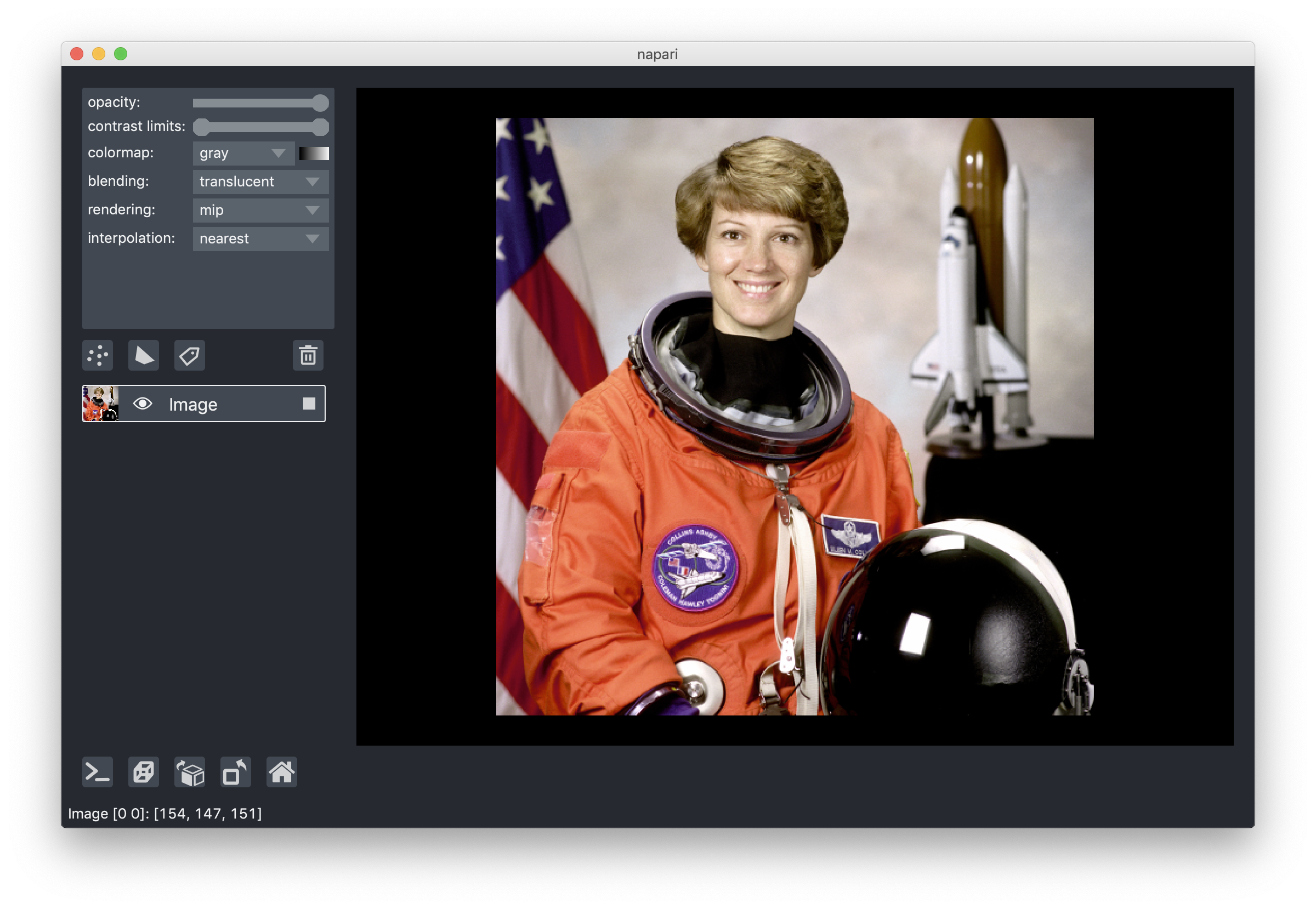
napari is a fast, interactive, multi-dimensional image viewer for Python. It's designed for browsing, annotating, and analyzing large multi-dimensional images. It's built on top of Qt (for the GUI), vispy (for performant GPU-based rendering), and the scientific Python stack (numpy, scipy).
We're developing napari in the open! But the project is in an alpha stage, and there will still likely be breaking changes with each release. You can follow progress on this repository, test out new versions as we release them, and contribute ideas and code.
We're working on tutorials, but you can also quickly get started by looking below.
