Collision Prevention Algorithms through Unexpected Obstacle Recognition and Distance and Velocity Estimation
Date: 2022-06-20
Author: Kyungha Noh, Hyebin Ryu
Github: https://github.com/khn224/DLIP_FINAL_LAB
Demo Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8jRxHMq5a_o
This tutorial is about "Collision Prevention Algorithms through unexpected obstacle recognition and distance and velocity estimation". Through this lab, You can make a program that does the following:
- Recognizes the pedestrian by the YOLOv5
- Estimates the distance from the camera and velocity and calculates the TTC(Time To Collision)
- Takes appropriate sign to avoid the collision with pedestrian.
This lab organized with the following background.
- Drivers' burden of driving in school zone increases due to the "Minsik Law".
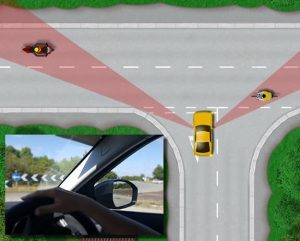
- It is difficult to recognize sudden obstacles due to the A-pillar blind spot (Figure 1, 2).
- As existing technology, company "Continental" provides an image with an OLED display on an A-pillar which is suitable for the driver's head position (Figure 3), and other automakers are proposing similar technologies. However, there is a limit to the recognition of the driving environment only with the human vision itself.
Then, what if there is a camera that can see the road without any blind spot and fast detection program like YOLO? Stable recognition and repond to obstacle can be realized. So, stay focused and follow the content.
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1. A-Pillar Blind Spots | Figure 2. Perspectives of A-Pillar | Figure 3. Continental's OLED Display |
 |
|---|
| Logitech Korea C310 WebCam HD |
For this tutorial, install the correct software version:
- Python 3.9
- CUDA 10.2, cuDNN 7.6
- PyTorch 1.9.1
- Anaconda for Python 3.9 or Anaconda of Latest Version
Installation Steps
1. Install Anaconda
Anaconda : Python and libraries package installer.
Follow: https://ykkim.gitbook.io/dlip/installation-guide/anaconda#conda-installation
2. Install Python
Python is already installed by installing Anaconda. But, we will make a virtual environment for a specific Python version.
-
Open Anaconda Prompt(관리자 권한으로 실행)
-
First, update conda
conda update -n base -c defaults conda
-
Second, Create virtual environment for Python 3.9. Name the environment as
py39. If you are in base, enterconda activate py39conda create -n py39 python=3.9.12
3. Install Libs
Install Numpy, OpenCV, Matplot, Jupyter
conda activate py39
conda install -c anaconda seaborn jupyter
pip install numpy
pip install matplotlib
pip install opencv-python
4. Install Visual Studio Code
Follow: https://ykkim.gitbook.io/dlip/installation-guide/ide/vscode#installation
5. Install GPU Driver, CUDA, cuDNN
Skip this step if you do not have GPU card.
