CloudQuery SharePoint Source community plugin: synchronize SharePoint data to any database destination at ease.
- Lists and Document Libraries data fetching
- Content Types based rollup
- User Information List data fetching
- Search Query data source
- User Profiles data source
- Managed Metadata data source
- SharePoint Online support
- SharePoint On-Premise support
- Fast and potentially blazin fast with spsync
Vote for a feature you need or create a PR.
kind: source
spec:
name: "sharepoint"
registry: "github"
path: "koltyakov/sharepoint"
version: "v2.1.0" # provide the latest version
destinations: ["postgresql"] # the list of used destinations
tables: ["*"] # required field, a list of tables to sync
spec:
# Spec is mandatory
# This plugin follows idealogy of explicit configuration
# we can change this in future based on the feedbackSince v1.8.0, the plugin ships with configuration utility spctl.
It can be downloaded from releases: spctl_[OS]_[ARCH].zip.
On a macOS System Settings / Security allowance is needed for it to run.
# sharepoint.yml
# ...
spec:
auth:
strategy: "azurecert"
creds:
siteUrl: "https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/cloudquery"
tenantId: "e1990a0a-dcf7-4b71-8b96-2a53c7e323e0"
clientId: "2a53c7e323e0-e1990a0a-dcf7-4b71-8b96"
certPath: "/path/to/cert.pfx"
certPass: "certpass"creds options are unique for different auth strategies. See more details in Auth strategies.
We recomment Azure AD (azurecert) or Add-In (addin) auth for production scenarios for SharePoint Online. Yet, other auth strategies are also available, e.g. saml, device. Some of the APIs could require using user contextual auth, for instance, Search API can't work without a user context.
SharePoint On-Premise auth is also supported, based on your farm configuration you can use: ntlm, adfs to name a few.
Need to hands on quickly without configuring Azure Apps or Addins or asking an admin to turn on app password? Try On-Demand auth:
# sharepoint.yml
# ...
spec:
auth:
strategy: "ondemand"
creds:
siteUrl: "https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/cloudquery"A single source yml configuration assumes fetching data from a single SharePoint site. If you need to fetch data from multiple sites, you can create multiple source configurations. Alternatevely, search based data fetching can be used for rollup scenarios grabbing data from as many sites as needed.
# sharepoint.yml
# ...
spec:
# A map of URIs with the list configurations
# If no lists are provided, nothing will be fetched
lists:
# List or Document library URI - a relative path without a site URL
# Can be checker in the browser URL (exclude site URL and view page path)
Lists/ListEntityName:
# REST `$select` OData modificator, fields entity properties array
# Wildcard selectors `*` are intentionally not supported
# If not provided, only default fields will be fetched (ID, Created, AuthorId, Modified, EditorId)
select:
- Title
- Author/Title
# Fields mapping via `->` arrow alias, when a specific field name is considered
- EditorId -> editor
# REST `$expand` OData modificator, fields entity properties array
# When expanding an entity use selection of a nested entity property(s)
# Optional, and in most of the cases we recommend to avoid it and
# prefer to map nested entities to the separate tables
expand:
- Author
# REST `$filter` OData modificator, a filter string
# Don't use filters for large entities which potentially
# can return more than 5000 in a view
# such filtering will throttle no matter top limit is set
filter: "Active eq true"
# Optional, an alias for the table name
# Don't map different lists to the same table - such scenario is not supported
alias: "my_table"
Lists/AnotherList:
select:
- Title
# content_types: # see more below
# mmd: # see more below
# search: # see more below
# profiles: # see more belowContent Types based rollup allows to fetch data from multiple lists or document libraries based on the Content Type configuration.
All items based on the parent content type are fetched from all lists and subwebs below the context site URL.
