WePrompt is a powerful text generative model that serves as an SQLAdvisor, a ProjectAdvisor, and much more! With its cutting-edge architecture, WePrompt can help guide you through various projects, offering valuable insights and suggestions.
├───RavenApi
│ 20B_tokenizer.json
│ convert_model.py
│ RavenApi.py
│ RavenCloud.py
│ weprompt.ipynb
│
├───├instructions
│ ProjectAdvisor.py
│ SQLAdvisor.py
│
└───├users
-20B_tokenizer.json: The model's tokenizer, essential for processing text inputs.
-convert_model.py: A strategy model converter that optimizes and speeds up the model loading process.
-RavenApi.py: The implementation of the Raven model as an API, enabling seamless integration with other applications.
-RavenCloud.py: A CLI (Command-Line Interface) for interacting with the Raven model directly via the terminal.
-weprompt.ipynb: A Jupyter notebook for running the model. Note that the terminal is required for execution.
-ProjectAdvisor.py: An initial prompt that guides the model to function as a ProjectAdvisor.
-SQLAdvisor.py: An initial prompt that guides the model to function as an SQLAdvisor.
Restricting the model to specific use cases allows for better control and performance.
The "users" folder contains directories for individual users, each containing their respective conversations.
The primary objective of this project was to explore the capabilities of the generative text model called RAVEN in its version 4, driven by an open-source community. Additionally, it aimed to assess the model's vision regarding future outputs and projects.
Python 3.4+
Virtualenv
pip
apt-get install -y git
git clone https://github.com/kimou6055/WePrompt.git
All of the following will be built into a virtualenv
open the cmd in the root folder do :
cd ../
Then do the follow: linux :
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python3-venv
python3 -m venv myenv
windows :
pip install virtualenv
python -m venv myenv
Then activate the environnement
windows :
venv\Scripts\activate
linux :
source venv/bin/activate
You can install the required Python libraries by running:
pip install rwkv
pip install torch
pip install pynvml
pip install fastapi
pip install pydantic
pip install mysql
pip install ninja
you can dowload the RAVEN V12 14B Params from this Link
Make sure to put the model in the RavenApi folder
Make sure to install CUDA :
Linux
Windows
To use cuda acceleration please do :
linux:
export PATH=/usr/local/cuda/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
windows:
Install VS2022 build tools (https://aka.ms/vs/17/release/vs_BuildTools.exe select Desktop C++). Reinstall CUDA 11.7 (install VC++ extensions). Run v2/chat.py in "x64 native tools command prompt".
To use :
cd WePrompt/RavenApi
python RavenApi.py
Then send a POST request at this address: http://localhost:8000/generate-response
in this syntax :
{
"user_message": " summarize our last conversation ",
"user_id": "22",
"discussion_id": "4",
"prompt_file": "ProjectAdvisor"
}
the response will be as the follow :
{
"generated_text": " Sure, here's a summary of our conversation:\n1. I created a new file called `Home.js` and added some basic HTML and CSS to it.\n2. I created a new file called `index.js` and added some basic code to it, including a function that sends a request to the MySQL database using the `axios` library.\n3. I created a new file called `App.js` and added some basic code to it, including a function that renders the Home component using the `ReactDOM.render()` method.\n4. I created a new file called `index.css` and added some basic styles to it, including a logo and some basic styling for the page\n\n"
}
You can use ProjectAdvisor.py or SQLAdvisor.py
PS : choose the proper strategy for your own hardware configuration while loading the RWKV model in RavenCloud.py or RavenApi.py
you can see other strategy options HERE
RWKV python implementation can be found HERE
cd WePrompt/RavenApi
python RavenApi.py
Then you can interact with the model directly through the terminal.
The 7B model performs exceptionally well on Google Colab's NVIDIA V100 and Tesla T4, consuming 20 GB of RAM for loading and 16 GB of VRAM. The strategy used for this model is CUDA FP16, with the first layer on the CPU and layers 2 to 33 on the GPU.
The 14B model performs well on Vast.ai instance 2X RTX 4000, consuming 30 GB of RAM for loading and 32 GB of VRAM. The strategy used for this model is CUDA 0:FP16 -> CUDA 1:FP16, with the first layer on the CPU, layers 2 to 16 on GPU 1, and layers 17 to 33 on GPU 2.
