Promesh is a modular, extensible resource designed for use in typical application development systems as well as distributed web-services environments. The project focus is providing a framework for robust, automated mesh generation, mesh quality analysis, adaptive mesh refinement, and data transfer between arbitrary meshes. Python bindings to the Promesh library can also be enabled.
Note: These installation guides have been tested for Ubuntu 18.04 and CentOS 7 systems.
Before Promesh can be installed, there are some dependencies and third
party libraries (TPLs) that must be acquired and installed. Some of these can be
obtained on Unix machines via apt install:
Ubuntu:
Start with:
apt update --fix-missing
- build-essential - GCC compiler. Alternatively, your favorite compiler.
- cmake - Alternatively, latest version also available from Kitware
- doxygen - Documentation requirement
- graphviz - Documentation requirement
- libgl1-mesa-dev - VTK requirement
- libxt-dev - VTK requirement
- zlib1g-dev - Netgen requirement
- tk-dev - OpenCASCADE requirement
- libfreetype6-dev - OpenCASCADE requirement
- mesacommon-dev - OpenCASCADE requirement
- libxmu-dev - OpenCASCADE requirement
- libxi-dev - OpenCASCADE requirement
Optional dependencies for additional functionality:
- cmake-curses-gui - CMake visualization tool
- libhdf5-dev - HDF5 requirement
- libpython3-dev - Required for Python bindings
- swig3.0 - Required for Python bindings
- libfltk1.3-dev - Gmsh requirement
- libmetis-dev - METIS requirement
CentOS:
Start with
yum update
yum upgrade
yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
yum groupinstall "Development Tools"
- centos-release-scl - Makes the developer toolset available
- devtoolset-7 - Provides the necessary compiler version.
- cmake3 - Provides the modern CMake required
- doxygen - Documentation requirement
- graphviz - Documentation requirement
- tk-devel - OpenCASCADE requirement
- mesa-libGL-devel - OpenCASCADE requirement
- libX11-devel - OpenCASCADE requirement
- libXmu-devel - OpenCASCADE requirement
- libXi-devel - OpenCASCADE requirement
- libXext-devel - OpenCASCADE requirement
Optional dependencies for additional functionality:
- hdf5-devel - HDF5 requirement
- python3-devel - Required for Python bindings
- swig3 - Required for Python bindings
- metis-devel - METIS requirement
Once devtoolset-7 is installed, ensure that the newer compiler is enabled with:
source /opt/rh/devtoolset-7/enable
Third party libraries must be downloaded individually and installed with certain options; instructions for each are provided. Note that as Promesh is in active development, the versions of these libraries that are used may change. For that reason, it is recommended to acquire the source code via GitLab/GitHub whenever possible, since that method allows for easy version updates.
Currently, the libraries are:
- VTK v8.2.0
- boost v1.45+
- OpenCASCADE v7.4.0
- Netgen v6.2.1910 (recommended)
- Kokkos v2+ (optional; if using GPU-enabled adaptive mesh refinement)
- Gmsh v4.5.1 (optional; GPL)
- OpenFOAM v2006 (optional; GPL)
Because these are third party, we cannot guarantee that the links below will be active or correct in perpetuity. To report a broken link, contact us.
Note that all the TPLs will be installed to the same directory. To streamline compilation and installation, an alias can be created:
export PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH=/path/to/desired/installation/path
VTK v8.2.0 is required. VTK provides the core mesh data structure upon which Promesh is based.
Source
VTK can be downloaded from the VTK GitLab. In a terminal, navigate to the directory that will contain the source code for each TPL then clone from the VTK GitLab via:
git clone https://gitlab.kitware.com/vtk/vtk.git
Enter the newly created VTK directory then check out the correct version:
cd vtk
git checkout v8.2.0
Alternatively, it can be obtained from the VTK website. It can be downloaded as a .tar or .zip. This archive can then be extracted to the desired source directory (not the installation path).
Build and Install
Build and install VTK by running the following commands:
mkdir build && cd build
| If your system is... | use the command... |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/vtk |
| CentOS | cmake3 .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/vtk |
make -j$(nproc)
make install
Boost is required for the base meshing capabilities of Promesh The file system included with Boost v1.45+ is required for mesh generation with OpenFOAM.
The best way to obtain Boost is to get it from your systems package manager, for example:
| If your system is... | use the command... |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | apt install libboost-all-dev |
| CentOS | yum install boost-devel |
If Boost is not available through your package manager, detailed installation instructions can be found here.
