Find average distance between random points in an N-dimensional cube.
This is a fun math exercise.
Consider a pair of point chosen randomly on a unit line segment:
- What is the average distance between them?
- Can you prove it mathematically?
- Can you test it by trying a lot of random points?
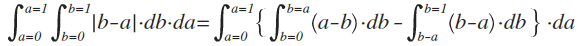 Plug into maxima:
Plug into maxima:
integrate((integrate(b-a,b,a,1)+integrate(a-b,b,0,a)),a,0,1);
(%o1) 1/3
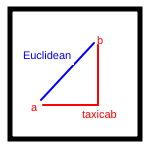
Consider 2 random points in a unit square:
There is more than one way to measure the distance between the points:
- Taxicab or Manhattan -- distance in each dimension separately
- Red in the diagram
- This makes the problem separable
- Each dimension adds 1/3 to the total average since each dimension is independent.
- Euclidean -- the conventional distance
- Blue in the diagram
- The equation is non-linear:
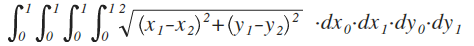
- General Lp metric:
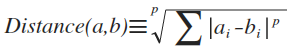
- Taxicab p=1
- Euclidean p=2
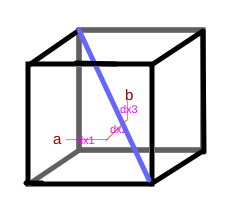
- The program can be generalized to arbitrarily higher dimensions
- One characteristic distance to note is the longest diagonal
- from point (0,0,0...) to (1,1,1,...)
- For dimension D and Lp metric p:
- diagonal = D^(1/p)
- Rather than solving the equtions directly, simulate with random points
- Each coordinate of each point is evenly distributed from 0.0 to 1.0
- Distance can be measured using the applicable metric
- The average distance can be measured
# Get code
git clone http://github.com/alfille/distance
# Go to program directory
cd distance
# Compile and make executable
make
chmod +x distance
# optional to install
sudo cp distance /usr/bin/distance
# otherwise run from directory
./distance
The only requirements are a working C complier and git
Actually, if you download the code you only need any C compiler
cc -o distance distance.c
./distance -h
distance -- find the average distance between random points in
a unit N-cube using Monti Carlo method.
By Paul H Alfille 2021 -- MIT license
Output is CSV file format to make easy manipulation.
A number of metrics are used including
1 (Manhattan) |x1-x2| in each dimension
2 (Euclidean) sqrt(sum((x1-x2)^2))
3 [sum((x1-x2)^3)]^1/3
Syntax:
distance [options]
Options:
-d 100 max dimensions
-p 3 max power (metric)
-r 1000000 random points each measure
-n normalize (to longest diagonal)
-h this help
The output is a CSV (comma-separated-values) file that can be imported into man programs (e.g. Excel)
./distance -p 10 -r 100000 -d 200 -n > Sample.csv
In fact that result is in the example directory
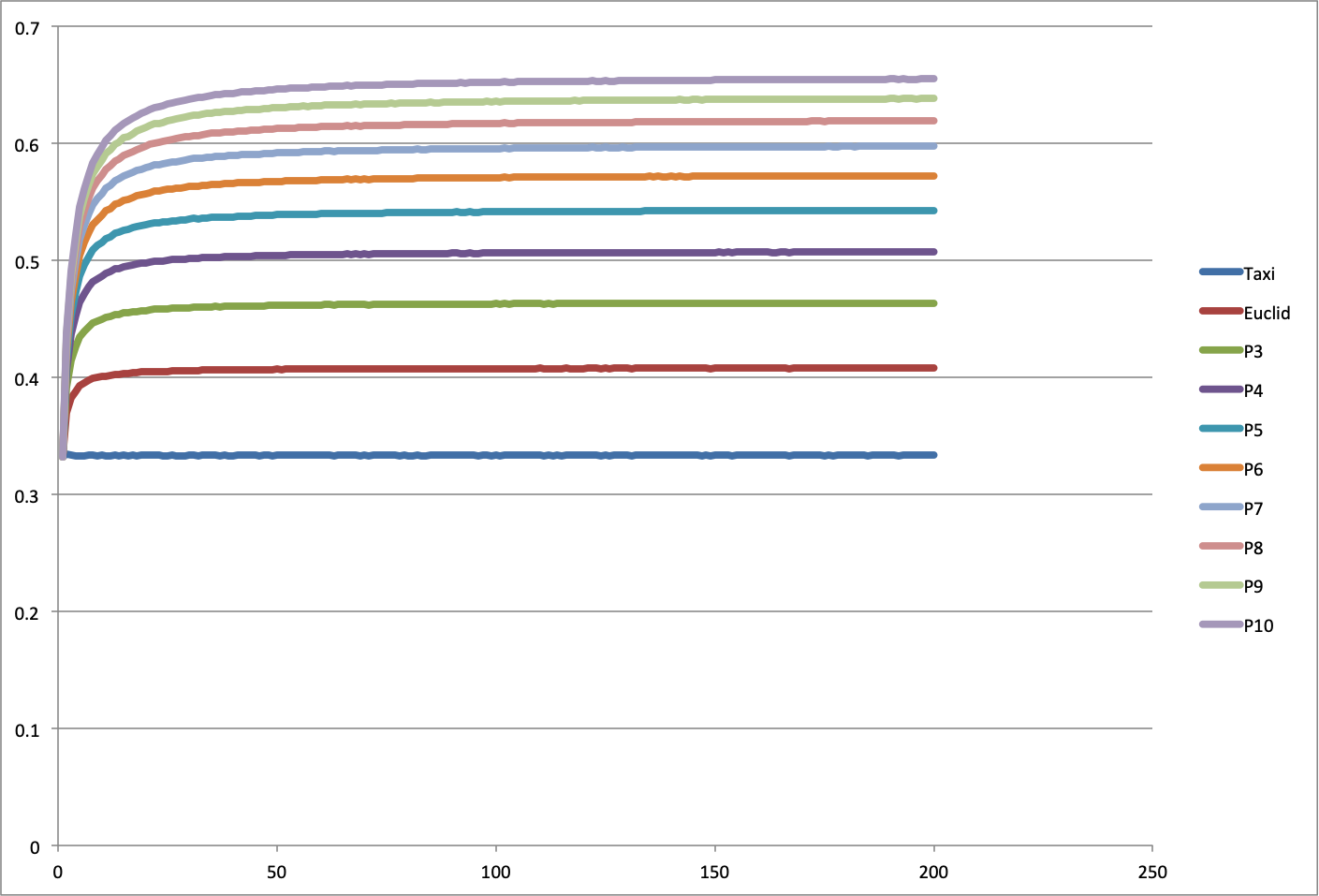
- x-axis: Dimension
- y-axis: Average segment length (normalized to longest diagonal)
- Curves: Different metrics from p=1 to p=10
Calculations are done in double precision floating point which limits the exponent to about 10^-300. Since the calculation involves multiplying numbers from 0.0 to 1.0 by themselves, dimension = 200 is probably safe. (i.e. 0.1^200)
Note that the normalized (to the longest diagonal) appears to reach an assymptotic value for each power at higher dimensions.