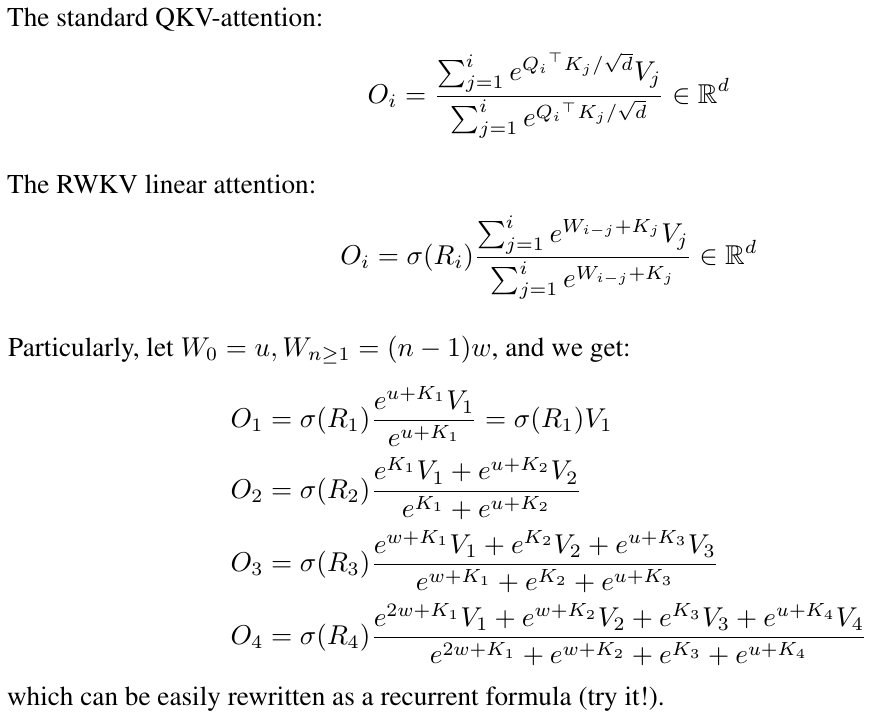
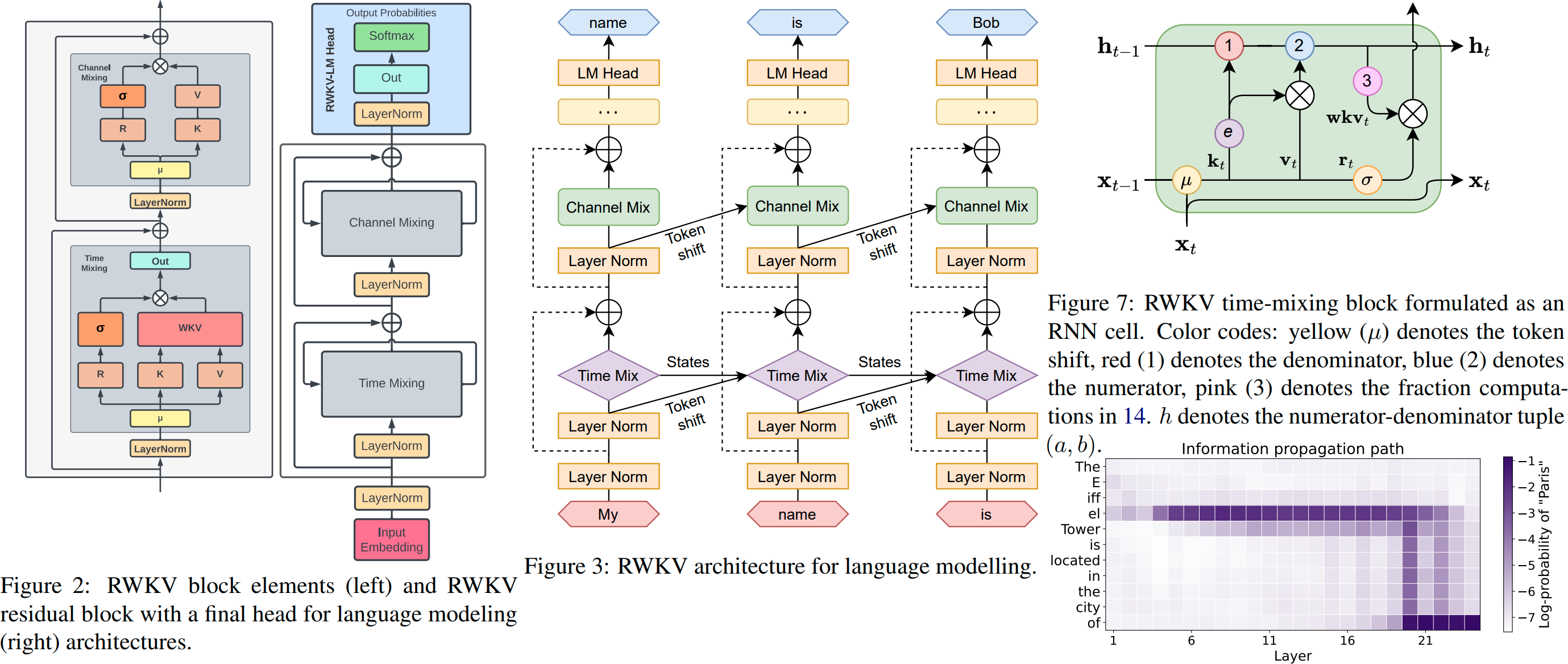
RWKV sounds like an impressive language model developed by BLINKDL that combines the strengths of both RNN and Transformer architectures. By blending these two approaches, RWKV achieves results similar to a Transformer-based language model, providing high performance while being directly trainable in a manner similar to a GPT-style Transformer (parallelizable).