# sharepoint.yml
# ...
spec:
# A map of Content Types with the rollup configurations
content_types:
# Base Content Type name or ID (e.g. "0x0101009D1CB255D" must be in quotes)
Task:
# REST `$select` OData modificator, fields entity properties array
select:
- Title
- AssignedTo/Title
# REST `$expand` OData modificator, fields entity properties array
expand:
- AssignedTo
# Optional, an alias for the table name
# the name of the alias is prefixed with `rollup_`
alias: "task"Quite often you'd need getting User Information List for Author and Editor fields joining. This is a special case, and we have a dedicated configuration for it.
# sharepoint.yml
# ...
spec:
lists:
_catalogs/users: # UIL list URI, source of People Picker lookup
select:
- Title
- FirstName
- LastName
- JobTitle
- Department
- EMail
- Deleted
filter: "UserName ne null"
alias: "user"Document listariries are the same as lists in SharePoint, but with a few differences. And it's common to expand File entity to get file metadata.
Also, a document library URI usually doesn't contain Lists/ prefix.
# sharepoint.yml
# ...
spec:
lists:
Shared Documents:
select:
- FileLeafRef
- FileRef
- FileDirRef
- File/Length
expand:
- File
alias: "document"To configure managed metadata fetching, you need to provide a term set ID (GUID) and an optional alias for the table name.
# sharepoint.yml
# ...
spec:
# A map of MMD term sets IDs (GUIDs)
mmd:
# Term set ID
8ed8c9ea-7052-4c1d-a4d7-b9c10bffea6f:
# Optional, an alias for the table name
# the name of the alias is prefixed with `mmd_`
alias: "department"User Profiles are fetched via Search API, so the search should be configured in the farm.
Search drived data source can be user only with user associated authentication strategies. E.g. it won't work with addin strategy.
# sharepoint.yml
# ...
spec:
# Include `profiles` property to fetch user profiles
# Object structure for extensibility (adding custom properties)
profiles:
enabled: true
# Optional, an alias for the table name
alias: "profile"Search drived data source can be user only with user associated authentication strategies. E.g. it won't work with addin strategy.
# sharepoint.yml
# ...
spec:
# A map of search queries
search:
# Query name (whatever you want to name a resulted table)
# Should be unique within other compound aliases
documents:
# Required, search query text
# https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/dev/general-development/sharepoint-search-rest-api-overview#querytext-parameter
query_text: "*"
# Optional, the managed properties to return in the search results
# https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/dev/general-development/sharepoint-search-rest-api-overview#selectproperties
# By defining the list of properties, you also tell the plugin
# to have correcponding columns in the table
select_properties:
- Size
- Title
- ContentTypeId
- IsDocument
- FileType
- DocId
- SPWebUrl
- SiteId
- WebId
- ListId
# Optional, whether duplicate items are removed from the results
# https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/dev/general-development/sharepoint-search-rest-api-overview#trimduplicates
trim_duplicates: true
profiles:
query_text: "*",
trim_duplicates: false
# The result source ID to use for executing the search query.
# https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/dev/general-development/sharepoint-search-rest-api-overview#sourceid
source_id: "b09a7990-05ea-4af9-81ef-edfab16c4e31"Follow quickstart instructions.
