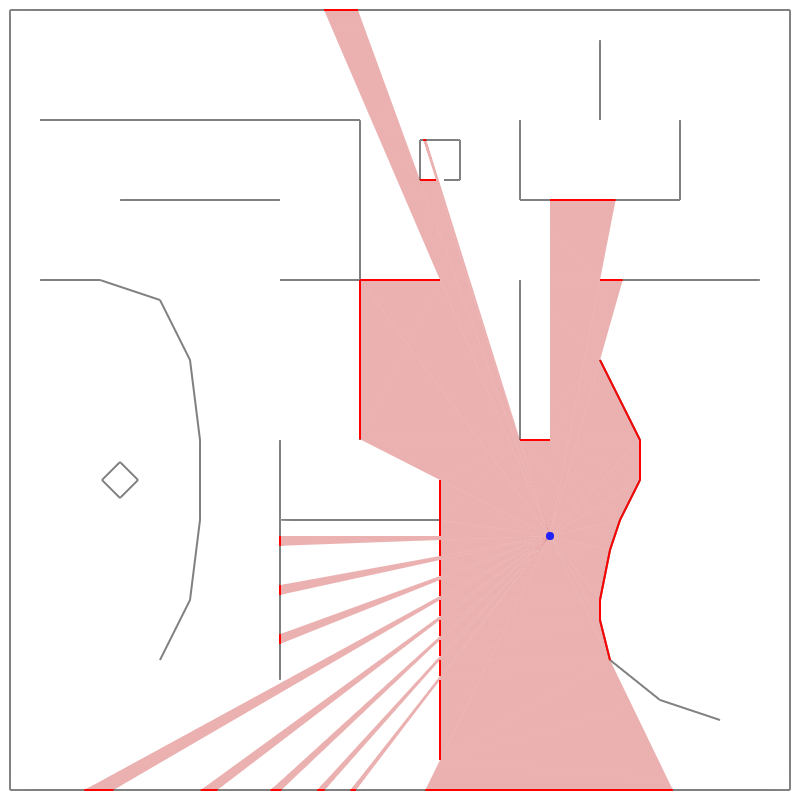
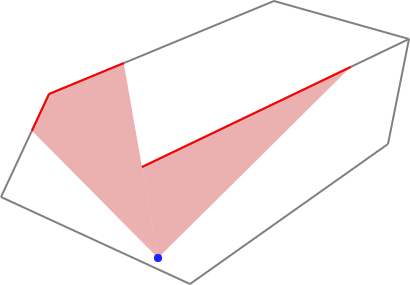
Compute visibility polygons by Triangular Expansion.
// Points to be triangulated
const points = [[53,98],[5,201],[194,288],[280,195],[392,148],[413,43],[278,5],[169,71],[146,171]],
// Edges to be constrained
edges = [[5, 8]],
// Triangulate
del = Delaunator.from(points),
// Constrain the triangulation
con = new Constrainautor(del);
con.constrainAll(edges);
// Query point
const qx = 162, qy = 262,
// Obstruction callback: use constrained edges as obstructions
obstructs = (edg) => con.isConstrained(edg),
// Left & right end-points of the initial viewing cone (optional)
ilx = 45, ily = 144, irx = 280, iry = 145,
// Compute visibility polygon
poly = triangularExpansion(del, qx, qy, obstructs, ilx, ily, irx, iry);
for(const [lx, ly, rx, ry] of poly){
drawTriangle(lx, ly, qx, qy, rx, ry);
}
Install from NPM:
npm install @kninnug/trivis
Use in Node.js:
const triangularExpansion = require('@kninnug/trivis');
or as an ECMAScript/ES6 module:
import triangularExpansion from '@kninnug/trivis';
or in the browser:
<script src="node_modules/@kninnug/trivis/lib/TriVis.js"></script>
or minified:
<script src="node_modules/@kninnug/trivis/lib/TriVis.min.js"></script>
The TriVis library does not depend on Delaunator itself, but the input is
expected to be in the format that Delaunator outputs. The ES module variant
(TriVis.mjs) depends on robust-predicates
and containing-triangle,
but the CommonJS, browser, and minified versions (lib/TriVis.cjs,
lib/TriVis.js, and TriVis.min.js) come with these dependencies compiled in,
and can be used standalone. The (source) TypeScript version is in TriVis.ts.
Parameters:
del: The triangulation in the format that Delaunator outputs.qx,qy: The coordinates of the query point.obstructs: A callback that receives an edge id of the triangulation and must indicate whether it obstructs the view. Edges on the hull of the triangulation are always considered to be obstructing.ilx,ily,irx,iry: If given, i.e. notNaN, the coordinates of the left and right points restricting the viewing cone. The angles between these points and the query point should not be greater than 180°. If these arguments are not given, the visibility polygon is computed in all directions.
Return value:
An array of 4-element arrays, [lx, ly, rx, ry] with the coordinates of the
left- and right-hand side end-points of the segments that make up the visibility
polygon. Each triplet (lx, ly) (qx, qy) (rx, ry) forms a counter-clockwise
triangle that is entirely visible from the query point. The segments are also
ordered counter-clockwise around (qx, qy).
- Convert to TypeScript.
- Move built files to
lib/.
- Update dependencies.
- Move test files to separate repository.
- Initial version.
- The Triangular Expansion algorithm is adapted from Efficient Computation of Visibility Polygons, March 18, 2014, Francisc Bungiu, Michael Hemmer, John Hershberger, Kan Huang, Alexander Kröller.
- Uses Vladimir Agafonkin's robust-predicates port of Jonathan Shewchuk's Adaptive Precision Floating-Point Arithmetic and Fast Robust Predicates for Computational Geometry.
- Ray-segment intersection computation adapted from Nicky Case's Sight & Light tutorial.
- The example image and initial idea for this library were inspired by Amit Patel's article on 2D visibility.