OpenCASCADE v7.4.0 is required. It provides the geometry kernel used in the Nucmesh and Packmesh modules.
Source
OpenCASCADE is available at the OpenCASCADE website. Note that you will have to make a free account to get access to the source code.
This archive can then be extracted to the desired source directory.
OpenCASCADE is also available through this GitHub page, which is an official mirror of the source code. In a terminal, navigate to the directory that will contain the source code for each TPL, then clone from the GitHub via:
git clone https://github.com/Open-Cascade-SAS/OCCT.git
Enter the newly created OCCT directory then check out the correct version:
cd OCCT
git checkout V7_4_0
Build and Install
Build and install OpenCASCADE by running the following commands:
mkdir build && cd build
| If your system is... | use the command... |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON |
| CentOS | cmake3 .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON |
make -j$(nproc)
make install
Netgen v6.2.1910 is strongly recommended. It provides enhanced mesh generation capabilities and is required for quad meshing.
Source
Netgen can be downloaded through its GitHub page. In a terminal, navigate to the directory that will contain the source code for each TPL, then clone from the GitHub via:
git clone https://github.com/NGSolve/netgen.git
Enter the newly created netgen directory then check out the correct version:
cd netgen
git checkout v6.2.1910
Build and Install
Note: OpenCASCADE must be installed prior to making and installing Netgen.
Build and install Netgen by running the following commands:
mkdir build && cd build
| If your system is... | use the command... |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/netgen -DUSE_GUI=OFF -DUSE_PYTHON=OFF -DUSE_SUPERBUILD=OFF -DUSE_OCC=ON -DOCC_INCLUDE_DIR=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade/include/opencascade -DOCC_LIBRARY=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade/lib/libTKernel.so |
| CentOS | cmake3 .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/netgen -DUSE_GUI=OFF -DUSE_PYTHON=OFF -DUSE_SUPERBUILD=OFF -DUSE_OCC=ON -DOCC_INCLUDE_DIR=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade/include/opencascade -DOCC_LIBRARY=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade/lib/libTKernel.so |
make -j$(nproc)
make install
Kokkos v2 is required for GPU-enabled mesh adaptation with Omega_h.
Source
Kokkos can be downloaded through its GitHub page. In a terminal, navigate to the directory that will contain the source code for each TPL, then clone from the GitHub via:
git clone https://github.com/kokkos/kokkos.git
Enter the newly created kokkos directory.
cd kokkos
Build and Install
Build and install Kokkos with CUDA backend using the following:
mkdir build && cd build
| If your system is... | use the command... |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | cmake ${KOKKOS_SRC} -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=${KOKKOS_SRC}/bin/nvcc_wrapper -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/kokkos -DCMAKE_POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE=ON -DCKOKKOS_ARCH=${CUDA_ARCH_CC} -DKOKKOS_ENABLE_CUDA=ON -DKOKKOS_ENABLE_CUDA_LAMBDA=ON -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON |
| CentOS | cmake3 ${KOKKOS_SRC} -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=${KOKKOS_SRC}/bin/nvcc_wrapper -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/kokkos -DCMAKE_POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE=ON -DCKOKKOS_ARCH=${CUDA_ARCH_CC} -DKOKKOS_ENABLE_CUDA=ON -DKOKKOS_ENABLE_CUDA_LAMBDA=ON -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON |
make install
where ${KOKKOS_SRC} is the source directory and ${CUDA_ARCH_CC} refers to
the architecture and compute capability of your GPU, from the list
Kepler30 Kepler32 Kepler35 Kepler37 Maxwell50 Maxwell52 Maxwell53 Pascal60 Pascal61 Volta70 Volta72.
Note: During the building and installation of Promesh, the user will need to provide the installation path for this library using the
-DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATHflag along with other dependencies of Promesh.
-DENABLE_MLAMR=ON
-DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH="\
${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade;\
${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/gmsh;\
${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/vtk;\
${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/netgen;
Gmsh v4.5.1 is optional, and it is important to note that enabling it will result in a GPL, rather than LGPL software.
Source
Gmsh can be downloaded through its GitLab page. In a terminal, navigate to the directory that will contain the source code for each TPL, then clone from the GitLab via:
git clone https://gitlab.onelab.info/gmsh/gmsh.git
Enter the newly created gmsh directory then check out the correct version:
cd gmsh
git checkout gmsh_4_5_1
Build and Install
Note: OpenCASCADE must be installed prior to making and installing Gmsh.