Follow:
6. Install Pytorch
Without GPU (Only CPU)
-
# CPU Only conda install -c anaconda seaborn jupyter conda install pytorch==1.9.1 torchvision==0.10.1 torchaudio==0.9.1 cpuonly -c pytorch pip install opencv-python torchsummary
-
With GPU
# CUDA 10.2 conda install -c anaconda cudatoolkit==10.2.89 cudnn seaborn jupyter conda install pytorch==1.9.1 torchvision==0.10.1 torchaudio==0.9.1 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch pip install opencv-python torchsummary
-
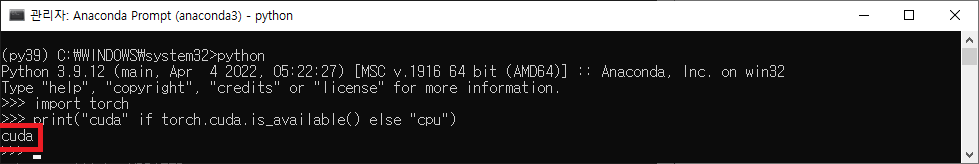
Check GPU in PyTorch
conda activate py39
python
import torch
print("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")If your result is,
-
cuda: GOOD, installed normally. You do not need to follow the steps below. -
cpu: Go to follow the "Troubleshooting" in below
Troubleshooting
Trouble # 1. GPU not detected in PyTorch : print not cuda but cpu
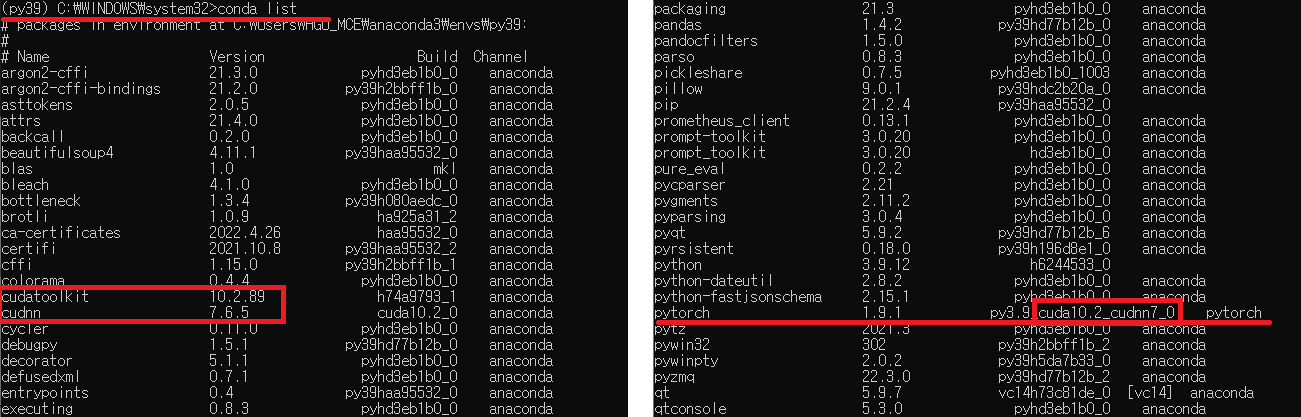
solution 1) Type conda list in the py39 environment
- check whether
cudatoolkit,cudnnare installed. - check whether
