This reference architecture provides a set of YAML templates for deploying microservices to Amazon EC2 Container Service (Amazon ECS) with AWS CloudFormation. This is a custom stack created for TransIndia Logistics.
You can launch this CloudFormation stack in the Singapore (AP Southeast) Region in your account by clicking the below button to launch:
- 2 Keypairs : 1 for bastion instance, 1 for ECS login
The repository consists of a set of nested templates that deploy the following:
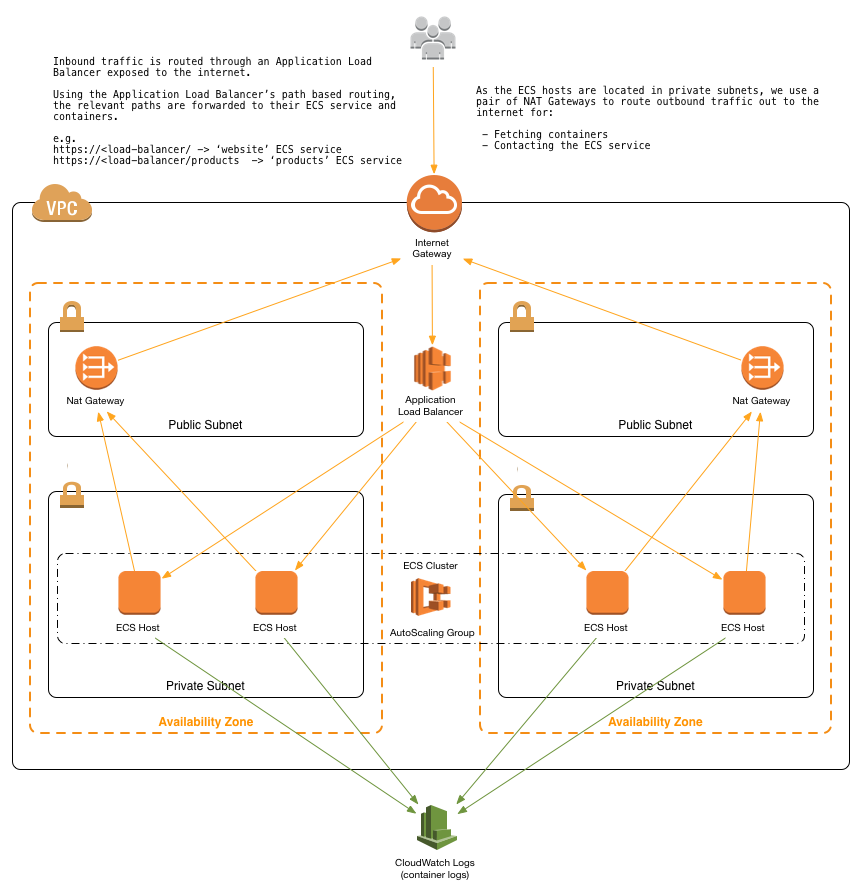
- A tiered VPC with public and private subnets, spanning an AWS region.
- A highly available ECS cluster deployed across two Availability Zones in an Auto Scaling group.
- A pair of NAT gateways (one in each zone) to handle outbound traffic.
- An Application Load Balancer (ALB) to the public subnets to handle inbound traffic.
- ALB path-based routes for each ECS service to route the inbound traffic to the correct service.
- API Gateway << To to be written >>
- Centralized container logging with Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
The templates below are included in this repository and reference architecture:
| Template | Description |
|---|---|
| master.yaml | This is the master template - deploy it to CloudFormation and it includes all of the others automatically. |
| infrastructure/vpc.yaml | This template deploys a VPC with a pair of public and private subnets spread across two Availability Zones. It deploys an Internet gateway, with a default route on the public subnets. It deploys a pair of NAT gateways (one in each zone), and default routes for them in the private subnets. |
| infrastructure/security-groups.yaml | This template contains the security groups required by the entire stack. They are created in a separate nested template, so that they can be referenced by all of the other nested templates. |
| infrastructure/load-balancers.yaml | This template deploys an ALB to the public subnets, which exposes the various ECS services. It is created in in a separate nested template, so that it can be referenced by all of the other nested templates and so that the various ECS services can register with it. |
| infrastructure/ecs-cluster.yaml | This template deploys an ECS cluster to the private subnets using an Auto Scaling group. |
-
Push you code to master branch in gitlab
-
This triggers a CI run using gitlab's default CI. a. Gitlabs CI will run the neccessary test cases. b. If the CI/CD build is completely successsful, Gitlab will build a docker container and push the TransIn's Docker repository. c. Gitlabs will trigger a mail to you at your company mail ID once the CI build is complete.
-
Push your container to a registry somewhere to Amazon ECR).
-
Copy one of the existing service templates in services/*.
-
Update the
ContainerNameandImageparameters to point to your container image instead of the example container. -
Increment the
ListenerRulepriority number (no two services can have the same priority number - this is used to order the ALB path based routing rules). -
Copy one of the existing service definitions in master.yaml and point it at your new service template. Specify the HTTP
Pathat which you want the service exposed. -
Deploy the templates as a new stack, or as an update to an existing stack.
It is not set up to scale automatically based on any policies (CPU, network, time of day, etc.).
Deploy another CloudFormation stack from the same set of templates to create a new environment. The stack name provided when deploying the stack is prefixed to all taggable resources (e.g., EC2 instances, VPCs, etc.) so you can distinguish the different environment resources in the AWS Management Console.
This set of templates deploys the following network design:
| Item | CIDR Range | Usable IPs | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| VPC | 10.180.0.0/16 | 65,536 | The whole range used for the VPC and all subnets |
| Public Subnet | 10.180.8.0/21 | 2,041 | The public subnet in the first Availability Zone |
| Public Subnet | 10.180.16.0/21 | 2,041 | The public subnet in the second Availability Zone |
| Private Subnet | 10.180.24.0/21 | 2,041 | The private subnet in the first Availability Zone |
| Private Subnet | 10.180.32.0/21 | 2,041 | The private subnet in the second Availability Zone |
ECS has the ability to perform rolling upgrades to your ECS services to minimize downtime during deployments. For more information, see Updating a Service.
To update one of your services to a new version, adjust the Image parameter in the service template (in services/* to point to the new version of your container image. For example, if 1.0.0 was currently deployed and you wanted to update to 1.1.0, you could update it as follows:
TaskDefinition:
Type: AWS::ECS::TaskDefinition
Properties:
ContainerDefinitions:
- Name: your-container
Image: registry.example.com/your-container:1.1.0
After you've updated the template, update the deployed CloudFormation stack; CloudFormation and ECS handle the rest.
To adjust the rollout parameters (min/max number of tasks/containers to keep in service at any time), you need to configure DeploymentConfiguration for the ECS service.
For example:
Service:
Type: AWS::ECS::Service
Properties:
...
DesiredCount: 4
DeploymentConfiguration:
MaximumPercent: 200
MinimumHealthyPercent: 50