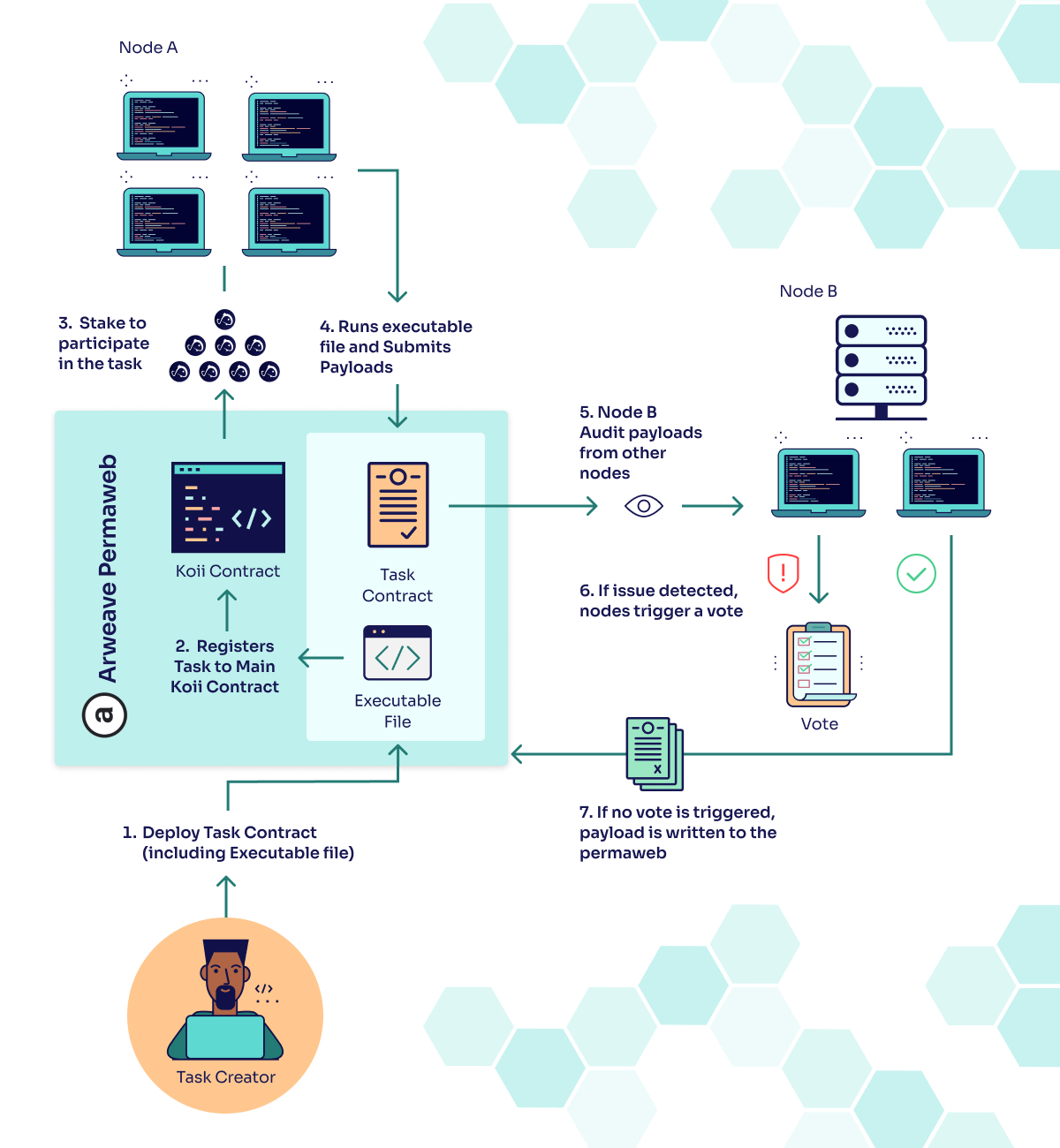
A Koii task is a way to create tasks that solve some computational problem to earn KOII as a reward. Koii tasks are created as an executable bundle that is first deployed to a decentralized network, and can then be run on Koii nodes.