pytorchis thecudaversion. - If it is not the same as the following figure, re-install. else go to SOLUTION 2
solution 2) NVIDIA graphics driver update
If the NVIDIA graphics driver is not installed or if it is an older version, the GPU may not be detected. Please refer to the
https://ykkim.gitbook.io/dlip/installation-guide/cuda-installation#9f39
to install Graphic Driver.
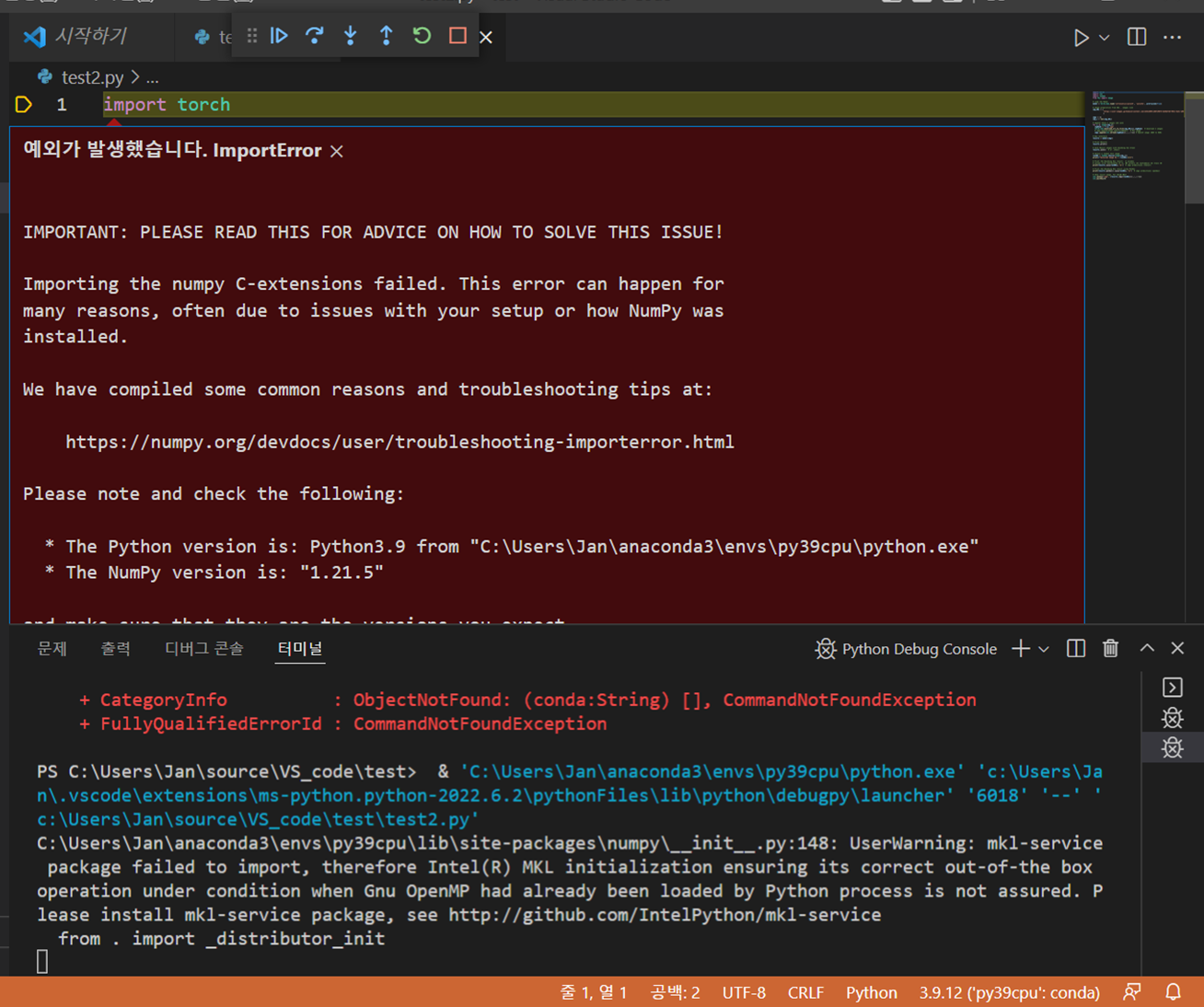
Trouble # 2. Build Error in VS Code (Numpy C-extension failed)
solution) Default Profile Setting in CODE
PressF1 key and type select default profile→ choose command prompt
like this figure.
 |
|---|
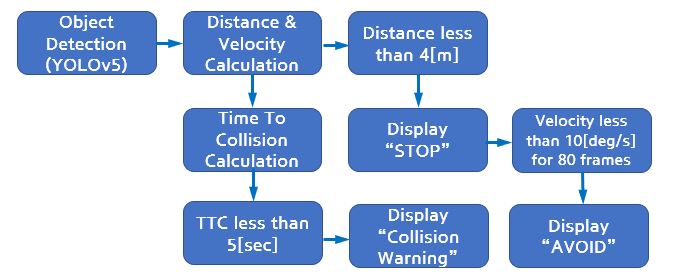
| Figure 4. Software Process |
The program will make decisions like Figure 4. Program detects the pedestrian and calculates its distance, velocity and TTC. If a pedestrian and camera has distance less than 4[m], program gives "STOP" sign and if it has velocity that can be considered as "static state", program tells to "AVOID" the obstacle(pedestrian).