Build and install Gmsh by running the following commands:
mkdir build && cd build
| If your system is... | use the command... |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/gmsh -DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade -DENABLE_BUILD_LIB=OFF -DENABLE_BUILD_SHARED=ON -DENABLE_PRIVATE_API=ON -DDEFAULT=ON -DENABLE_CGNS=OFF -DENABLE_NETGEN=OFF -DENABLE_HXT=ON -DENABLE_FLTK=ON -DENABLE_BUILD_DYNAMIC=ON -DENABLE_OPENMP=ON |
| CentOS | cmake3 .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/gmsh -DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade -DENABLE_BUILD_LIB=OFF -DENABLE_BUILD_SHARED=ON -DENABLE_PRIVATE_API=ON -DDEFAULT=ON -DENABLE_CGNS=OFF -DENABLE_NETGEN=OFF -DENABLE_HXT=ON -DENABLE_FLTK=ON -DENABLE_BUILD_DYNAMIC=ON -DENABLE_OPENMP=ON |
make -j$(nproc)
make install
OpenFOAM v2006 is optional, and it is important to note that enabling it will result in a GPL, rather than LGPL software. OpenFOAM provides enhanced meshing support, including snappyHexMesh, cfMesh, and blockMesh.
The easiest way to install OpenFOAM is via the precompiled system package, with instructions available here. To install on Ubuntu, execute the following commands:
curl -s https://dl.openfoam.com/add-debian-repo.sh | sudo bash
apt-get install openfoam2006-default
For CentOS:
yum install dnf-plugins-core
yum config-manager --set-enabled PowerTools
yum install epel-release
dnf copr enable openfoam/openfoam
yum install openfoam2006
Once all the third party libraries have been installed, Promesh can be downloaded and installed.
To acquire Promesh, you can download it from Illinois Rocstar's GitHub or clone it with the following command:
git clone https://github.com/IllinoisRocstar/Nemosys.git
Warning: The Promesh installation path (
PROMESH_INSTALL_PATH) should not be the same as the source location (PROMESH_PROJECT_PATH). It is however acceptable that Promesh and its dependencies be installed in the same directory, such thatPROMESH_INSTALL_PATHleads to the same directory asPROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH
Set the Promesh installation path:
export PROMESH_INSTALL_PATH=/full/path/to/Promesh/install
Now, we can compile the Promesh library, create its Python bindings, and build other utilities. Note that the current name for the Promesh project as installed from GitHub is Nemosys, so the PROMESH_PROJECT_PATH should be set to the directory into which Nemosys was cloned above:
cd ${PROMESH_PROJECT_PATH}
mkdir build && cd build
The CMake commad must include a prefix path that indicates the location of the dependencies. The command below can be altered to include or exclude TPLs as needed.
See the build options for more information on the available CMake options.
| If your system is... | use the command... |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | cmake .. -DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH="${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade;${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/vtk;${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/netgen" -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_INSTALL_PATH}/Promesh -DENABLE_TESTING=ON -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release |
| CentOS | cmake3 .. -DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH="${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade;${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/vtk;${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/netgen" -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PROMESH_INSTALL_PATH}/Promesh -DENABLE_TESTING=ON -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release |
To complete the installation:
make -j$(nproc)
make install
Executing the commands above will build all libraries, executables, and
bindings. The libraries are installed in $PROMESH_INSTALL_PATH/lib.
Executables are installed in $PROMESH_INSTALL_PATH/bin. If Python
bindings are enabled, the pyNemosys module is installed for the user. The
pyNemosys module can be imported in Python as import pyNemosys. The build
configuration can be modified through the CMake Curses interface, ccmake, or
by passing the command line options to cmake.
The following table contains all available CMake options to configure Promesh functionality. Any necessary third-party library for each option is listed in the notes section.