One notable advantage of RWKV is that it is entirely attention-free, meaning it does not rely on self-attention mechanisms that are typically resource-intensive. Instead, to calculate the hidden state at position t+1, RWKV only requires the hidden state at position t. This design choice leads to efficient memory usage, making it particularly suitable for NV-RAM (Non-Volatile Random Access Memory) environments.
Additionally, by utilizing the "GPT" mode, it becomes possible to quickly compute the hidden state for the "RNN" mode. This further enhances training speed and efficiency.
Overall, RWKV appears to offer exceptional performance, reduced NV-RAM memory usage, fast training, and the potential for an "infinite" ctx_len (context length). This combination of features makes it a promising and powerful language model.
RWKV is an attention mechanism used in the context of language models, particularly in Transformers. It stands for:
R - Reference : The letter "R" represents the linear reference. The reference is calculated by linearly combining elements of the sequence using learned weights. It serves as a point of reference for evaluating the importance of other elements in the sequence when calculating attention scores.
W - Weights : The letter "W" refers to the weights used to linearly combine the elements of the sequence to calculate the reference. These weights are learned during the model training and are used to assign relative importance to each element of the sequence when constructing the linear reference.
K - Key : The letter "K" represents the keys associated with the elements of the sequence. Keys are used to measure the similarity between each element of the sequence and the linear reference. Attention scores are calculated by comparing the keys with the reference.
V - Value : The letter "V" represents the values associated with the elements of the sequence. Values correspond to the information that needs to be aggregated or represented when calculating attention. They are weighted by the attention scores and aggregated to form the final attention representation.
In summary, RWKV is a method of calculating attention in a Transformer model, where a reference is derived from the sequence elements using learned weights (W) and compared to the keys (K) to compute attention scores. The corresponding values (V) are then combined based on these attention scores to produce the final attention representation. This mechanism allows the model to focus on relevant parts of the input sequence during processing.
Reduced Complexity: RWKV Linear-Attention can be more computationally efficient compared to QKV-Attention, as it uses a linear reference instead of a combination of queries, keys, and values. This can be advantageous in terms of execution speed and resource utilization.
Capturing Long-Distance Dependencies: RWKV Linear-Attention is designed to better capture long-distance dependencies in a sequence. By using a linear reference, it can consider more complex relationships between elements, which can be beneficial in tasks where long-distance relationships are crucial.
Reduction of Positional Bias: In QKV-Attention, queries and keys may be sensitive to the position of elements in the sequence, leading to positional bias. RWKV Linear-Attention, with its linear reference, can reduce this bias and improve the model's robustness.
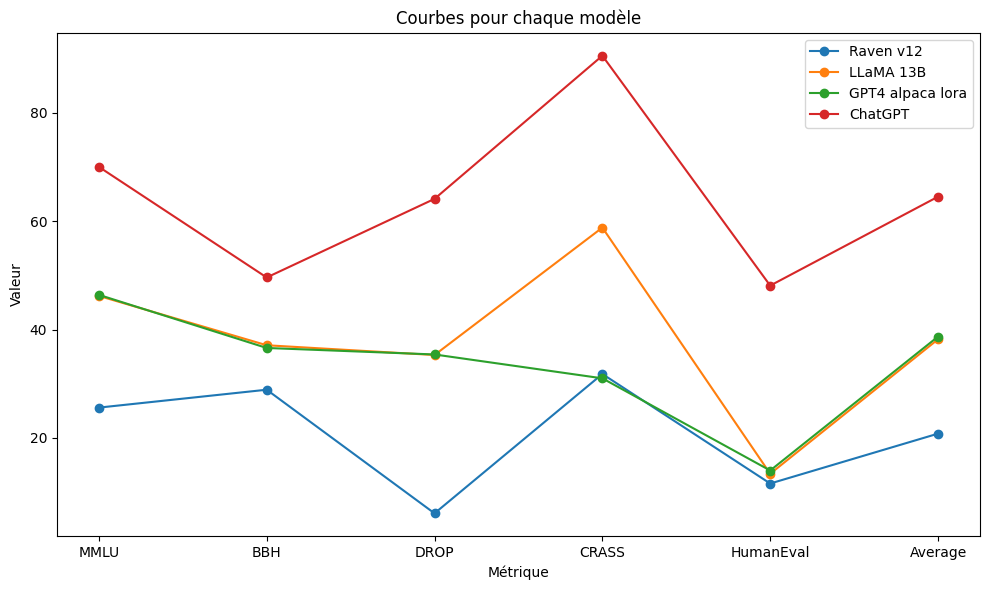
| Model | Foundation | Parameters (B) | MMLU | BBH | DROP | CRASS | HumanEval | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raven v12 | RWKV | 14 | 25.6 | 28.9 | 6.1 | 31.8 | 11.6 | 20.8 |
| LLaMA 13B | LLaMA | 13 | 46.2 | 37.1 | 35.3 | 58.8 | 13.4 | 38.2 |
| GPT4 alpaca lora | LLaMA | 30 | 46.4 | 36.6 | 35.4 | 31.0 | 14.0 | 38.7 |
| ChatGPT | GPT-3.5 | 70 | 70.0 | 49.6 | 64.1 | 90.5 | 48.1 | 64.5 |
-MMLU (Memory Model Load Utilization): This metric measures the memory usage of the model in gigabytes (GB). It indicates the amount of memory required to load the model into the system.