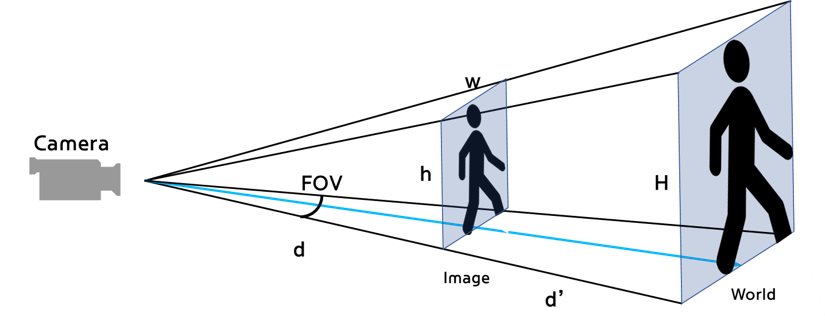
1) Distance $$ 𝑑+𝑑’ = 𝐷 = 3[𝑚] $$
2) Radial Velocity $$ 𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑜𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 =\frac {𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒_{𝑖𝑡ℎ 𝑓𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑒} − 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒_{𝑖−1𝑡ℎ 𝑓𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑒}} {𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒_{𝑖𝑡ℎ 𝑓𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑒} − 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒_{𝑖−1𝑡ℎ 𝑓𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑒}}[𝑚/𝑠] $$ 3) Horizontal Velocity $$ 𝐹𝑂𝑉=41°, 𝑤=640[𝑝𝑖𝑥𝑒𝑙] $$
4) Calculation of TTC $$ 𝑇𝑇𝐶= 𝐷𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒÷𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑜𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦[𝑠𝑒𝑐] $$ 5) Noise Elimination - Moving Average Filter
Velocity values were fluctuated because, the speed change for each frame is not constant. Therefore, by using average filter, calculated with more reasonable velocities. $$ \bar{𝑣_{𝑀}}=\frac 1 𝑛 \sum_{𝑖=0}^{𝑛−1}𝑣_{𝑀−𝑖} $$
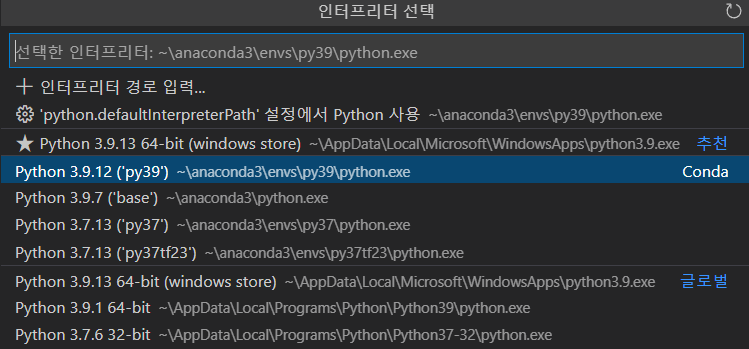
1. Select interpreter in Visual Studio Code and Import libraries
select "Python 3.9.12 ('py39') conda"
import torch
import cv2 as cv
import math
import numpy as np2. Define functions and initialize variables
def convert(size, box): # Convert bounding box vertices(x1,y1,x2,y2) to (center point, width, height) form
x = (box[0] + box[2]) / 2.0
y = (box[1] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = int(x)
y = int(y)
w = int(w)
h = int(h)
return (x,y,w,h)
def MovingAvg(Array): # Moving average filter (window size=30)
Nwindow =30 # Size of window
fwindow = Array[-Nwindow:] # Sliced window
avg=sum(fwindow)/Nwindow # Average value
return avg
RECORD = 0 # For webcam
VIDEO = 1 # For video file
MODE = VIDEO # Select Mode
# Video FileName
Filename1 = "test1.mp4" # Situation 1: Unexpected pedestrian stands in front of the car
Filename2 = "test2.mp4" # Situation 2: Pedestrian crosses the street
Filename3 = "test3.mp4" # Situation 3: Pedestrian crosses the street + Suddenly a pedestrian appears
if MODE == RECORD: # For realtime webcam recording
cap = cv.VideoCapture(cv.CAP_DSHOW+1)
elif MODE == VIDEO: # For pre-recorded video
cap = cv.VideoCapture(Filename3)
fps = 30 # Frames per second
fourcc = cv.VideoWriter_fourcc('D', 'I', 'V', 'X') # Output videofile codec type
out = cv.VideoWriter('demo.avi', fourcc, fps, (640, 480))# For exporting the output videofile
