There is no comprehensive genomic terminology available in the public domain that would support harmonization of genomic oncology data, which is necessary for standardized analytics in a research network.
To address these challenges and to develop interoperability between genomic data and clinical care, a collaboration between the OHDSI Oncology Workgroup and the VICC consortium is seeking to develop a canonical representation of equivalent variants to serve as standard concepts in the OMOP Standardized Vocabularies. [1]
KOIOS is a tool developed by Odysseus Data Services Inc that allows you to find matching and missing concepts in OMOP Genomic Vocabulary for most types of raw patient-level genomic data. The current tool functionality allows to extract relevant variant information from VCF files, or detect HGVS in any TXT/CSV file. In the next step, KOIOS finds corresponding HGVS references in ClinGen for each variant, and maps the results to OMOP Genomic vocabulary. Extracted HGVS references can be used as either synonyms for the existing OMOP Genomic concepts, or as new entities.
I. Download all files and folders as a .zip archive from:
[https://github.com/OHDSI/Koios](https://github.com/OHDSI/Koios)
II. Move 'Koios.zip' archive to your desired directory and unzip it.
III. Put VCF files to /Koios/input/ directory.
Supported input file formats:
- .vcf
- .vcf.gz
- .txt file with HGVS
- .csv file with HGVS
IV. Run main.py file (in terminal or command prompt)
Syntax:
-
cd ../full_path_to_folder/../Koios/
-
python3 main.py [-h ][--help ]f.e. python3 main.py -h
python3 main.py --help
Options for running main.py:
Parameter Default usage Description
------------------------------------------------------------
--help -h False Display help message.
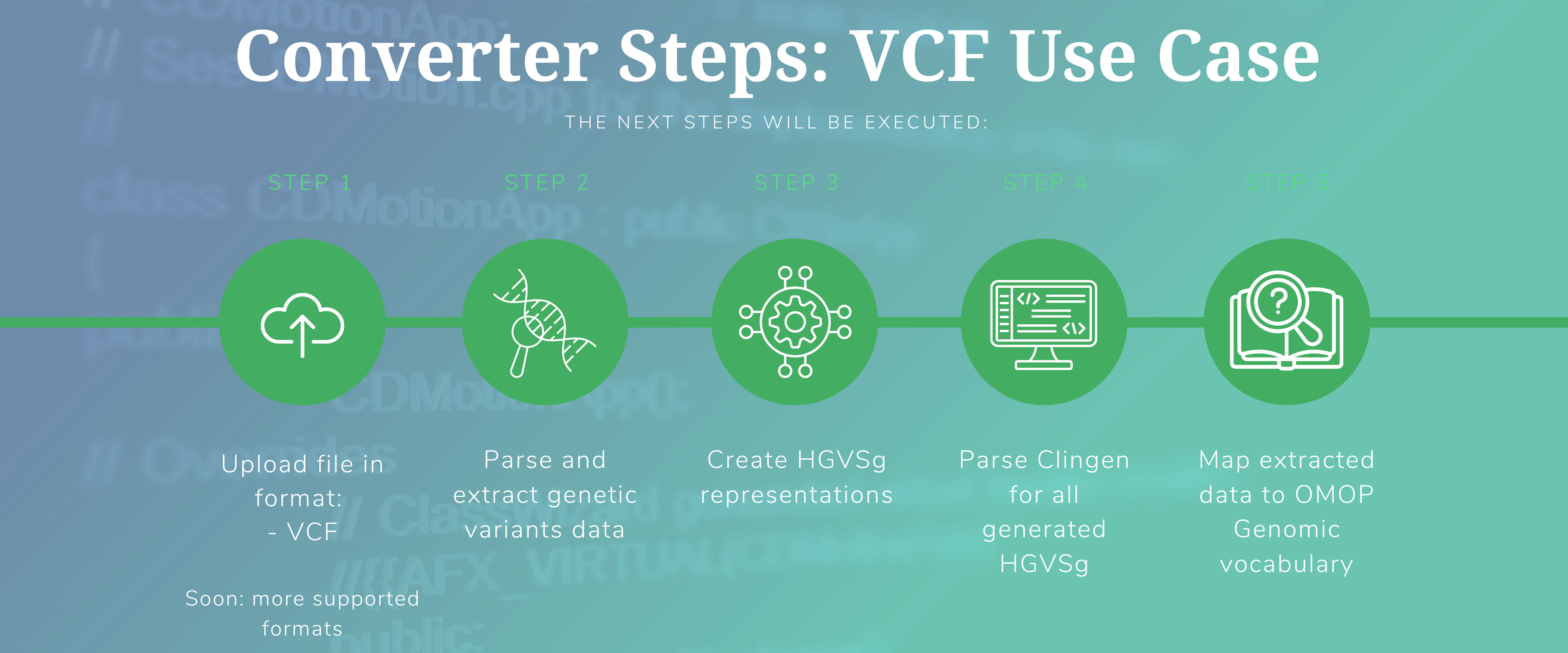
After you start running the converter in default mode, the next steps will be executed:
1.1) Parse a VCF file and extract variants data. A VCF file contains the variants of a single patient.
1.2) Create HGVSg representations.
Format:
Reference : Description
Steps:
- Extract Build and Chromosome Number (tag CHROM in the VCF file). Map this information to Global Assembly Definitions [1] provided by Genome Reference Consortium to find Reference Sequence Accession Number.
Example: 'NC_000001.11' for Chromosome 1 and Build 38
- Extract position (tag POS in the VCF file)
Example: 114713909
- Extract the reference genotype (tag REF in the VCF file)
- Extract the alleles that differ from the reference read (tag ALT in the VCF file). Transformation is coded as: REF>ALT, f.e. G>T
Result: NC_000001.11:g.114713909G>T
2.1) Generate ClinGen links based on HGVSg formed in the previous step.
Example link: [2]
2.2) Parse all available HGVS references matching the HGVSg representations.
File format:
VCF_file_name_clingen.csv
Columns:
HGVSg_vcf: HGVSg formed at step 1.2)
link: linked to ClinGen API formed at step 2.1)
communityStandardTitle: Clingen communityStandardTitle tag
allele_class: r.n. only data about genomicAlleles is extracted
type: Clingen type tag
chromosome: Clingen chromosome tag. Chromosome number of each allele
allele_n: Number of allele
hgvs: Clingen hgvs tag. HGVS reference
hgvs_n: Number of HGVS reference
hgvs_referenceGenome: Clingen referenceGenome tag
referenceSequence: Clingen referenceSequence tag
hgvs_referenceSequence: Clingen referenceSequence tag
3.2) Save matching hgvs as a .csv file. Output file location:
- /omopvsf/output
Next steps are executed in the HGVS mode.
<img src="static/imgs/steps-hgvs.png" width="" alt="alt_text" title="image_tooltip>
For this mode, you need to already have a file that contains a column with HGVS in one of these formats:
- NC_000001.11:g.1361836A>G
- chr7:g.87053221C>T
Currently, KOIOS supports two formats of such input files: .txt and .csv. First, KOIOS will detect a column where most of the values are HGVS in one of formats displayed above. Then, it will preprocess HGVS and bring them to standard format - HGVS nomenclature standard [3]. The next steps will be similar to steps 2, 3 of the VCF mode.
Thank you for using this converter.
OHDSI
Odysseus Data Sevices
Links
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assembly/GCF_000001405.26/
[2] https://reg.genome.network/allele?hgvs=NC_000001.11:g.114713909G>T
[3] https://varnomen.hgvs.org/bg-material/simple/
Technical contact:
Nadia Kadakova nadia.kadakova@odysseusinc.com