-BBH (Billion BERT Operations per Hour): BBH measures the number of BERT (transformer-based neural network) operations performed by the model each hour, in billions. This metric is used to evaluate the processing speed of the model.
-DROP (Data Retrieval Operations per Hour): DROP measures the number of data retrieval operations performed by the model each hour. It is typically a measure of how quickly the model can access and retrieve the necessary data for processing.
-CRASS (Custom Reasoning Accuracy and Speed Score): CRASS is a composite metric that evaluates both the accuracy and speed of custom reasoning of the model. It combines criteria of accuracy and speed to assess the model's performance on specific reasoning tasks.
-HumanEval (Human Evaluation Score): This metric indicates the scores given by human evaluators to assess the quality and relevance of the responses provided by the model. Human evaluation is often conducted to evaluate the model's real-world performance in terms of adequacy, coherence, and overall response quality.
Average: This column represents the average scores of different metrics for each model.
-Parameters (B): Raven v12 has only 14 billion parameters, which is much less than ChatGPT's 70 billion. Fewer parameters can imply more efficient hardware resource management and quicker model utilization.
-MMLU (Mean Words Per Language Unit): Raven v12 has an MMLU of 25.6, while LLaMA 13B and GPT4 alpaca lora have higher values, 46.2 and 46.4 respectively. A lower MMLU may indicate the ability to express ideas more concisely and understandably.
-BBH (Blind Baseline Human): Raven v12 scores 28.9 for BBH, while GPT4 alpaca lora scores 36.6. A higher BBH score suggests that Raven v12 is closer to human responses than GPT4 alpaca lora.
-DROP (Reading Comprehension of Paragraphs): Raven v12 scores 6.1 for DROP, whereas ChatGPT scores 64.1. This could indicate that Raven v12 is less likely to produce inaccurate or irrelevant responses when dealing with reading passages.
-CRASS (Comprehensive Reasoning on a Simple System): Raven v12 scores 31.8 for CRASS, while GPT4 alpaca lora has a similar score of 31.0. Hence, Raven v12 is as competent as GPT4 alpaca lora in reasoning about simple systems.
-HumanEval (Human Evaluation): Raven v12 scores 11.6 for HumanEval, while GPT4 alpaca lora scores 14.0. A higher HumanEval score for Raven v12 suggests that it is better perceived by human evaluators.
Raven v4, a model based on the foundation of RWKV-4 has a promising architecture, however, the version of its weights trained by the community is not very powerful, the model can perform basic tasks like writing SQL queries and simple code in Python or Java for example, but if you want to use it as a project structure it will not be able to guide you very well, because of its obsolete training data. Nevertheless, it's a good model for understanding and following the thread of a discussion. The important thing is that the model has an architecture that favors its low-cost training and that with well-chosen custom training data, it can be worth a gpt-3.5 or even better and more specialized, depending on your data.
Here is a presentation for the RWKV model in the Wevioo intenship context.
Check the paper RWKV: Reinventing RNNs for the Transformer Era HERE
Projects with Raven v4 would be simple chatbots that would respond on demand either to universal, known questions in the model's training data, or to personalised data, in which case we would be more interested in finetuning models with 500M or 1.5B parameters at a low training cost, while taking advantage of its architecture and the fact that, with a certain implementation, the model remembers the conversation.
Credits for the RWKV-4-Raven model goes to BlinkDL
Credits for project structure and implementation goes to Med Karim Akkari