# Initialize count
count = 0 # Frame number
center_points_prev_frame = [] # Center point of a bounding box of the previous frame
depth_prev_frame = [] # Radial distance of the object
tracking_objects = {} # Center points of the tracking object
track_id = 0 # ID of the tracking object
depthConst = 480*0.8 # Pixel-to-distance coefficient
FOVconst = 41 / 640 # Pixel-to-angle coefficient
velocity = 0.0 # Angular velocity of the object
radial_velocity = 0.0 # Radial velocity of the object
AvgRadVel = 0.00000001 # Average radial velocity
bufRadialVel = [] # Buffer of average radial velocity for moving average filter
static_count = 0 # Count up if object is static
StopSignCount = 0 # Count up if stop sign is displayed
pts1 = np.array([[0,0],[640,0],[640,480],[0,480]]) # Point vector of whole frame
detected = False # True when object is detected
TimeToCollision = 0.0 # TTC
Epsilon = 0.00000001 # To prevent zero division error
time_prev = cv.getTickCount() / cv.getTickFrequency() # Time of previous frame3. Import pretrained model from github and set threshold
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5x', pretrained=True) # You can choose among yolo5n,yolo5s,yolo5m,yolo5l,yolo5x
model.conf = 0.6 # Confidence threshold of the model
model.iou = 0.4 # IoU threshold of the model4. Object detection(detect only person)
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read() # Read frame
if not ret: # If frame is not read, break
break
if MODE == RECORD : # Save frame to output videofile when mode: RECORD
out.write(frame)
height ,width = frame.shape[:2] # Height, width of the frame
time_curr = cv.getTickCount() / cv.getTickFrequency() # Time of current frame
time_del = time_curr - time_prev # Time per frame
cord = [] # Point vectors of bounding box of the detected object
idx = [] # Index of the detected object
heightList =[]# List of bounding box height
maxH =0 # Maximum height of the bounding box of the detected object
maxHindex =0 # Index of the bounding box which has the maximum height
count += 1 # Count up when each frame starts
# Point current frame
center_points_cur_frame = [] # Center point of the bounding box of current frame
depth_cur_frame = [] # Radial distance of the object of current frame
results = model(frame) # Run inference
LABEL , COORD = results.xyxyn[0][:, -1].to('cpu').numpy(), results.xyxyn[0][:, :-1].to('cpu').numpy() # Label, coordinate data from the inference results
for i , la in enumerate(LABEL):
if la == 0 :# Detect only for person
idx.append(i) # Append index of the detected object
