[Description]
|--- .mvn
|--- src
| |--- main
| |--- java
| |---hng_java_boilerplate
| |---<feature implementations>
| |---Program.java
| |---utils
| |--- resources
| |--- static
| |--- templates
| |--- application.properties
| |--- test
| |--- java
| |---hng_java_boilerplate
| |---<implementations tests>
|--- .gitignore
|--- mvnw
|--- mvnw.cmd
|--- README.md
Ensure you have your computer setup correctly for development by installing the following
- Java 17 or higher
- Install Java SDK/JDK
- Use your favourite IDE or Text editor
If you don't have git on your machine, install it.
Fork this repository by clicking on the fork button on the top of this page. This will create a copy of this repository in your account.
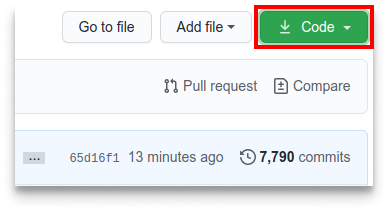
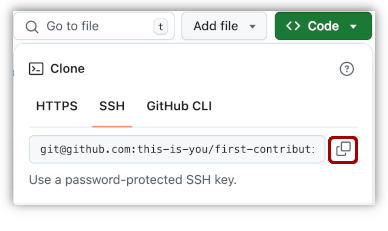
Now clone the forked repository to your machine. Go to your GitHub account, open the forked repository, click on the code button and then click the copy to clipboard icon.
Open a terminal and run the following git command:
git clone "url you just copied"where "url you just copied" (without the quotation marks) is the url to this repository (your fork of this project). See the previous steps to obtain the url.
For example:
git clone git@github.com:this-is-you/hng_project.gitwhere this-is-you is your GitHub username. Here you're copying the contents of the first-contributions repository on GitHub to your computer.
Change to the repository directory on your computer (if you are not already there):
cd hng_projectNow create a branch using the git switch command:
git switch -c your-new-branch-nameFor example:
git switch -c add-alonzo-churchMake your changes to the codebase. Ensure your code follows the project's coding standards and guidelines.
Run the existing tests to ensure your changes do not break anything. If you added new functionality, write corresponding tests and run them.
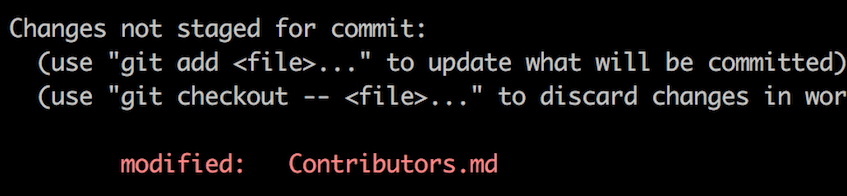
Now open Contributors.md file in a text editor, add your name to it. Don't add it at the beginning or end of the file. Put it anywhere in between. Now, save the file.
If you go to the project directory and execute the command git status, you'll see there are changes.
Add those changes to the branch you just created using the git add command:
Push your changes using the command git push:
git push -u origin your-branch-namereplacing your-branch-name with the name of the branch you created earlier.
If you get any errors while pushing, click here:
-
remote: Support for password authentication was removed on August 13, 2021. Please use a personal access token instead. remote: Please see https://github.blog/2020-12-15-token-authentication-requirements-for-git-operations/ for more information. fatal: Authentication failed for 'https://github.com//first-contributions.git/'
Go to GitHub's tutorial on generating and configuring an SSH key to your account.
