Open Service Broker is an implementation of the Open Service Broker API. It enables platforms such as Cloud Foundry & Kubernetes to provision and manage services.
Open Service Broker is built in a modular way and one service broker can host multiple services.
Service broker offers extra functionality regarding Billing, Backup/Restore on top of the Open Service Broker API.
Services can be provisioned synchronously and/or asynchronously and the goal of this project is to provide a framework with which any service can easily be provisioned.
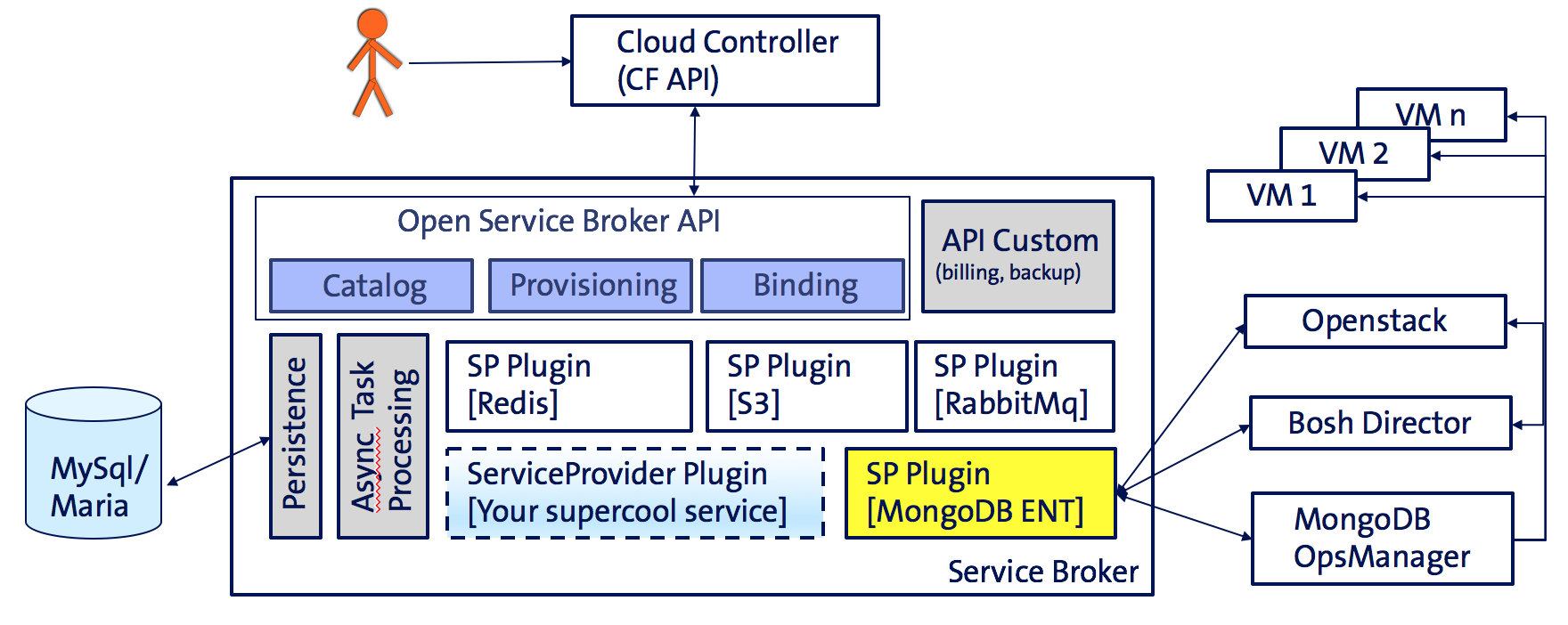 The image above shows the high level architecture.
The image above shows the high level architecture.
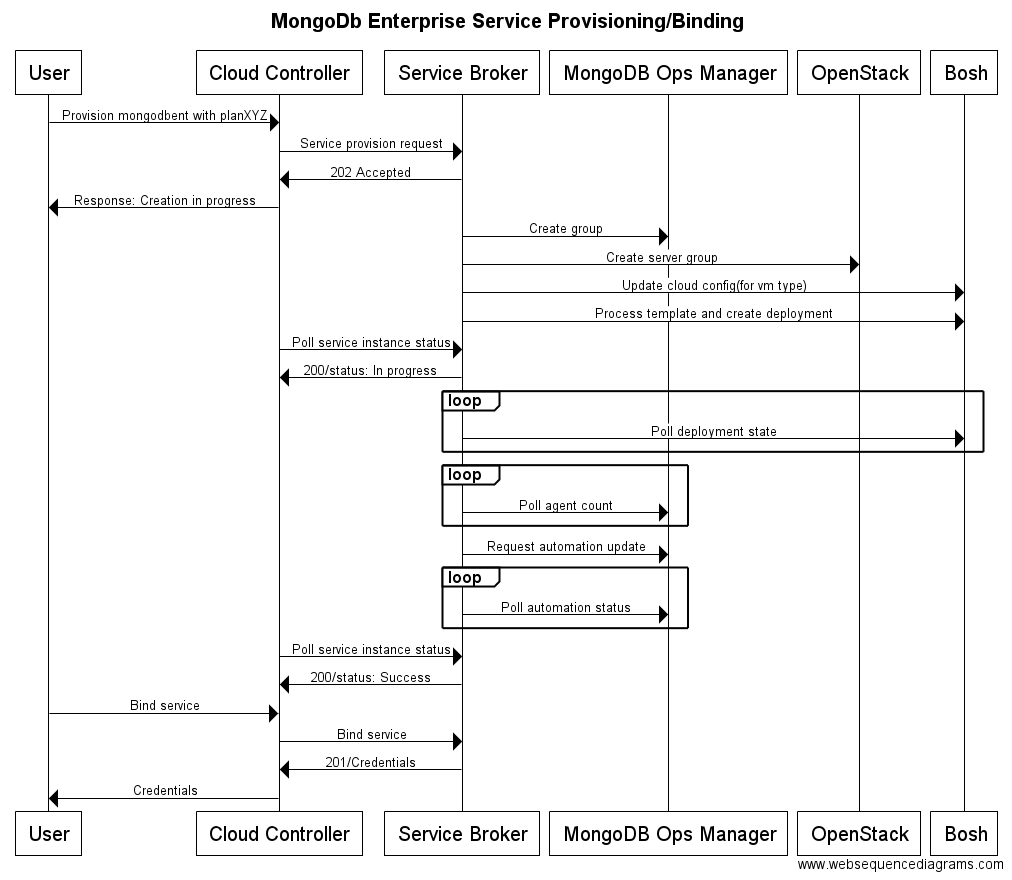
The following flow chart shows interactions for service provisioning and service binding for MongoDB Enterprise service.