detected =True # Set detected flag to true
for i , index in enumerate(idx):
cord.append(COORD[index])# Append coordinate of detected object
# Detect objects on frame
boxes = cord # (x1,y1,x2,y2) type bounding box data
x_shape, y_shape = frame.shape[1], frame.shape[0] #Size of the frame or roi
for i,box in enumerate(boxes): # Append bounding box height
heightList.append(cord[i][1] -cord[i][3])
if detected and len(heightList)>0: # Detect the nearest object
maxH = max(heightList) # Maximum height of the bounding box of the detected object
maxHindex = heightList.index(maxH)# Index of the bounding box which has the maximum height
row = cord[-maxHindex-1] # Each bounding box data
x1, y1, x2, y2 = int(row[0]*x_shape), int(row[1]*y_shape), int(row[2]*x_shape), int(row[3]*y_shape)# Point vectors of bounding box of the detected object
(x, y, w, h) = convert((width,height), (x1,y1,x2,y2))# Converted bounding box data to (x,y,w,h) form
center_points_cur_frame.append((x, y)) # Append center point of the bounding box of current frame
depth_cur_frame.append(round(depthConst / (y2-y1),2)) # Append radial distance of the object of current frame
cv.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)# Draw bounding box
5. Object tracking, Calculate distance, velocity, time-to-collision and display appropriate signs
# Only at the beginning we compare previous and current frame
if count <= 2:
for pt in center_points_cur_frame:
for pt2 in center_points_prev_frame:
distance = math.hypot(pt2[0] - pt[0], pt2[1] - pt[1])# L2 norm between center point of the previous bounding box and current bounding box
velocity = ( FOVconst *(distance) * math.pi / 180.0 / time_del ) * depthConst / (y2-y1)# Calculate angular velocity of the object
if distance < 20: # Object tracking L2 norm is less than 20
tracking_objects[track_id] = pt # Append center point of the bounding box of the tracking object
track_id += 1 # Set Id of the traking object
for depth_cur in depth_cur_frame:
for depth_prev in depth_prev_frame:
radial_velocity = (depth_cur-depth_prev) / time_del # Calculate radial velocity of the object
bufRadialVel.append(radial_velocity) # Append radial velocity
AvgRadVel = radial_velocity # Calculate average radial velocity
if depth_cur < 4.0: # Display stop sign if the distance is less than 4m
cv.putText(frame, "STOP", (100,240), 0, 6, (0, 0, 255), 7)
else:
object_exists = False # Object detection flag
tracking_objects_copy = tracking_objects.copy() # Make a copy of tracking objects
center_points_cur_frame_copy = center_points_cur_frame.copy() # Make a copy of center points of the current frame