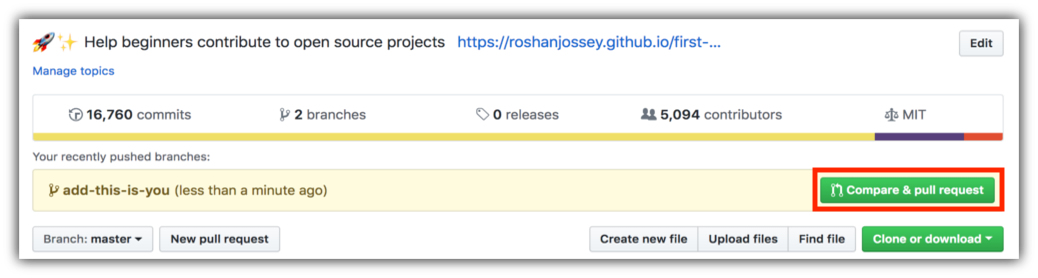
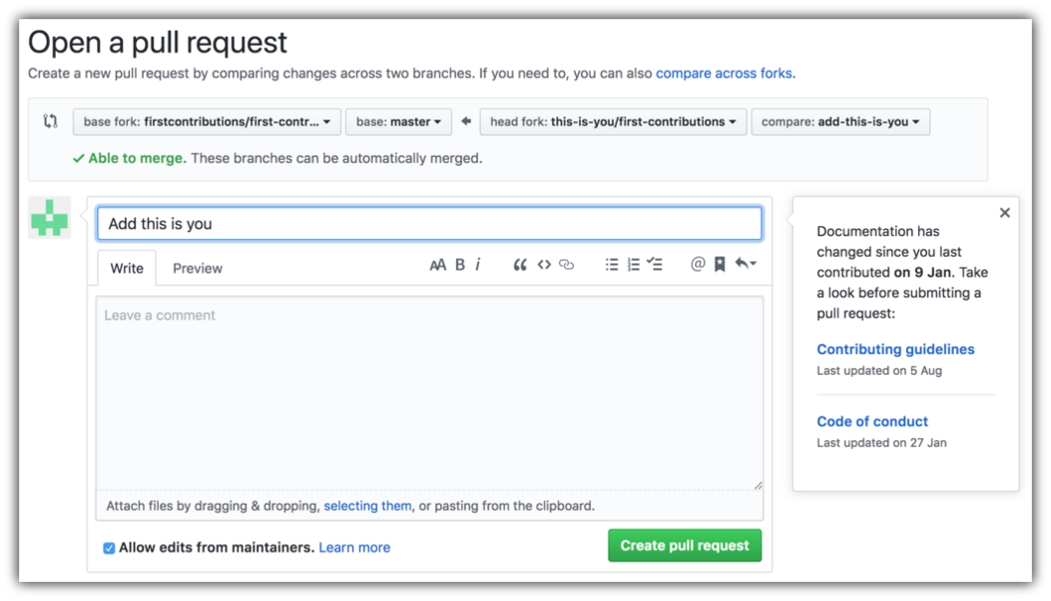
If you go to your repository on GitHub, you'll see a Compare & pull request button. Click on that button.
Now submit the pull request.
Soon your changes will be merged into the staging branch of this project. You will get a notification email once the changes have been merged.
First, clone the repository to your local machine using Git.
git clone https://github.com/your-username/[app-name].git
cd [app-name]Opening the project in your dev environment should automatically restore all your dependencies.
You can also install dependencies by running the following mavin command in your root folder.
mvn dependency:resolve- Ensure PostgreSQL is installed and running
- Create a new database in the database
CREATE DATABASE {database_name} - Flyway Migrations
- migration files should be placed in the
src/main/resources/db/migrationdirectory - Each migration file should follow the naming convention
V<version>__<description>.sql.e.gV1__create_users_table.sqlV1__init_database.sql
- sample migration file
- migration files should be placed in the
-- V1__create_users_table.sql
CREATE TABLE users (
id VARCHAR(255) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL UNIQUE
);
-- V2__create_profiles_table.sql
CREATE TABLE profiles (
id VARCHAR(255) PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(255),
last_name VARCHAR(255),
phone VARCHAR(255),
avatar_url VARCHAR(255)
);
-- V3__create_products_table.sql
CREATE TABLE products (
id VARCHAR(255) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
user_id VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id)
);
-- V4__create_organisations_table.sql
CREATE TABLE organisations (
id VARCHAR(255) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
description TEXT
);
-- Many-to-Many Relationship Table
CREATE TABLE user_organisation (
user_id VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
organisation_id VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (user_id, organisation_id),
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id),
FOREIGN KEY (organisation_id) REFERENCES organisations(id)
);- update the
application.propertiesfile with your database credentials and configure flyway
<!-- database configuration-->
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:{connection_string}
spring.datasource.username=your_username
spring.datasource.password=your_password
<!-- flyway configuration-->
spring.flyway.enabled=true
spring.flyway.locations=classpath:db/migration
spring.flyway.user={database_username}
spring.flyway.password={database_password}- Apply migrations
./mvnw flyway:migrate
Press F5 on your keyboard to run the application in debug mode for your Vscode or use whatever your IDE requires (You may need to open a .java file to trigger this).
Depending on the IDE/code editor, you should be greeted with a Hello world text when you navigate to localhost:8080.
- using curl (user_one_id: id of the user created in the database)
curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/api/v1/users/user_one_id - Using Postman
- Open Postman
- Create a new GET request to curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/api/v1/users/user_one_id
- send the request and verify the response
- Expected Response
{
"name": "John Doe",
"id": "some-user-id",
"email": "johndoe@example.com",
"profile": {
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe",
"phone": "1234567890",
"avatar_url": "http://example.com/avatar.jpg"
},
"organisations": [
{
"org_id": "some-org-id-1",
"name": "Some Org",
"description": "Some Org Description"
},
{
"org_id": "some-other-org-id-2",
"name": "Some Other Org",
"description": "Some Other Org Description"
}
],
"products": [
{
"product_id": "some-product-id",
"name": "Some Product",
"description": "Some Product Description"
},
{
"product_id": "some-other-product-id",
"name": "Some Other Product",
"description": "Some Other Product Description"
}
]
}