This repository contains the code of Spiral, which has been modified to work alongside the Ethereum-PIR project.
If you would like to bypass our build system and instead install on a fresh Ubuntu 20.04 machine, please refer to these instructions.
Building Spiral can be complicated. To reduce the possibility for errors, I have
abstracted the setup process into individual containerised execution
environments. Each environment is based on an Ubuntu image, and contains all
the required dependencies to build, run and debug Spiral applications.
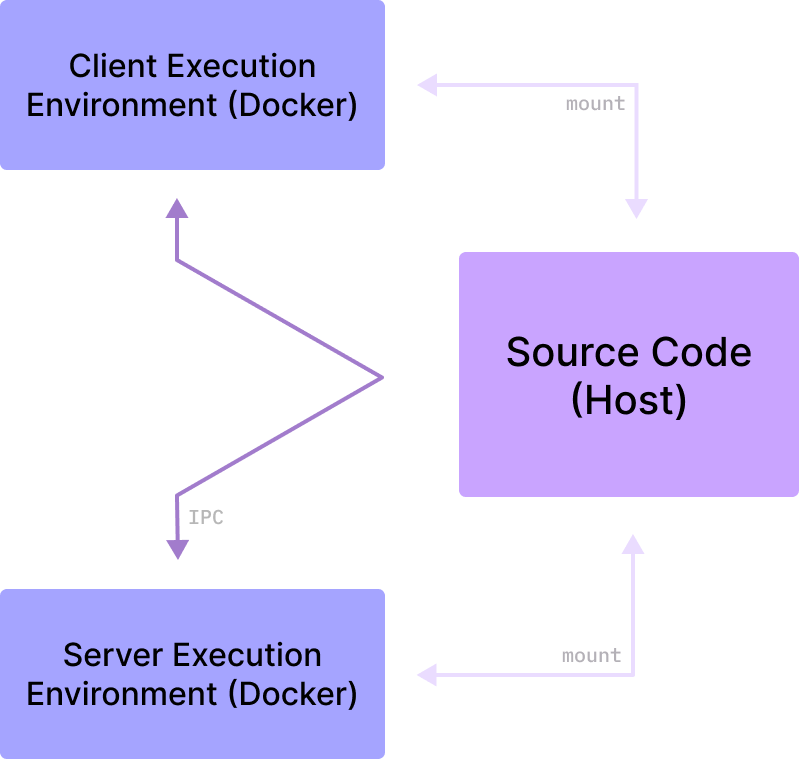
The source code of Spiral is hosted on your local machine, and is mounted
into /tmp/Spiral of the respective execution environment. This 'volume
mount' allows you to edit the source code on your local machine, and have the
changes reflect directly in the environment.
- An x86-64 machine is a must. The code uses Intel-based SIMD instructions to accelerate the query-database processing.
- Docker is required to build and run the execution environments.
- A native Linux environment is strongly preferred. This process has been tested on an Arch Linux machine.
- CLion is the recommended IDE for development.
Although an x86-64 machine is required, ARM machines (such as M1,2,3 Macs) might be able to run Spiral using an x86_64 emulator. An emulator is very expensive, so ensure you have adequate resources to run Spiral.
Clone the repository onto your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/kinda-raffy/Spiral.git Spiralor
gh repo clone kinda-raffy/Spiral SpiralThen, cd into the root of the repository:
cd SpiralFirst create a single toolchain image using Docker:
docker build -t spiral_toolchain .The Client and Server are separate applications that must be run adjacent to one another. To do this, create two terminals and follow the instructions for both terminals unless otherwise specified.
- Run the execution environment with the appropriate container settings.
Ensure that the
docker run -it \ -u root \ -v /HOST_PATH_TO_SPIRAL/Spiral:/tmp/Spiral \ -v /HOST_PATH_TO_SPIRAL/Spiral/Process_Workspace:/home/ubuntu/Process_Workspace \ --rm spiral_toolchain:latest \ /bin/bash -c "cd /tmp/Spiral; exec bash"HOST_PATH_TO_SPIRALis the path to the root of the repository on your local machine (Excluding the root project folder namedSpiral/). - Decide on the database configuration you would like to use. Certain
configurations, such as the database and element size, are required
at compilation. This section has some popular
configurations. You can also find a comprehensive list of configurations in
the configuration directory. For this example,
we will use a database of size
2^20with elements of32bytes each. This configuration has the build folder name ofbuild_20_32. If you do choose to use an alternative configuration, ensure you replacebuild_20_32withbuild_<database_size>_<element_size>. - Generate the build files. Note: replace
build_20_32with the build folder name of your desired database configuration. This command can be ran in any of the two terminals./usr/bin/cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \ -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=/home/ubuntu/vcpkg/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake \ -DUSE_TIMERLOG=ON \ -DUSE_NATIVELOG=OFF \ -DUSE_LOG=ON \ -S /tmp/Spiral -B /tmp/Spiral/build_20_32 # Ensure you replace build_20_32 with your build folder name. - Build the Client and Server executables. Over here, you will need to specify
a number of build parameters. These parameters are determined during
automatic parameter selection, and can be found in the 'build
options' of the configuration table. If you are
using a configuration from this directory, then
these options are listed under
Build Configuration:.- On the client terminal, specify the
Clienttarget./usr/bin/cmake --build /tmp/Spiral/build_20_32 \ --target Client -v -j4 \ -- PARAMSET=PARAMS_DYNAMIC \ TEXP=4 \ TEXPRIGHT=56 \ TCONV=4 \ TGSW=4 \ QPBITS=14 \ PVALUE=4 \ QNUMFIRST=1 \ QNUMREST=0 \ OUTN=2 - On the server terminal, specify the
Servertarget./usr/bin/cmake --build /tmp/Spiral/build_20_32 \ --target Server -v -j4 \ -- PARAMSET=PARAMS_DYNAMIC \ TEXP=4 \ TEXPRIGHT=56 \ TCONV=4 \ TGSW=4 \ QPBITS=14 \ PVALUE=4 \ QNUMFIRST=1 \ QNUMREST=0 \ OUTN=2
- On the client terminal, specify the
- Create a toolchain image using Docker:
docker build -t spiral_toolchain . - Open the root project in CLion.