for object_id, pt2 in tracking_objects_copy.items():
for pt in center_points_cur_frame_copy:
distance = math.hypot(pt2[0] - pt[0], pt2[1] - pt[1])#L2 norm between center point of the previous bounding box and current bounding box
velocity = ( FOVconst *(distance) * math.pi / 180.0 / time_del ) * depthConst / (y2-y1)#Calculate angular velocity of the object
# Update IDs position
if distance < 40: #Object tracking
tracking_objects[object_id] = pt # Append center point of the bounding box of the tracking object
object_exists = True
if pt in center_points_cur_frame:
center_points_cur_frame.remove(pt) # Remove duplicated points
continue
# Remove IDs lost
if not object_exists:
tracking_objects.pop(object_id)
for depth_cur in depth_cur_frame:
for depth_prev in depth_prev_frame:
radial_velocity = (depth_cur-depth_prev) / time_del #Calculate the instantaneous radial velocity
bufRadialVel.append(radial_velocity)# Append radial velocity
AvgRadVel = MovingAvg(bufRadialVel)+Epsilon # Calculate average radial velocity by moving average filter
TimeToCollision = -depth_cur/AvgRadVel # Calculate TTC
if depth_cur < 4.0 and StopSignCount < 80: # Display stop sign for 80 frames if the distance is less than 4m
cv.putText(frame, "STOP", (100,240), 0, 5, (0, 0, 255), 10)
copyframe = frame.copy()
cv.fillConvexPoly(copyframe,pts1,(0,0,255)) # Paint the whole frame slightly red to warn
frame = cv.addWeighted(frame,0.7,copyframe,0.3,0) # Adjust opacity
StopSignCount+=1
if velocity < 15: # Count when angular velocity is less than 15 deg/s
static_count += 1
if StopSignCount >= 80 and static_count >50: # Display avoid sign if the object is stationary
static_count += 1
if object_exists:
cv.putText(frame, "AVOID", (100,240), 0, 5, (0, 165, 255), 10)
elif not object_exists:
static_count = 0 # Reset static count
StopSignCount =0 # Reset stop sign count
# Add new IDs found
for pt in center_points_cur_frame:
tracking_objects[track_id] = pt
track_id += 1
for object_id, pt in tracking_objects.items():# Display Distance,Velocity , TTC and collision waring
cv.putText(frame, f"Distance[m]: { round(depthConst / (y2-y1),2)}", (10, 30), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 0), 5)
cv.putText(frame, f"Distance[m]: { round(depthConst / (y2-y1),2)}", (10, 30), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 255,255), 2)
cv.putText(frame, "velocity(horizontal)[m/s] : " + str(round(velocity, 2)), (10, 60) , 0, 0.7, (0, 0, 0), 5)
cv.putText(frame, "velocity(horizontal)[m/s] : " + str(round(velocity, 2)), (10, 60) , 0, 0.7, (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv.putText(frame, "velocity(radial)[m/s] : " + str(round(AvgRadVel, 2)), (10, 90) , 0, 0.7, (0, 0, 0), 5)
