flag
--offline.- Specify the ID/OOD split time step with
--split_time.
- Specify the ID/OOD split time step with
- To run Eval-Stream, add the flag
--eval_next_timesteps. - Set the training batch size with
--mini_batch_size. - Set the number of training iterations with
--train_update_iters. - [Optional] If using a data directory or checkpoint directory other than
./Dataand./checkpoints, specify their paths with--data_dirand--log_dir.
- Set the number of groups (e.g., number of time windows) with
--num_groups. - Set the group size (e.g., length of each time window) with
--group_size. - Specify the weight of the CORAL loss with
--coral_lambda(default: 1.0). - Add
--non_overlappingto sample from non-overlapping time windows.
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=arxiv --method=coral --offline --split_time=2016 --coral_lambda=0.9 --num_groups=4 --group_size=4 --mini_batch_size=64 --train_update_iter=6000 --lr=2e-5 --weight_decay=0.01 --num_workers=8 --random_seed=1 --log_dir=./checkpoints
- Set the number of groups (e.g., number of time windows) with
--num_groups. - Set the group size (e.g., length of each time window) with
--group_size. - Add
--non_overlappingto sample from non-overlapping time windows.
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=drug --method=groupdro --offline --split_time=2016 --num_groups=3 --group_size=2 --mini_batch_size=256 --train_update_iter=5000 --lr=2e-5 --random_seed=1 --log_dir=./checkpoints --data_dir=./Data/Drug-BA
- Set the number of groups (e.g., number of time windows) with
--num_groups. - Set the group size (e.g., length of each time window) with
--group_size. - Specify the weight of the IRM penalty loss with
--irm_lambda(default: 1.0) - Specify the number of iterations after which to anneal the IRM penalty loss wtih
--irm_penalty_anneal_iters(default: 0).
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=fmow --method=irm --offline --irm_lambda=1.0 --irm_penalty_anneal_iters=0 --num_groups=3 --group_size=3 --mini_batch_size=64 --train_update_iter=3000 --lr=1e-4 --weight_decay=0.0 --split_time=10 --num_workers=8 --random_seed=1 --log_dir=./checkpoints
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=huffpost --method=erm --offline --mini_batch_size=32 --train_update_iter=6000 --lr=2e-5 --weight_decay=0.01 --split_time=2015 --num_workers=8 --random_seed=1 --log_dir=./checkpoints
- Specify the interpolation ratio
$\lambda \sim Beta(\alpha, \alpha)$ with--mix_alpha(default: 2.0).
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=mimic --method=erm --offline --lisa --mix_alpha=2.0 --prediction_type=mortality --mini_batch_size=128 --train_update_iter=3000 --lr=5e-4 --num_workers=0 --random_seed=1 --split_time=2013 --data_dir=./Data --log_dir=./checkpoints/
- Specify the interpolation ratio
$\lambda \sim Beta(\alpha, \alpha)$ with--mix_alpha(default: 2.0).
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=mimic --method=erm --offline --mixup --mix_alpha=2.0 --prediction_type=readmission --mini_batch_size=128 --train_update_iter=3000 --lr=5e-4 --num_workers=0 --random_seed=1 --split_time=2013 --data_dir=./Data --log_dir=./checkpoints/
- Set the buffer size with
--buffer_size(default: 1000).
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=precipitation --method=agem --buffer_size=1000 --offline --mini_batch_size=128 --train_update_iter=5000 --lr=0.001 --split_time=7 --random_seed=1 --log_dir=./checkpoints
- Set the regularization strength (e.g., weight of the EWC loss) with
ewc_lambda(default: 1.0).
Sample command:
python main.py --dataset=yearbook --method=ewc --ewc_lambda=0.5 --online --mini_batch_size=32 --train_update_iter=3000 --lr=0.001 --offline --split_time=1970 --random_seed=1 --log_dir=./checkpoints
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=arxiv --method=ft --mini_batch_size=64 --train_update_iter=1000 --lr=2e-5 --weight_decay=0.01 --offline --split_time=2016 --num_workers=8 --random_seed=1 --log_dir=./checkpoints
- Set the SI regularization strength with
--si_c(default: 0.1). - Set the dampening parameter with
--epsilon(default: 0.001).
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=drug --method=si --si_c=0.1 --epsilon=0.001 --lr=5e-5 --mini_batch_size=256 --train_update_iter=5000 --split_time=2016 --random_seed=1 --log_dir=./checkpoints --data_dir=./Data/Drug-BA
- Specify the number of iterations for which to learn representations using SimCLR with
--train_update_iter. - Specify the number of iterations to finetune the classifier with
--finetune_iter.
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=fmow --method=simclr --offline --mini_batch_size=64 --train_update_iter=1500 --finetune_iter=1500 --lr=1e-4 --weight_decay=0.0 --split_time=13 --num_workers=8 --random_seed=1
- Specify the number of iterations for which to learn representations using SimCLR with
--train_update_iter. - Specify the number of iterations to finetune the classifier with
--finetune_iter.
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=yearbook --method=swav --mini_batch_size=32 --train_update_iter=2700 --finetune_iter=300 --lr=0.001 --offline --random_seed=1 --split_time=1970
Example command:
python main.py --dataset=huffpost --method=swa --offline --mini_batch_size=32 --train_update_iter=6000 --lr=2e-5 --weight_decay=0.01 --split_time=2015 --num_workers=8 --random_seed=1 --log_dir=./checkpoints
In scripts/, we provide a set of scripts that can be used to train and evaluate models on the Wild-Time datasets. These scripts contain the hyperparameter settings used to benchmark the baselines in our paper.
All Eval-Fix scripts can be found located under scripts/eval-fix. All Eval-Stream scripts are located under under scripts/eval-stream.
For your reference, we provide some checkpoints for baselines used in our paper under the Eval-Fix setting. Please download the checkpoints here and put them under model_checkpoints/.
To use these checkpoints, add the flags --load_model --log_dir=./model_checkpoints to your command.
All code for Wild-Time is available under an open-source MIT license. We list the licenses for each Wild-Time dataset below:
- Yearbook: MIT License
- FMoW: The Functional Map of the World Challenge Public License
- MIMIC-IV (Readmission and Mortality): PhysioNet Credentialed Health Data License 1.5.0
- Drug-BA: MIT License
- Precipitation: CC BY-NC 4.0
- Huffpost: CC0: Public Domain
- arXiv: CC0: Public Domain
We thank the authors of all baselines. Most of our implementations follow the official implementations. We thank Zhenbang Wu for his assistance in preprocessing the MIMIC-IV dataset.