A Koii task is market-based software that is deployed on the Arweave blockchain. Tasks run on Koii nodes to perform a repeatable and auditable process like
- Verifying Proofs
- Web scraping
- Indexing decentralized storage
- Proxy Services
- Message passing
Each Koii Task receives it's own namespace and runtime on a node, including
- a customizeable REST API (powered by express.js)
- a Redis cache
- external interactions via Axios
- a filesystem store
- APIs to sign and encrypt payloads using either RSA or ECDSA key pairs
Nodes can run as many tasks in parallel as they want, and receive rewards based on the their ability to provide competitive results that pass verification by other nodes. Desktop clients will be released in the future to provide better control for CPU and i/o management for different tasks.
KOII tasks consists of two vital parts
- A smart contract
Executable.js
This smart contract will have all the state data related to that particular KOII task. The smart contract consist of an
- initial state which acts a starting point to your KOII tasks state.
- index.js Provides all necessary handles for your smart contract
Each contract is first stored on decentralized storage, and then registered to the Koii network by setting a bounty in the main Koii contract. This introduces the offering into the marketplace, and provides a reward that will be unlocked when the task is successfully completed.
Each executable file is a self-contained web-server, and runs tasks as if it were deployed to a hosting solution like Heroku or AWS Lambda. Each task has access to a number of supported toolkits, which can be initialized using the setup() function, and implemented in the execute() function.
The code for KOII task should be written inside executable.js.
This file has access to a namespace object via dependency injection which has several useful APIs including:
koi-sdksmartWeaveredisfilesystem(fs)express
Here are the detail of each component of namespace:
The Koii SDK is accessible via tools object, Please refer to the official docs here for supported interactions and key pair management tips.
SmartWeave is used to interact with other smart contracts and Koii Tasks stored on Arweave and is accessible via the smartWeave object.
For more information on Arweave Smart contract visit SmartWeave
Each Koii task namespace also has a redis wrapper for high-speed term key:value storage. Redis must be installed in order to use this wrapper. Each Task has its own namespaceId prepended to all the keys in redis.
This API exposes two methods in order to communicate with Redis.
redisSet(key,value)redisGet(key)
For example if you call redisSet("Hello","world") you can get it by calling redisGet("Hello") but behind the scenes it is actually adding namespace prefix with the key like so
hellowill be stored as09ea3bcd43helloThis is done to isolate the KOII tasks data from others.
The KOII task namespace also has an fs module exposed to it.
await namespace.fs("readFile", filename, options);The first parameter to namespace.fs is the function name from fs.promise module followed by the parameters that the function expects and returns a promise.
In some types of KOII task you want to expose some endpoint in order to receive data from outside world. As an example, the daily Koii Attention Tracking Task requires nodes to receive the PoRT (Proofs of Real Traffic) from the end user, which can be implemented in only one line.
// Format: namespace.express(method, path, callback);
// Example
namespace.express("post", "/submit-port", submitPort);This file consist of two important methods setup() and execute() which are called by the node while running the KOII task.
- The
setup()method should be used to register endpoints on the webserver Example - The
execute()method is the root function which will be called by the node as it processes the Task Example - A third (optional) method, which is not executed by the node unless programmed inside of
execute()is the Audit function, which can be used to define a slashing behaviour for bad actors. Example
The easiest way to get started is to copy this repository exactly, which will let you use the built-in commands.
yarn deploy [contract]
Examples:
yarn deploy koiyarn deploy attention
yarn deploy_executable
yarn build
node test/attention.test.js path/to/wallet.jsonnode test/koi.test.js
yarn build
yarn execute attention [task_contract]yarn execute attention [task_contract] serviceto test bundler mode