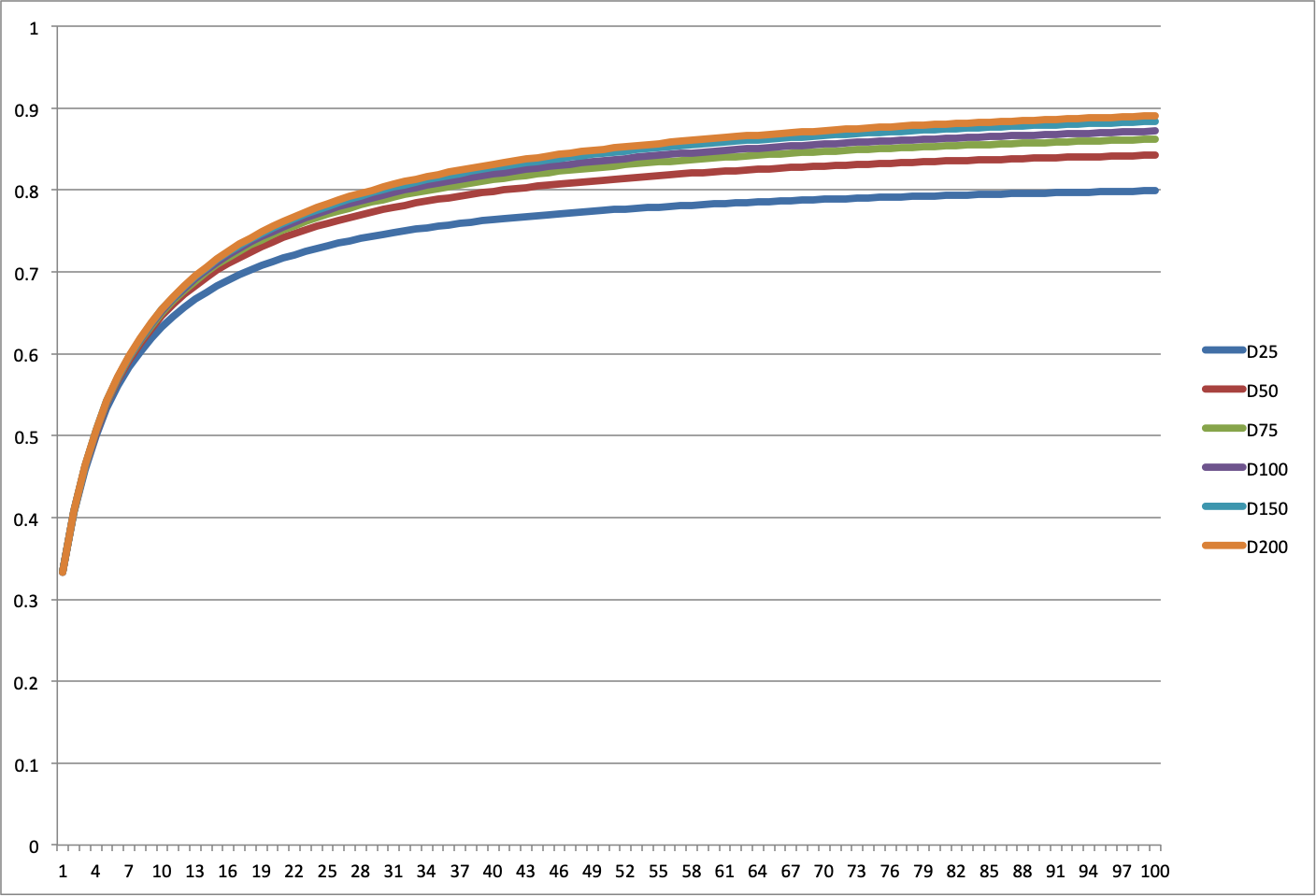
- x-axis: power (p in Lp metric)
- y-axis: Average segment length (normalized to longest diagonal)
- Curves: Various dimensions (25,50,75,100,150,200)
- Since Linf devolves to Max metric, it makes sense that values approach 1.0
If you have references to a better mathematical treatment, please include in the github comments, or to me directly at paul.alfille@gmail.com