Navigate to https://desktop.telegram.org/ to download Telegram Desktop.
Search for @BotFather Telegram bot and click START button:
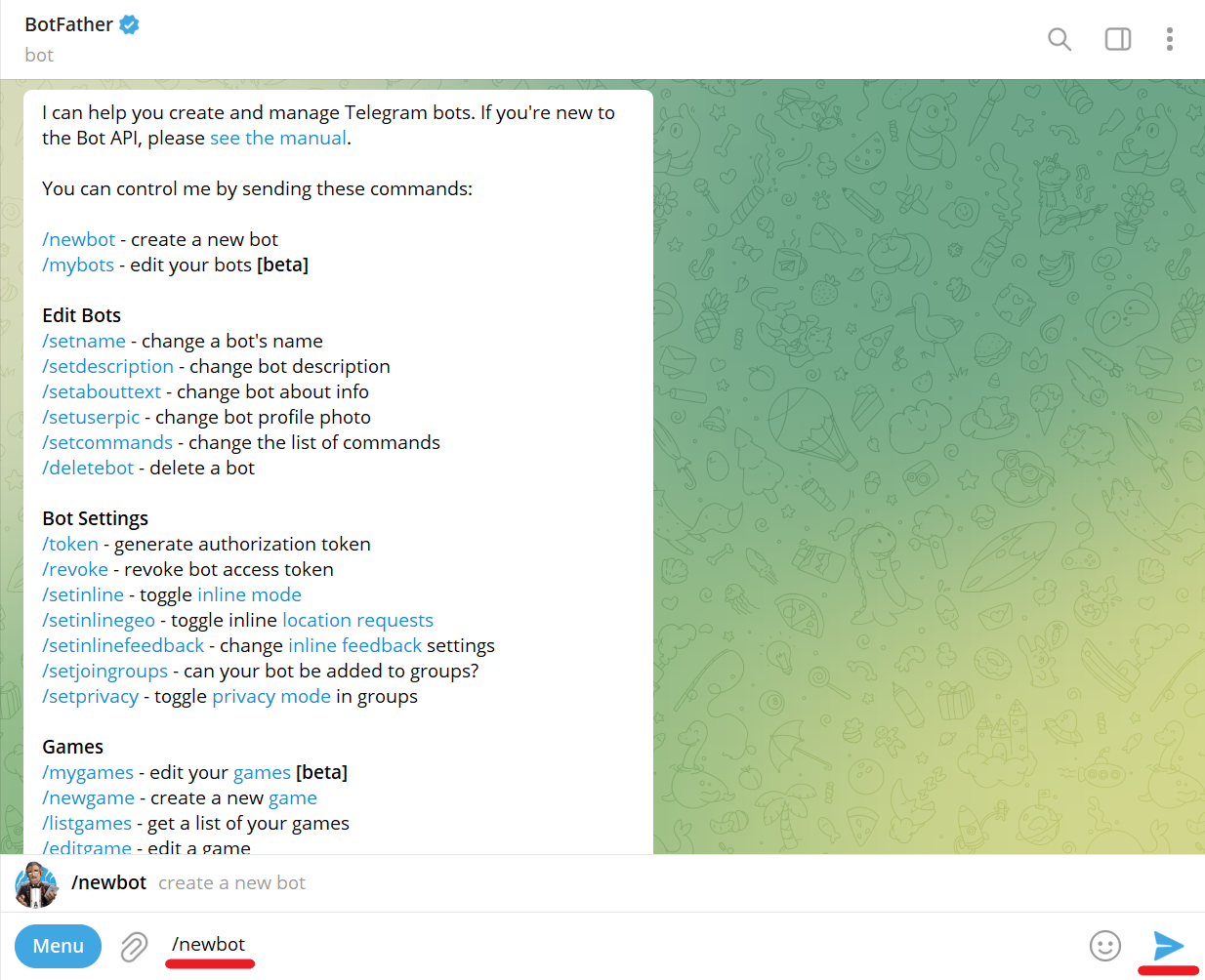
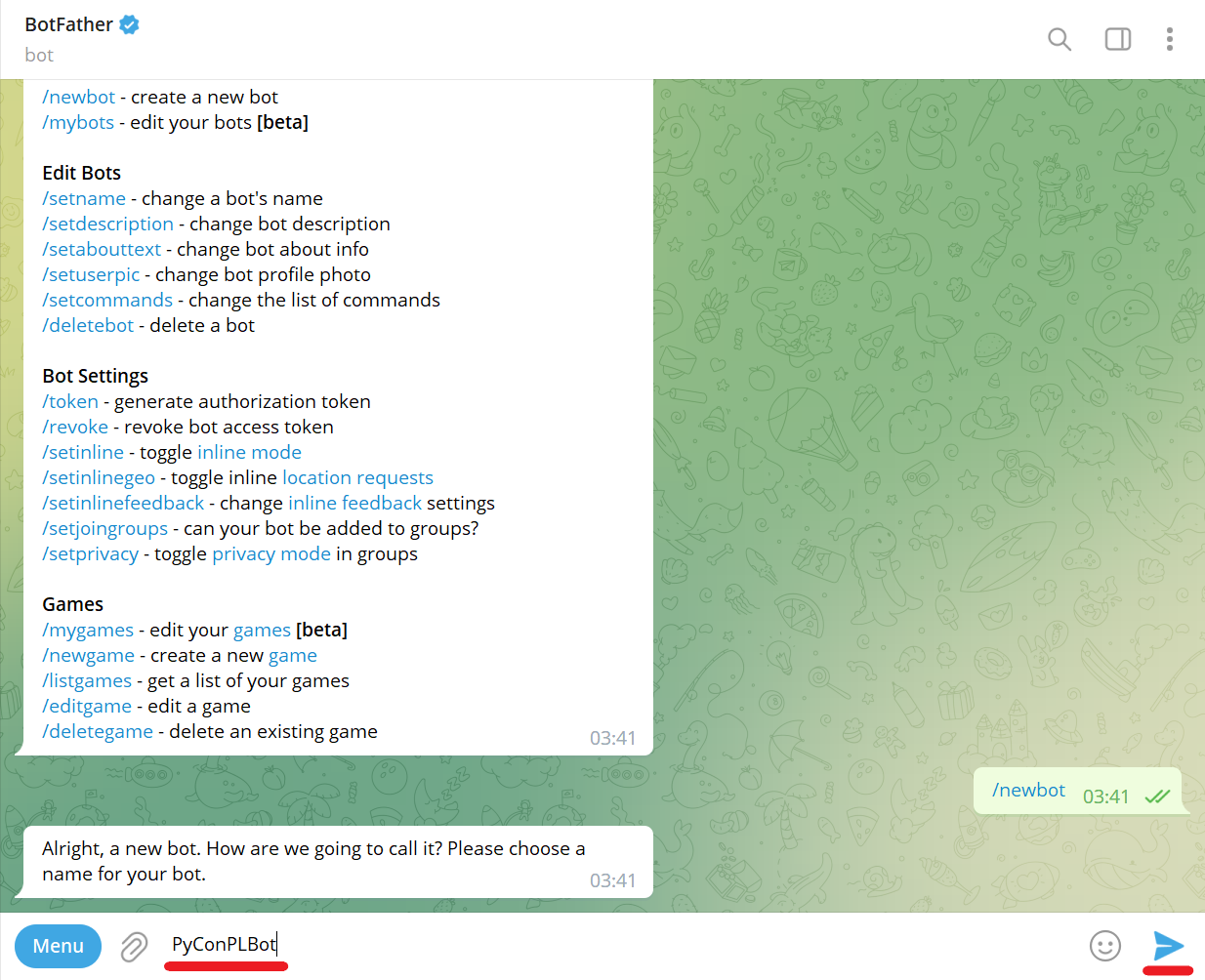
