Always using Upper in the start of each word
MyFirstClass ProjectSchool
Lower Case first word and after upper the start of each word
myFirstClass projectSchool myName
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Hello World");
}/**
* Java doc comment
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Hello World");
}public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Hello World");
}can be started with null, They are objects.
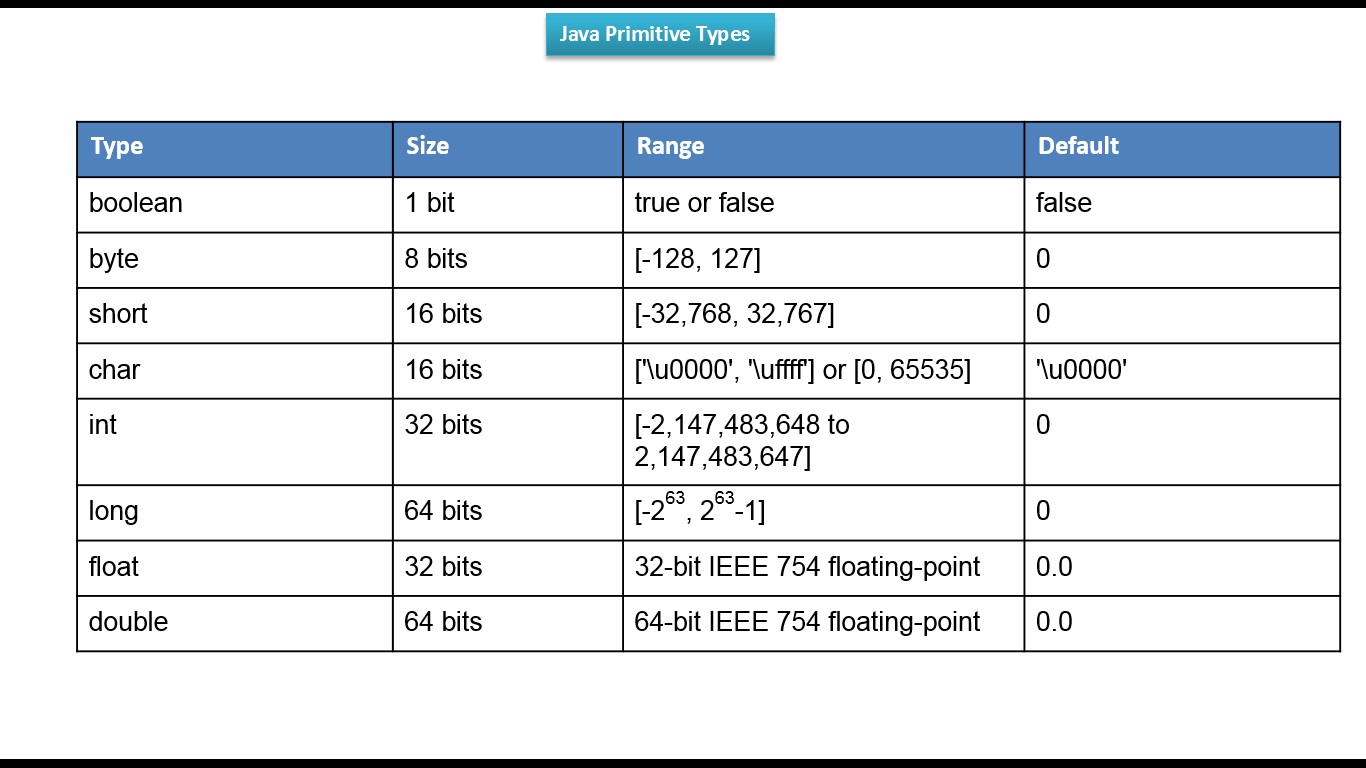
Default values of reference.
- byte, short, int, long, float and double - 0
- char - ' '
- boolean - false
- String null
Has an specific number of items that are set at the start.
array.lenght - Size of the array
type[] variable = new type[slots];
int[] age = new int[3];
int[] age = {1,2,3,4,5};
int[] age = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
primitive_type variable_name value;
int age 10;
boolean compare true;insert the letter that corresponde to the wanting type, example: f or F = Float, d or D = Double.
float salary = 2500.8fForcing variable to receive a value, even if the value is higher than max, this result in some weird results.
int age = (int) 10000000000l;+ - * /
In java divison between 2 int numbers will result print
% - result of division ** - power
&& - and // - or ! - not
variable += number variable -= number variable *= number variable /= number
variable++ - run first then sum one variable-- - run first then reduce one ++variable - sum one first then run --variable - reduce one first then run
condition ? if true : if false
Verify a condition, if true run the code block, if not pass
int idade = 65;
boolean isAdulto = idade >= 18;
if(isAdulto){
System.out.println("Authorizado");
}else if(idade >= 60) {
System.out.println("Terceira idade");
}else {
System.out.println("Não Authorizado");
}Verify if a varible match one of the mapped cases
char sexo = 'F';
switch (sexo){
case 'M':
System.out.println("Homem");
break;
case 'F':{
System.out.println("Mulher");
break;
}
default: {
System.out.println("Opção invalida");
break;
}
}Stays in the loop while the condition given is not a true boolean or a break happens inside the condition.
int cont = 0;
while (cont < 10){
System.out.println(cont);
cont++;
}
similar to while, but first do the code then verify condition.
cont = 0;
do {
System.out.println("do " + cont);
cont++;
}while (cont < 10);
Loop statment until condition is boolean true.
for (start, condition, step)
for (int i=0; i<10; i++){
System.out.println("for " + i);
}
Similar to default for statment, but he uses a iterable directly
for (int num:numbers3){
System.out.println(num);
}
psvm- create main classsout- generate:System.out.println()