- Java 1.8
- MySQL / MariaDB Server
Build Service Broker using the gradlew script in the root directory of the repository.
$ ./gradlew clean build -x test -x integrationTest -x functionalTest -PtomcatThe parameter called tomcat is for controlling if a tomcat runtime is integrated into the war.
Command below gives you a self executable jar
$ ./gradlew clean build -x test -x integrationTest -x functionalTest To run the service broker locally a mariadb or mysql database with name CFbroker is required. The database tables will be generated automatically by the application. See the configuration section for more details.
docker run --name appc-cf-service-broker-db -e MYSQL_DATABASE=CFBroker -e MYSQL_ALLOW_EMPTY_PASSWORD=yes -p 3306:3306 -d mariadbTo run the built artifact, from the root directory the following commands can be executed:
java -jar -Dspring.config.location=file:/some/path/servicebroker.yml broker/build/libs/service-broker-2.0.0-SNAPSHOT.war The config file passed can overwrite any default values. Providing an external config file is optional and when no external config file is provided, the default values are dictated by application.yml file(s).
or
./gradlew broker:bootRunAt the time being, Service Broker is recommended to run with only one instance to avoid concurrency issues. This issue will be fixed soon.
When importing this project into IntelliJ, select the "create separate module per source set option".
Follow the documentation to register the broker to Cloud Foundry.
Before a cf create-service-broker or update-service-broker call is made, please make sure that Service Broker is configured correctly.
For configuring the catalog, see the service definition section.
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -Djava.awt.headless=true -Xmx2048m -XX:MaxPermSize=1024m -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC"The configuration file for the Service Broker is located under
broker/src/main/resources/application.yml
Via the example call below, service definitions for a given service id can be retrieved.
curl -u 'username:password' -X GET 'http://localhost:8080/custom/admin/service-definition/{service_id}'Service Broker provides a way to update service definitions via HTTP calls.
Here is an example:
curl -u 'username:password' -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-binary '@path/to/definition/file' 'http://localhost:8080/custom/admin/service-definition'This interface can be used for both adding a new service or updating an existing one. For an existing service, if a plan that is in use is tried to be removed an exception will be thrown.
A service and its plan(s), which are not used i.e. which have no service instances, can be removed via a REST interface.
Here is an example for how to delete a service that has the id service_id:
curl -u 'username:password' -X DELETE 'http://localhost:8080/custom/admin/service-definition/{service_id}'{
"guid": "udn9276f-hod4-5432-vw34-6c33d7359c12",
"name": "mongodbent",
"description": "MongoDB Enterprise HA v3.2.11",
"bindable": true,
"asyncRequired": true,
"internalName": "mongoDbEnterprise",
"displayIndex": 1,
"tags": [],
"metadata": {
"version": "3.2.11",
"displayName": "MongoDB Enterprise"
},
"plans": [
{
"guid": "jfkos87r-truz-4567-liop-dfrwscvbnmk6",
"name": "replicaset",
"description": "Replica Set with 3 data bearing nodes with 32 GB memory, 320 GB storage, unlimited concurrent connections",
"templateId": "mongodbent-bosh-template",
"free": false,
"displayIndex": 0,
"containerParams": [
{
"template": "",
"name": "plan",
"value": "mongoent.small"
},
{
"template": "",
"name": "vm_instance_type",
"value": "mongoent.small"
}
],
"metadata": {
"storageCapacity": "320GB",
"memory": "32GB",
"nodes": "3",
"maximumConcurrentConnections": "unlimited",
"dedicatedService": true,
"highAvailability": true,
"displayName": "Small"
}
}
]
}The Swagger API documentation can be accessed at http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
Any bosh based service can be easily brokered. See here for Swisscom's bosh releases.
Check the class BoshBasedServiceProvider for details.
https://github.com/swisscom/mongodb-enterprise-boshrelease
Any Kubernetes based service can be provisioned with Open Service Broker. The asynchronous task is being created to prepare the provisioning of the service instance. Kubernetes Facade is using the client to execute a bunch of "templated" HTTP calls on Kubernetes Server. All the templates are automatically read from provided directory and matched with k8s endpoint.