cv.putText(frame, "velocity(radial)[m/s] : " + str(round(AvgRadVel, 2)), (10, 90) , 0, 0.7, (0, 255, 255), 2)
if TimeToCollision < 8 and TimeToCollision >0 : # Display collision warning if TTC is less than 8 sec
cv.putText(frame, "Time to collision[s] : " + str(round(TimeToCollision, 2)), (10, 120), 0, 0.7, (0, 0, 0), 5)
cv.putText(frame, "Time to collision[s] : " + str(round(TimeToCollision, 2)), (10, 120), 0, 0.7, (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv.putText(frame, "COLLISION WARNING!", (150,400), 0, 1, (0, 0, 0), 5)
cv.putText(frame, "COLLISION WARNING!", (150,400), 0, 1, (0, 165, 255), 2)6. Update variables
time_prev = time_curr
cv.imshow("Frame", frame)
if MODE == VIDEO:
out.write(frame)
# Make a copy of the points
center_points_prev_frame = center_points_cur_frame.copy()
depth_prev_frame = depth_cur_frame.copy()The program calculated time-to-collision and successfully displayed a collision warning. Also, it successfully printed a stop sign when distance from the object was less than 4 meters. Finally, it well indicated a command to avoid an obstacle in a static state.
| Situation 1. Collision warning | Situation 2. STOP+Collision warning | Situation 3. AVOID |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Figure 5. Experimental results
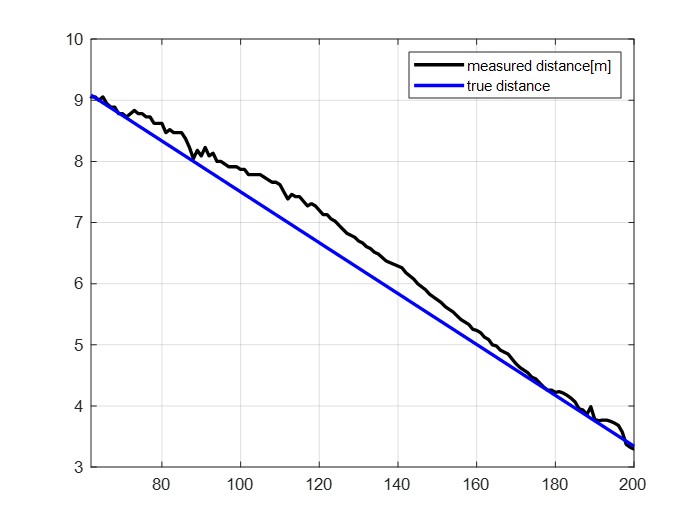
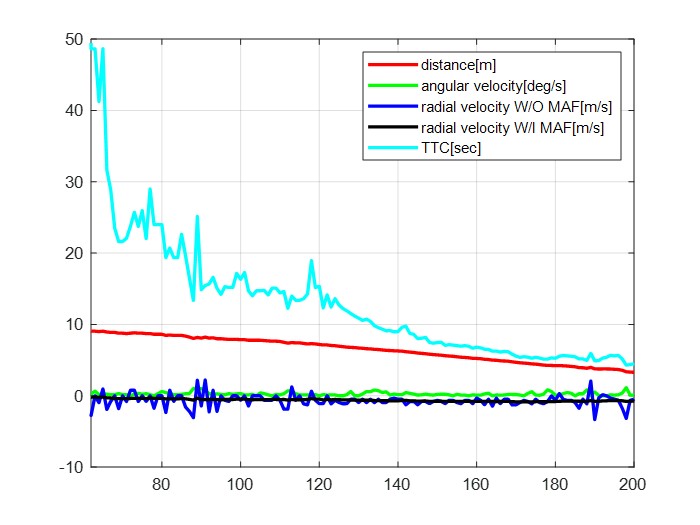 |
 |
|---|---|
| (a) measured value | (b) comparison true and measured distance |
 |
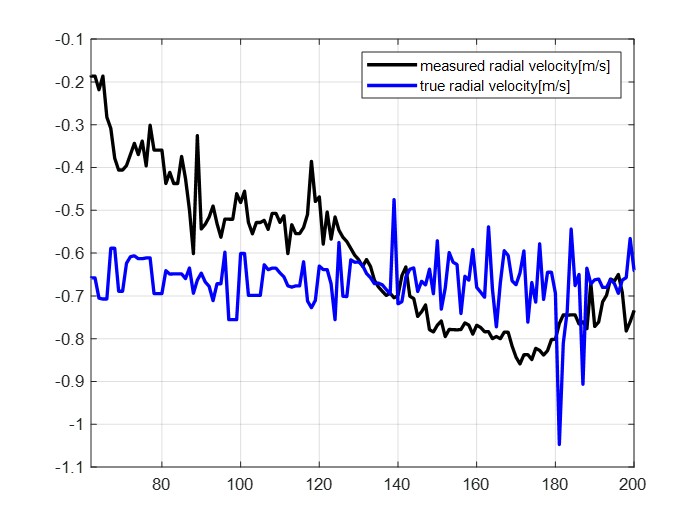 |
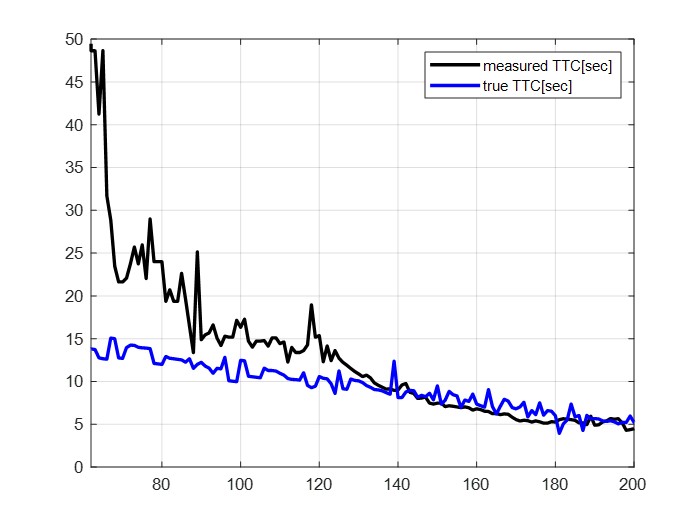
| (b) comparison true and measured TTC | (b) comparison true and measured radial distance |
Figure 6. Validation result
Table 1. RMSE of measurements
| distance | radial velocity | TTC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0.2609 | 0.2391 | 6.9226 |
To validate the measurements, we made a video approaching to person in constant velocity. Figure 6 shows the results and Table 1 shows the RMSE between true value and measurement value. Error is inevitable because our method is only gives rough values. In distance and radial velocity measurement, the RMSE value were below 0.3 . Therefore, it is quite suitable for practical application such as an unexpected obstacle emergence or avoidance situation. However, in TTC measurement, RMSE value was relatively high. But it is because measured velocity and distance values are very rough.
https://pysource.com/2021/10/05/object-tracking-from-scratch-opencv-and-python/
https://pythonprogramming.net/detecting-distances-self-driving-car/