This repository provides python codes for the term project of courses CE 260 and CE 290 in UC Berkeley.
Authors: Kaihang Zhang, Siqi Feng, Yuqi Wang, Yati Liu
As the post-pandemic era begins and inter-regional travel grows, the aviation industry is beginning to recover. Air traffic demand information can be helpful to repair the airline market in a more cost-effective way. However, if the trip demand data are not available, statistical models could be applied to generate them. In this proposal, we will introduce our variational autoencoder (VAE)-based approach for air traffic generation. Our purpose is twofold. First, we will try to figure out the underlying socioeconomic features behind the air traffic flow, which is considered as an encoding process. Then, we will use our model to reconstruct the traffic flow using the features from the first process, which is considered as a decoding step. With a complete model in hand, we are able to generate air traffic flow by inputting socioeconomic data (e.g., demographic data).
VAE was first proposed by Kingma and Welling (2014) to infer the latent variables of an observed data distribution. The basic idea is to apply variational inference to approximate an intractable conditional distribution that is used to calculate the latent features of an observation. Later, numerous applications were developed by researchers, many of which, though still limited, are from the field of transportation. Boquet et al. (2020) proposed a VAE-based online unsupervised data imputation approach with the assumption of latent space, in order to deal with unobserved traffic data with missing values. Islam and Abdel-Aty (2021) developed a similar VAE-based data imputation method as an independent preprocessing step before traffic prediction. Bårli et al. (2021) proposed two methods based upon the ability of VAE to learn from traffic trajectories and abstract feature representations of legitimate traffic. Most recently, Gammelli et al. (2021) formulated a variational poisson recurrent neural network model to predict the bike-sharing demand. However, there is little effort in investigating the traffic generation problem using census data via VAE.
Variational autoencoder (VAE) is the key methodology in our project. VAE can be considered as one type of autoencoder. A typical autoencoder has two components, the first one is an encoder, which recognizes data into features, and the second component is a decoder, which reconstructs the feature into data again. Unlike conventional autoencoders, VAE considers the features as distributions rather than fixed values. This modification helps VAE become more robust against random input noises, which commonly occur in real-world conditions.
We will utilize VAE to firstly find out the underlying features behind the observed traffic demand data (such as OD pairs) and then make a reasonable reconstruction based on the features. The latter purpose achieves our goal of traffic generation. VAE was initially designed to approximate an intractable conditional distribution (or function) which is used to infer the latent features behind observed data. In the air traffic scenario, the relationship between the actual air traffic flow and the socioeconomic census data is hardly tractable. Therefore, VAE is a reasonable approach to tackle our air traffic generation problem.
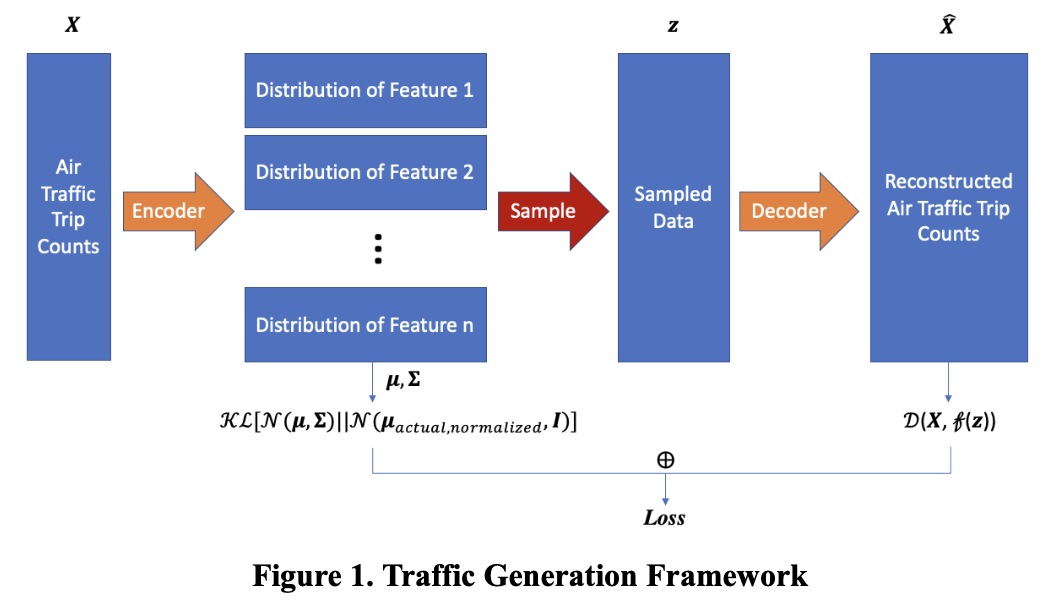
A possible approximation approach for the target conditional distribution is to use a neural network, which is powerful enough to make an approximation for the unknown relationships between the latent features and actual flow data. The framework illustration is shown in Figure 1 below. Since the model will involve socioeconomic data as features, we will make the encoded features as similar to the real census data as possible, i.e., to reduce the feature deviation. This step provides a guarantee that the encoded features are interpretable. On the other hand, the reconstructed OD pairs need to be similar to the real traffic demand, i.e., to reduce the reconstruction loss. Summing up the feature deviation and reconstruction deviation as a whole, we can obtain a total loss, and our objective function is to minimize the total loss. The model is trainable using backpropagation via machine learning optimization techniques such as stochastic gradient descent.
Two datasets will be utilized, which are the census data and the air traffic trip data. We will use the Smart Location Data (SLD) (https://www.epa.gov/smartgrowth/smart-location-database-technical-documentation-and-user-guide) as the census data. SLD consists of over a hundred features containing demographic data, land-use data, transit accessibility statistics and so on. The air traffic trip data can be found from the Bureau of Transportation Statistics (https://transtats.bts.gov/Fields.asp?gnoyr_VQ=FHK), where we can get the passenger origin-destination trip counts for each quarter.
Bårli, E. M., Yazidi, A., Viedma, E. H., & Haugerud, H. (2021). DoS and DDoS mitigation using Variational Autoencoders. Computer Networks, 199, 108399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108399
Boquet, G., Morell, A., Serrano, J., & Vicario, J. L. (2020). A variational autoencoder solution for road traffic forecasting systems: Missing data imputation, dimension reduction, model selection and anomaly detection. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 115, 102622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102622
Gammelli, D., Wang, Y., Prak, D., Rodrigues, F., Minner, S., & Pereira, F. C. (2021). Predictive and prescriptive performance of bike-sharing demand forecasts for inventory management. ArXiv:2108.00858 [Cs, Math]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2108.00858
Islam, Z., & Abdel-Aty, M. (2021). Sensor-based transportation mode recognition using variational autoencoder. Journal of Big Data Analytics in Transportation, 3(1), 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42421-021-00035-2
Kingma, D. P., & Welling, M. (2014). Auto-encoding variational bayes. ArXiv:1312.6114 [Cs, Stat]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6114