For LGPL licensed software:
| Option name | Option description | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_CONSRV_SURFACE_TRANSFER |
Enable conservative surface transfer | OFF | Requires IMPACT |
ENABLE_CONSRV_VOLUME_TRANSFER |
Enable conservative volume transfer | OFF | Requires MPI |
ENABLE_DOCUMENTATION |
Create and install the HTML based API documentation | ON | Requires Doxygen |
ENABLE_HDF5 |
Enable HDF5 extensions | OFF | Requires HDF5 |
ENABLE_METIS |
Enable Metis partitioner | OFF | Requires METIS |
ENABLE_MLAMR |
Enable machine learning based AMR | OFF | Requires frugally-deep library |
ENABLE_MPI |
Enable MPI support | OFF | Requires MPI compiler |
ENABLE_NETGEN |
Enable Netgen meshing engine | ON | Requires Netgen |
ENABLE_OMEGAH_CUDA |
Enable GPU for Omega_h | OFF | Requires Kokkos |
ENABLE_OPENCASCADE |
Enable OpenCASACADE support | ON | Requires OpenCASCADE (OCCT) |
ENABLE_OPENMP |
Enable OpenMP | ON | |
ENABLE_PYTHON_BINDINGS |
Enable Python bindings | OFF | Requires Python 3 and SWIG 3 |
ENABLE_TESTING |
Enable testing | ON |
For GPL licensed software, additional build options can be included:
| Option name | Option description | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_CFMSH |
Enable cfMesh Meshing engine | OFF | Requires OpenFOAM, requires that ENABLE_GPL is ON |
ENABLE_GMSH |
Enable Gmsh | OFF | Requires that ENABLE_GPL is ON |
ENABLE_GPL |
Allow linking against GPL libraries | OFF | Will make the combined project fall under GPL license requirements |
Enabling cfMesh
cfMesh is an open-source meshing engine implemented on top of OpenFOAM.
Promesh comes with a fully integrated cfMesh-based meshing module. To enable
the capability, Promesh should be compiled with ENABLE_CFMSH=ON.
Note: cfMesh depends on OpenFOAM, so before starting the compile process make sure to load OpenFOAM environment variables. Depending on the version, OpenFOAM can be loaded by sourcing the bashrc, or cshrc scripts provided in the
OpenFoam-x.y/etc/. On a default installation, this can be done with. /usr/lib/openfoam/openfoam2006/etc/bashrc
Refer to the OpenFOAM documentation for further instructions. After the OpenFOAM environment is loaded, enable a cfMesh build by adding this line to the cmake command:
-DENABLE_CFMSH=ON -DENABLE_GPL=ON
Enabling CUDA for Omega_h
Omega_h can be built with CUDA support using the Kokkos backend, assuming Kokkos is built with CUDA support. Currently, only Kokkos version 2 is supported. To enable this, make sure that the following flag is set:
-DENABLE_OMEGAH_CUDA=ON
and that CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH (or $PATH) contains
${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/kokkos/lib/CMake. Note that both Kokkos and
Promesh must be built as shared libraries (-DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON).
From the build directory, execute the following command to test the installation:
make test
This will run all tests that are applicable to your installation of Promesh.
Depending on how many modules are enabled, this may take anywhere from seconds to
several minutes. Specific tests can be run using ctest -R <testname>, for example:
ctest -R nucMeshTest
To get a list of possible test names, use:
ctest -N
Using Promesh requires setting the environment. In most cases, this will be
done by setting the LD_LIBRARY_PATH in the terminal from which Promesh cases
will be run, via a command like the one below:
export PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH=/path/to/dependencies/installation/path
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/vtk/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/opencascade/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/netgen/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
For the GPL licensed version of Promesh, additional library paths must be set for Gmsh and OpenFOAM:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${PROMESH_DEPS_INSTALL_PATH}/gmsh/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/lib/openfoam/openfoam2006/platforms/linux64GccDPInt32Opt/lib/openmpi-system:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
The OpenFOAM environment must also be set:
. /usr/lib/openfoam/openfoam2006/etc/bashrc
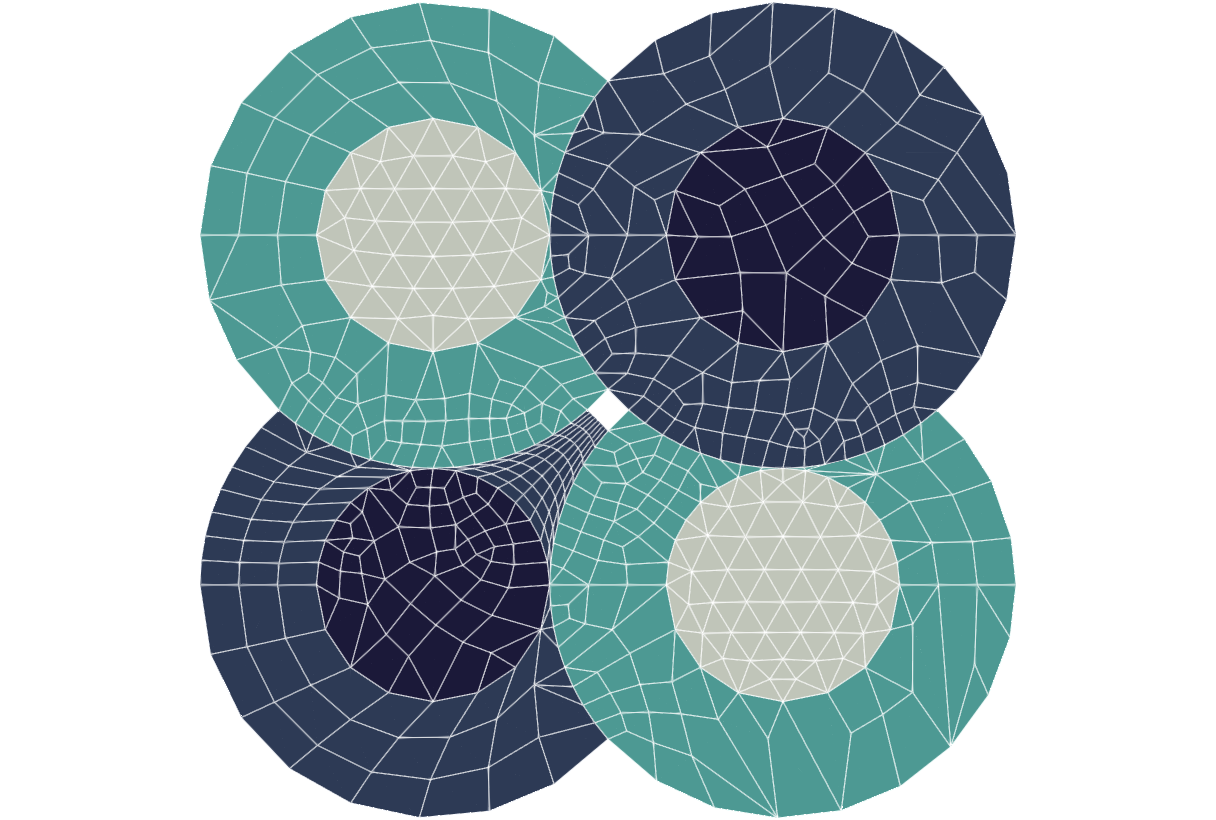
The simplest method to run a Promesh program is to start with a JSON input file. A sample one is provided below:
{
"Program Type": "NucMesh Generation",
"Mesh File Options": {
"Output Mesh File": "test.vtu"
},
"NucMesh Options": {
"Shapes": [
{
"Type": "Rectangular Array",
"Grid Distance": [1.5, 1.5],
"Pattern": [[0, 1],[1, 0]],
"Shapes": [
{
"Type": "Circles",
"Rings": [
{
"Radius": 0.5,
"Mesh": {"Type": "T"},
"Material": "A"
},
{
"Radius": 1.0,
"Mesh": {
"Type": "S",
"Number of Elems": [3, 8]
},
"Material": "B"
}
]
},
{
"Type": "Circles",
"Rings": [
{
"Radius": 0.5,
"Mesh": {"Type": "Q"},
"Material": "C"
},
{
"Radius": 1.0,
"Mesh": {
"Type": "S",
"Number of Elems": [3, 8]
},
"Material": "D"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}To run this program, copy and paste the input above into your favorite text editor
and save it in the build folder as test_run.json. Within a terminal, navigate
to the build folder and enter:
./nemosysRun test_run.json
This should generate the following printout in the terminal:
srvBase constructed
Gmsh initialized
geoMeshBase constructed
srvBase destructed
geoMeshBase constructed
vtkGeoMesh constructed
vtkGeoMesh destructed
geoMeshBase destructed
geoMeshBase destructed
Gmsh finalizedA test.vtu file should appear within the build directory. This can be visualized
with Paraview or your visualization software of choice:
To report errors, broken links, or other feedback, contact the Promesh team at promesh@illinoisrocstar.com or open an issue in GitHub at https://github.com/IllinoisRocstar/Nemosys/issues