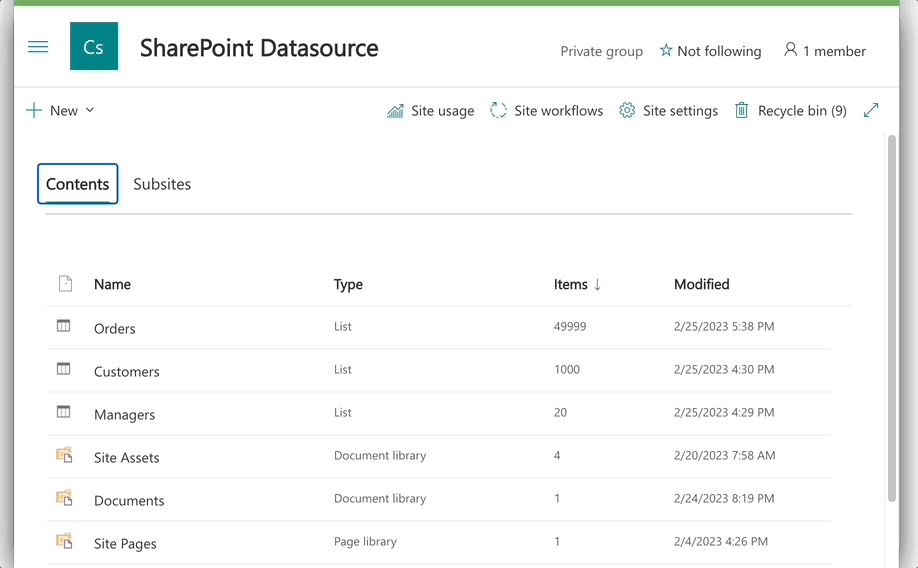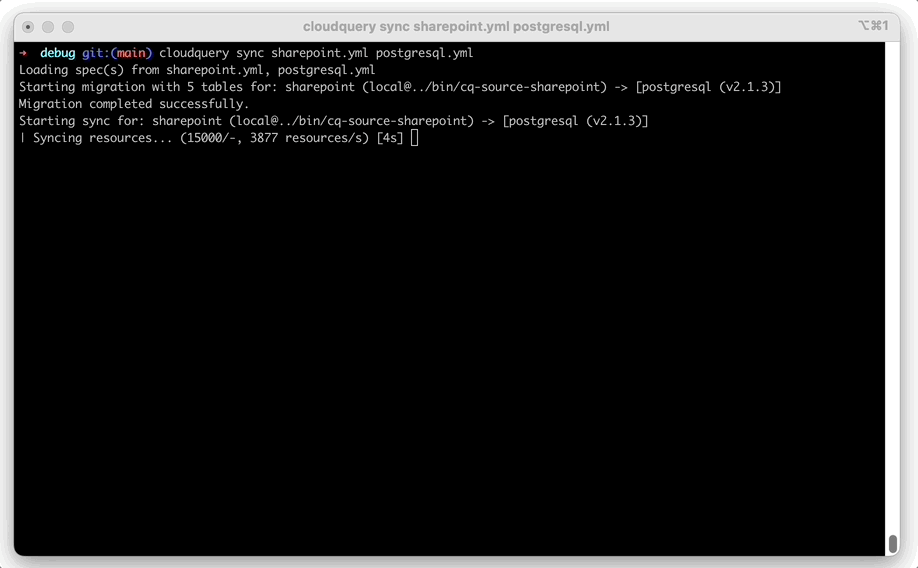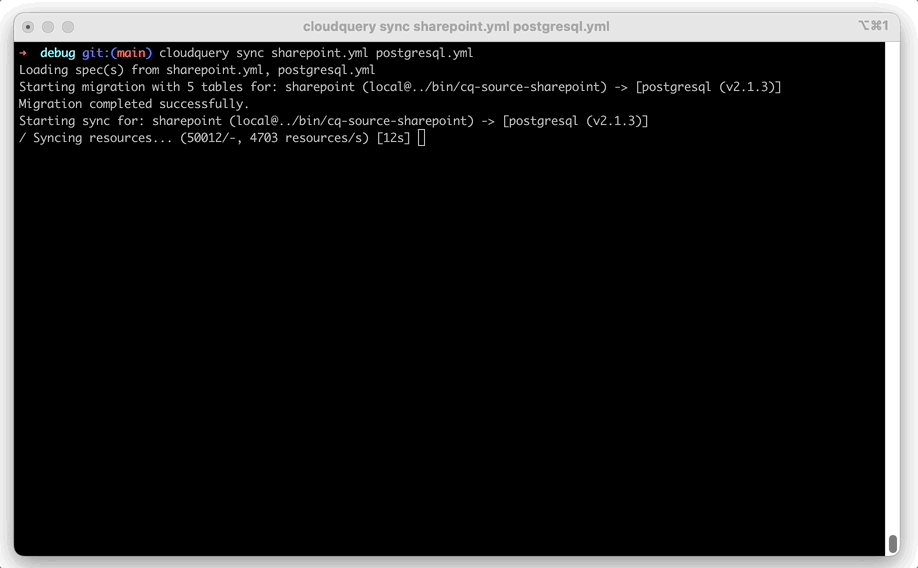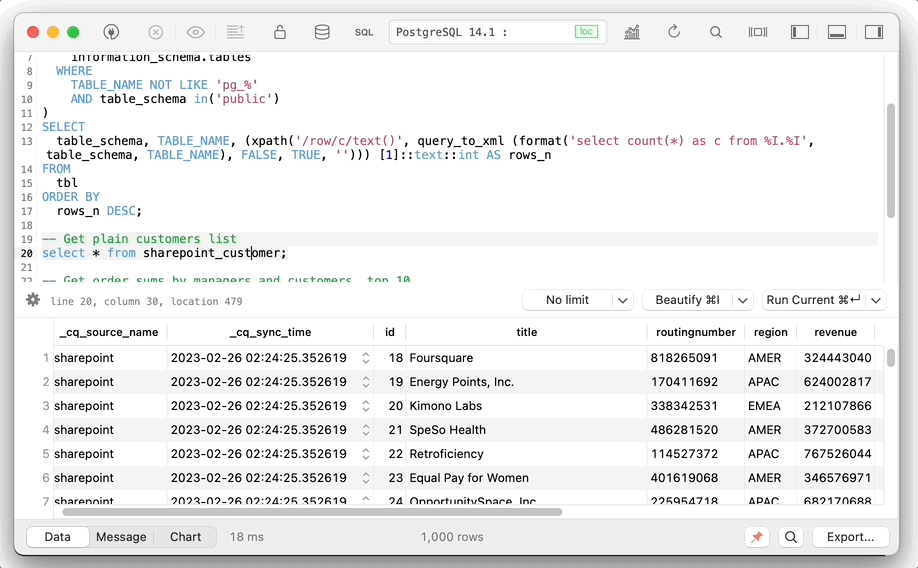
Provision and seed some sample data. See more. Which satisfy the schema below.
# .env or env vars export
# See more details in https://go.spflow.com/auth/strategies