If you want to contribute back to napari codebase, you need to install from source code: see the from source section.
If you do not want to use napari as python code and only use it as GUI app, the bundled app is the easiest way to install. This is also the only method that does not require python knowledge to work with napari, see the from bundled app section.
If you are using napari from Python to programmatically interact with the app, you can install via pip, conda-forge, or from source. We recommend that you use conda to help manage the virtual environment. Otherwise you may see compilation issues that are specific to your particular machine, which is difficult for us to debug.
napari can be installed on most macOS, Linux, and Windows systems with Python 3.7, 3.8, and 3.9 using pip. However, for Windows users, you need to preinstall Microsoft Visual C++ Build Tools in order to install VisPy (one of the packages we depend on) on Windows machines.
The simplest command to install with pip is:
pip install "napari[all]"(See Specifying a GUI Backend below for an explanation of the [all] notation.)
Note: while not strictly required, it is highly recommended to install
napari into a clean virtual environment using an environment manager like
conda or
venv. For example, with conda:
conda create -y -n napari-env python=3.8
conda activate napari-env
pip install "napari[all]"To clone the repository locally and install in editable mode use
git clone https://github.com/napari/napari.git
cd napari
pip install -e ".[all]"
# or, to install in editable mode AND grab all of the developer tools
# (this is required if you want to contribute code back to napari)
pip install -r requirements.txtFor more information or troubleshooting see our installation tutorial
ℹ️ Specifying a GUI Backend
napari needs a library called Qt to run its user interface (UI). In Python, there are two alternative libraries to run this, called PyQt5 and PySide2. By default, we don't choose for you, and simply running
pip install napariwill not install either. You might already have one of them installed in your environment, thanks to other scientific packages such as Spyder or matplotlib. If neither is available, running napari will result in an error message asking you to install one of them.Running
pip install "napari[all]"will install the default framework – currently PyQt5, but this could change in the future.To install napari with a specific framework, you can use:
pip install "napari[pyqt5]" # for PyQt5 # OR pip install "napari[pyside2]" # for PySide2
(The examples below require the scikit-image package to run. We just use data samples from this package for demonstration purposes. If you change the examples to use your own dataset, you may not need to install this package.)
From inside an IPython shell, you can open up an interactive viewer by calling
from skimage import data
import napari
viewer = napari.view_image(data.astronaut(), rgb=True)To use napari from inside a script, use napari.run():
from skimage import data
import napari
viewer = napari.view_image(data.astronaut(), rgb=True)
napari.run() # start the "event loop" and show the viewerCheck out the scripts in our examples folder to see some of the functionality we're developing!
napari supports six main different layer types, Image, Labels, Points, Vectors, Shapes, and Surface, each corresponding to a different data type, visualization, and interactivity. You can add multiple layers of different types into the viewer and then start working with them, adjusting their properties.
All our layer types support n-dimensional data and the viewer provides the ability to quickly browse and visualize either 2D or 3D slices of the data.
napari also supports bidirectional communication between the viewer and the Python kernel, which is especially useful when launching from jupyter notebooks or when using our built-in console. Using the console allows you to interactively load and save data from the viewer and control all the features of the viewer programmatically.
You can extend napari using custom shortcuts, key bindings, and mouse functions.
For more details on how to use napari checkout our tutorials. These are still a work in progress, but we'll be updating them regularly.
For more information about our plans for napari you can read our mission and values statement, which includes more details on our vision for supporting a plugin ecosystem around napari.
You can see details of the project roadmap here.
Contributions are encouraged! Please read our contributing guide to get started. Given that we're in an early stage, you may want to reach out on our Github Issues before jumping in.
napari has a Code of Conduct that should be honored by everyone who participates in the napari community.
You can learn more about how the napari project is organized and managed from our governance model, which includes information about, and ways to contact, the @napari/steering-council and @napari/core-devs.
If you find napari useful please cite this repository using its DOI as follows:
napari contributors (2019). napari: a multi-dimensional image viewer for python. doi:10.5281/zenodo.3555620
Note this DOI will resolve to all versions of napari. To cite a specific version please find the DOI of that version on our zenodo page. The DOI of the latest version is in the badge at the top of this page.
We're a community partner on the image.sc forum and all help and support requests should be posted on the forum with the tag napari. We look forward to interacting with you there.
Bug reports should be made on our github issues using the bug report template. If you think something isn't working, don't hesitate to reach out - it is probably us and not you!