- Load the parent
./CMakeLists.txtfile as the CMake project. - Go to
File > Settings > Build, Execution, Deployment > Toolchains, and add the built Docker image as a new toolchain called 'Docker_Spiral'. - CLion will automatically detect pre-configured build profiles and should build the project automatically.
| Build Folder Name | Description | Build Options |
|---|---|---|
build_20_256 |
Database size of 2^20 with elements of 256 bytes each. |
-- PARAMSET=PARAMS_DYNAMIC TEXP=8 TEXPRIGHT=56 TCONV=4 TGSW=9 QPBITS=21 PVALUE=256 QNUMFIRST=1 QNUMREST=0 OUTN=2 |
build_10_32 |
Database size of 2^10 with elements of 32 bytes each. |
-- PARAMSET=PARAMS_DYNAMIC TEXP=4 TEXPRIGHT=56 TCONV=4 TGSW=4 QPBITS=14 PVALUE=4 QNUMFIRST=1 QNUMREST=0 OUTN=2 |
build_20_32 |
Database size of 2^20 with elements of 32 bytes each. |
-- PARAMSET=PARAMS_DYNAMIC TEXP=4 TEXPRIGHT=56 TCONV=4 TGSW=5 QPBITS=16 PVALUE=16 QNUMFIRST=1 QNUMREST=0 OUTN=2 |
build_30_32 |
Database size of 2^30 with elements of 32 bytes each. |
-- PARAMSET=PARAMS_DYNAMIC TEXP=16 TEXPRIGHT=56 TCONV=4 TGSW=13 QPBITS=21 PVALUE=256 QNUMFIRST=1 QNUMREST=0 OUTN=2 |
For additional configurations, refer to the configuration directory.
These instructions assume you have the two terminals from the build process still open. Otherwise, re-run the execution environments on two separate terminals.
The client and server executables require 3 arguments. The first two are
related to the number of dimensions and folding during query-data processing. To
put it simply, these will determine the number of 'actual' records in the
database. These arguments are selected during automatic parameter selection
which is done via the select_params.py script. For convenience, these two
arguments are listed in the configuration table or
under Run Cofiguration: in the configuration
directory. If you are using this directory, then only the
first two numbers after ./spiral are relevant. For example, for the
file 20_32.config, the run configuration lists the following:
Run Configuration:
./spiral 7 6 7055 a
In this case, the first two numbers are 7 and 6.
The third argument is the name of the data file that contains a list of hashes
in json. This is file name (colorB_10.json) and not the file
path (Database_Data/colorB_10.json). These data files are located in the
Database_Data directory and a list of approapiate database sizes for each data
file can be found in the meta file. The client requires
the database file to verify the
hashes received from the server are correct.
Finally, the client and server executables must be executed with the same
arguments and the client should begin before the server.
- On the client terminal, run the
Clientexecutable./tmp/Spiral/build_20_32/Client/Client 7 6 <FileName>
- On the server terminal, run the
Serverexecutable./tmp/Spiral/build_20_32/PIR_Server/Server 7 6 <FileName>
- After building the CMake project, select the build option and the target you would like to run.
- Run (Shift+F10) or Debug (Shift+F9) the selected target.
- The
ClientandServerexecutables must be run with the same parameters to ensure message verification is successful. - The
Clientshould always be ran before theServer. Otherwise, the receiving pipe onServermight hang.
The Client and Server executables communicate with each other using OS
pipes.
The following diagram describes the transactions that occur between the two
executables.
If you face any issues during the build or execution process, please open an issue in this repository. Provide in-depth details of the following:
- Your environment (OS, CPU, RAM).
- All the commands you have tried to run and their ouputs to the lead up to this issue.
- The full error message you are receiving.