Grad-CAM implementation for TensorFlow 2.0 in Eager Execution mode.
To use you can put the script within your project folder and import it into a Jupyter Notebook or your IDE of preference or install as a pip wheel. You will find the .whl file in dist folder in this repo. After you've cloned the repo, go to the directory in terminal/command line and execute: pip install eager_gradcam_tf-0.2.1-py3-none-any.whl. After that, import it to your code with import eagergradcamtf.
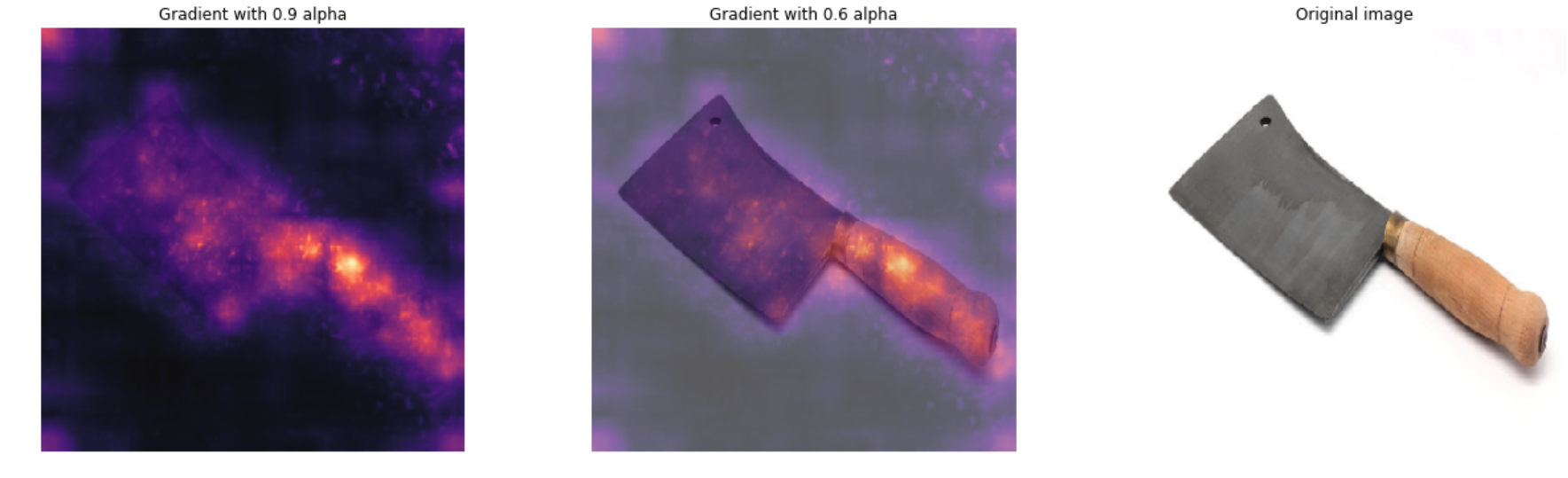
Use grad-cam function to view gradients and gradient/photo overlay. A quick presentation using InceptionV3 can be found in Notebook 4. A comparison of ResNet50, Xception and InceptionV3 can be found in Notebook 5.
optional kwargs
|----------------------------------|
| |
grad_cam(image, model, image_dims, return_switch, watch_layer_instances)
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | tf.keras.layers instance to watch or tuple of those (default is Conv2D)
| | | |
| | | 'gradients' to return list of gradients, 'maps' to return list of feature maps
| | |
| | tuple containing image dimensions e.g. (299, 299)
| |
| Model or Sequential object with eager execution enabled
|
path to image
Feel free to play around with the notebooks I provided, they describe most of the steps I went through to figure out the best possible way to allow Grad-CAM to work in eager mode.
This implementation has been tested on ResNet50, Xception and Inception V3 architecture in TensorFlow 2.0 with Keras API. With that being said I cannot guarantee that this implementation is absolutely accurate and will be happy to hear from the community to get suggestions of improvements to this project.
You can read the original paper by Ramprasaath R. Selvaraju, Michael Cogswell, et al. at https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.02391
-
images/cleaver.jpg --> Coyau / Wikimedia Commons / CC BY-SA 3.0
-
images/granny_smith.jpg --> benjamint444 / Wikimedia Commons / CC BY-SA 3.0
-
images/banjo.jpg --> Gregg Miner / Wikimedia Commons / CC BY-SA 3.0