SP_SITE_URL=https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/siteor use "ondemand" auth.
# sharepoint.yml
kind: source
spec:
name: "sharepoint"
registry: "github"
path: "koltyakov/sharepoint"
version: "v2.1.0" # https://github.com/koltyakov/cq-source-sharepoint/releases
destinations: ["sqlite"]
tables: ["*"]
spec:
auth:
strategy: "ondemand"
creds:
siteUrl: ${SP_SITE_URL}
# align creds with the used strategy
lists:
_catalogs/users:
select:
- Title
- FirstName
- LastName
- JobTitle
- Department
- EMail
- Deleted
filter: "UserName ne null"
alias: "user"
Shared Documents:
select:
- FileLeafRef
- FileRef
- FileDirRef
- Author/Title
- File/Length
expand:
- Author
- File
alias: "document"
Lists/Managers:
select:
- Title
alias: "manager"
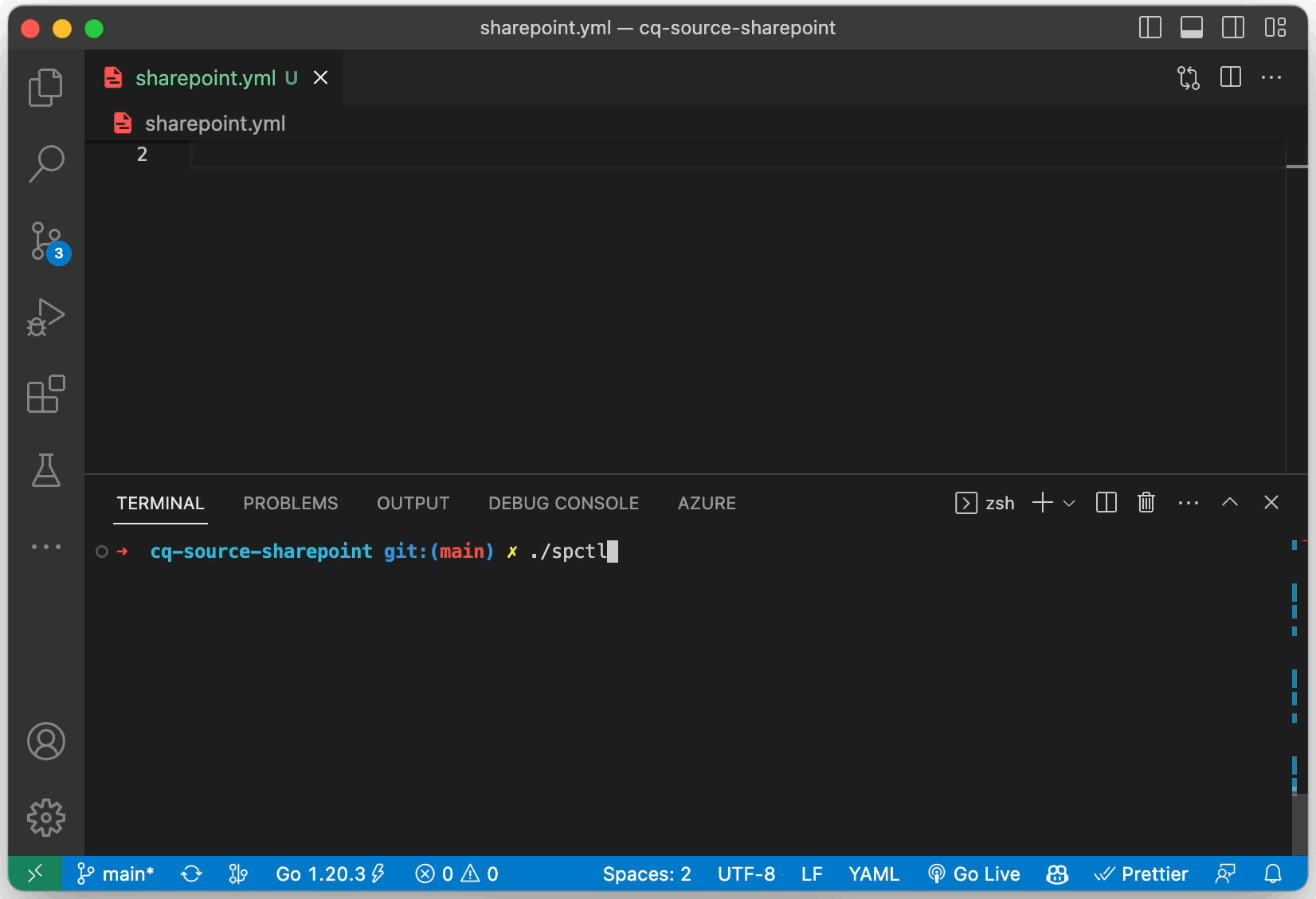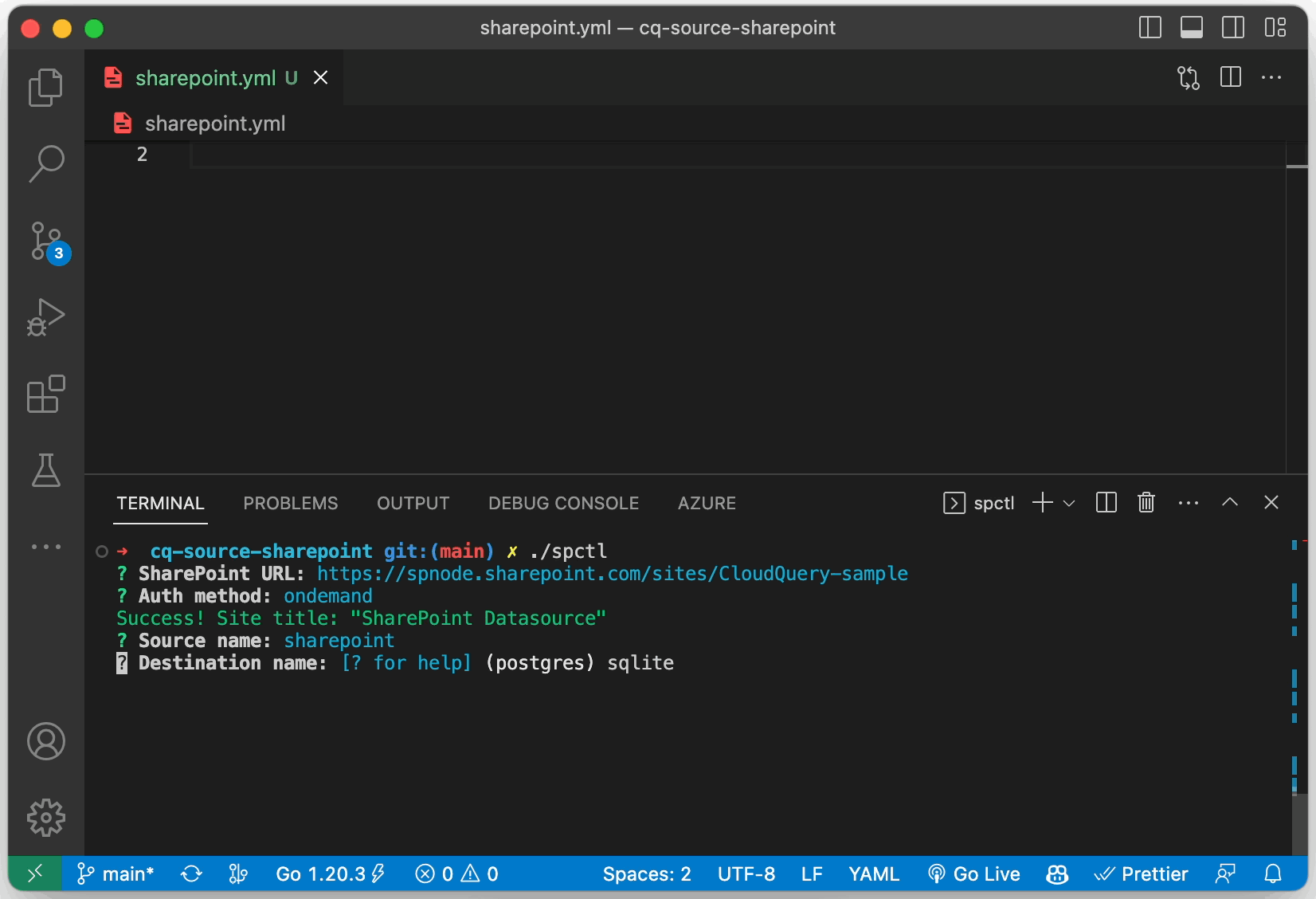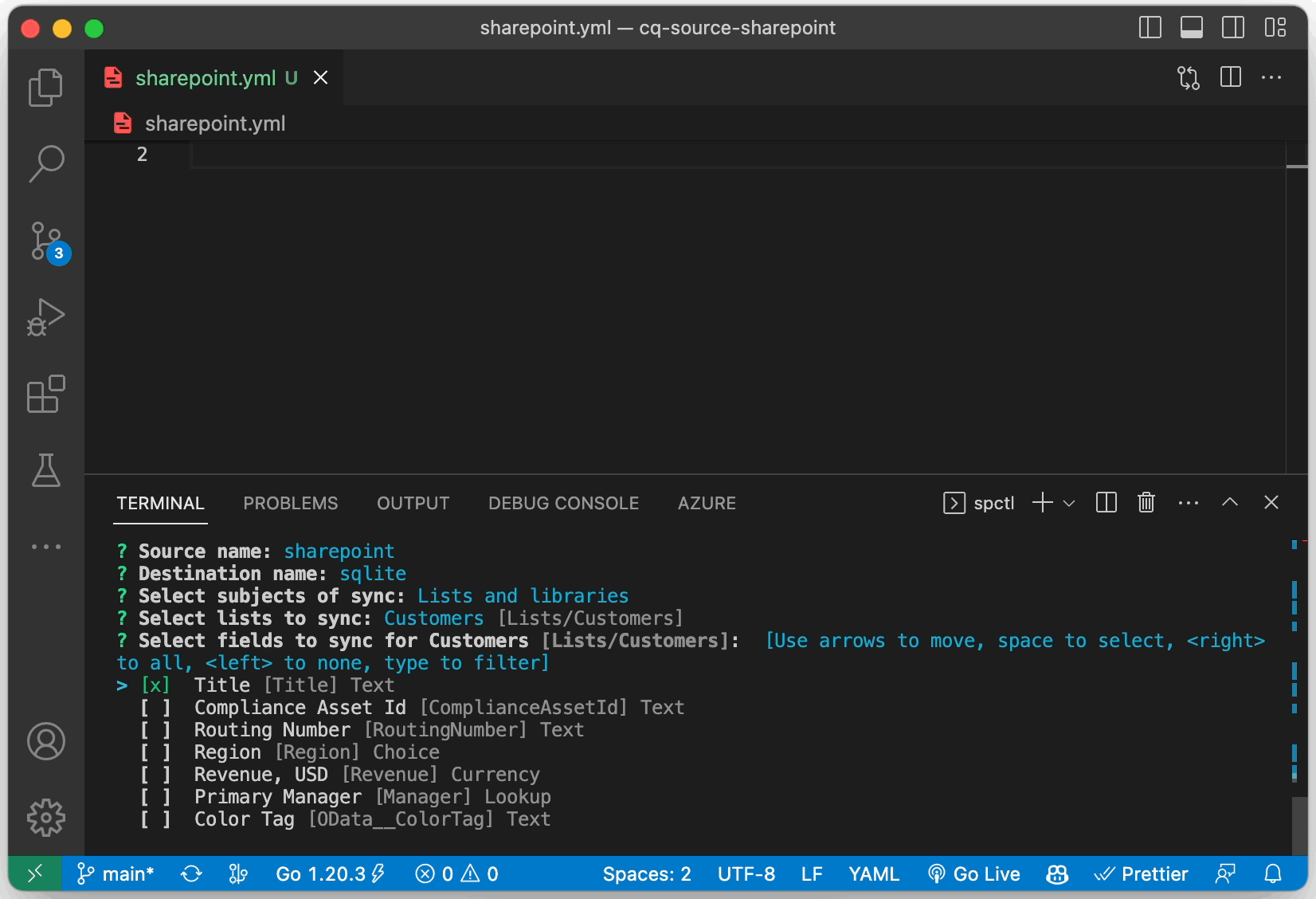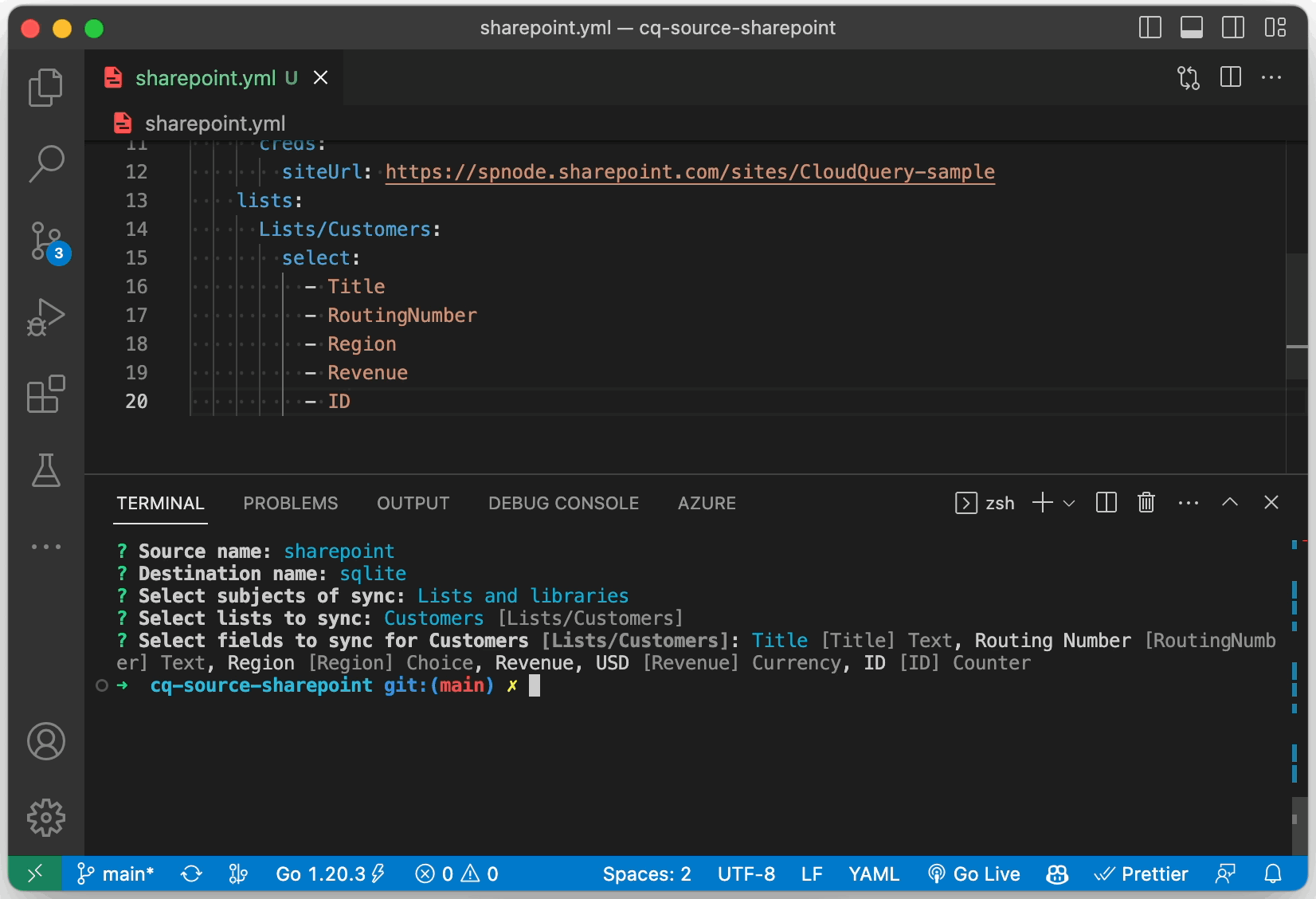
Lists/Customers:
select:
- Title
- RoutingNumber
- Region
- Revenue
- ManagerId
alias: "customer"
Lists/Orders:
select:
- Title
- CustomerId
- OrderNumber
- OrderDate
- Total
alias: "order"For the sake of simplicity, we'll use SQLite destination.
# sqlite.yml
kind: destination
spec:
name: sqlite
path: cloudquery/sqlite
version: "v2.4.15"
spec:
connection_string: ./sp.db# With auth environment variables exported
cloudquery sync sharepoint.yml sqlite.ymlYou should see the following output:
Loading spec(s) from sharepoint_reg.yml, sqlite.yml
Downloading https://github.com/koltyakov/...sharepoint_darwin_arm64.zip
Downloading 100% |█████████████████████████████████████| (5.2/5.2 MB, 10 MB/s)
Migration completed successfully.
Starting sync for: sharepoint (v2.0.0) -> [sqlite (v2.4.15)]
Sync completed successfully. Resources: 37478, Errors: 0, Panics: 0, Time: 21sCheck for destination database data.
Powered by gosip.