Send bot name (e.g., PyConPLBot):
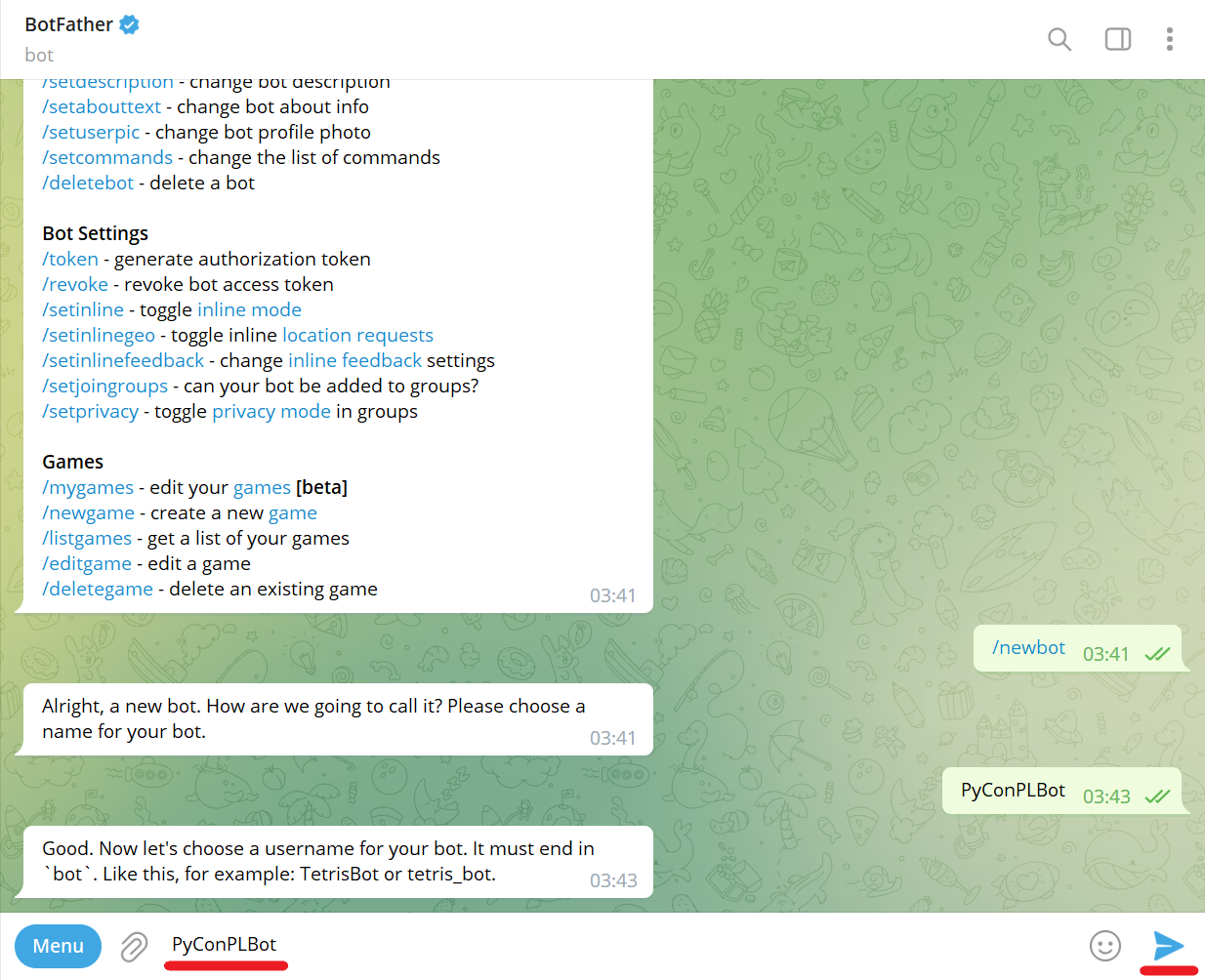
Send bot username (e.g., PyConPLBot). It must end with bot:
Copy and save the token (e.g., 5741693832:AAFyfYpqWRHaGVhTt9CO4edV7bTlNR7bvaA):
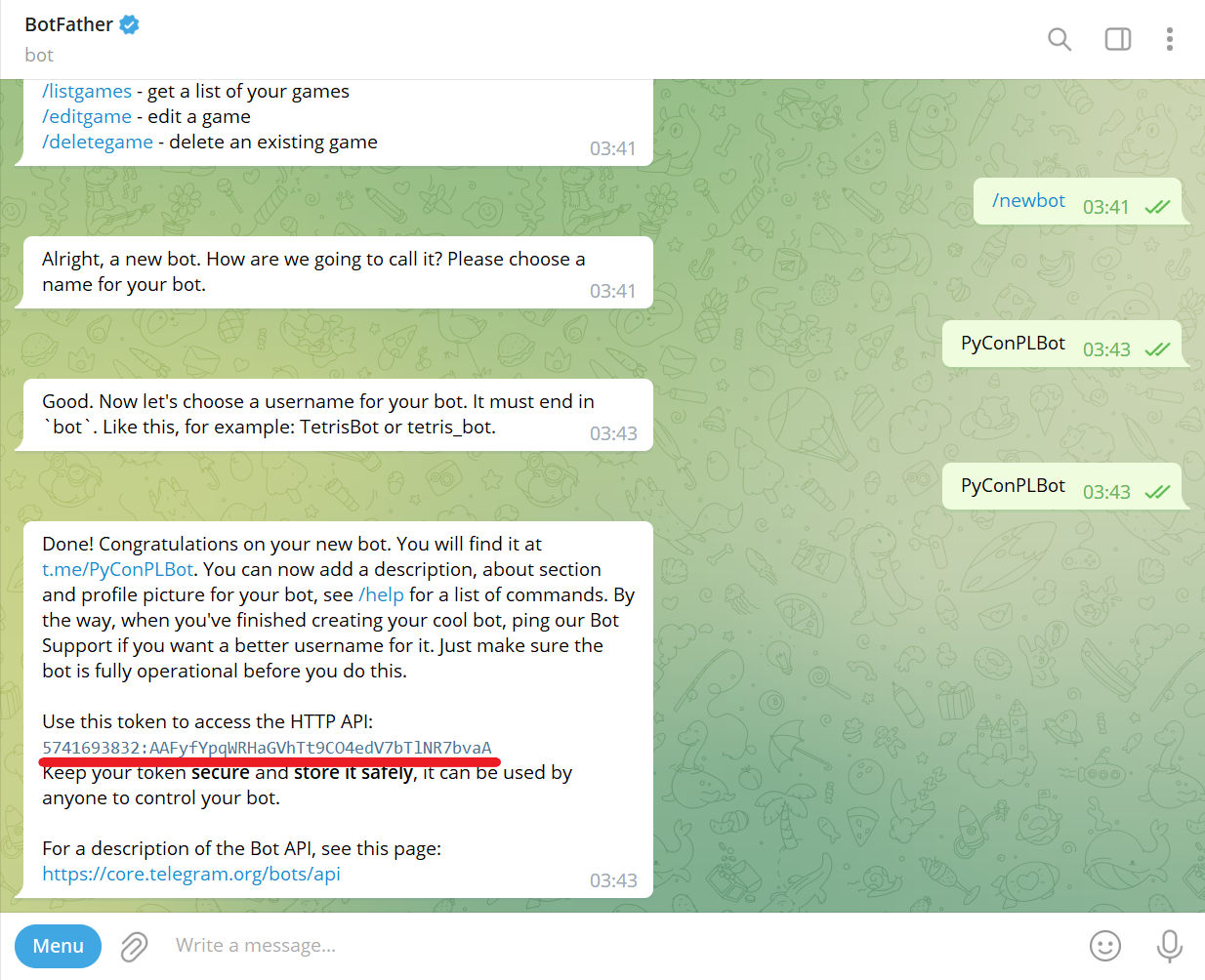
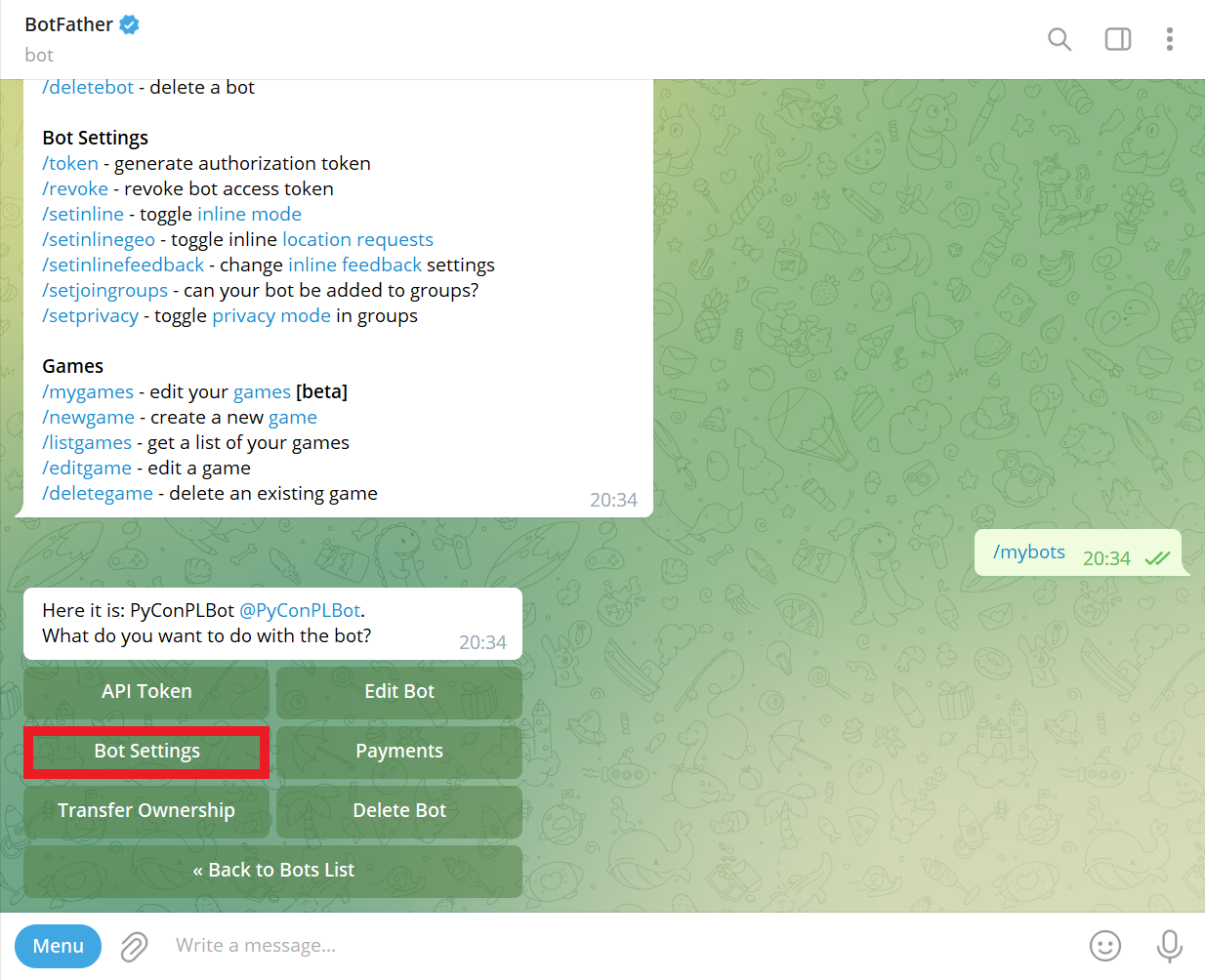
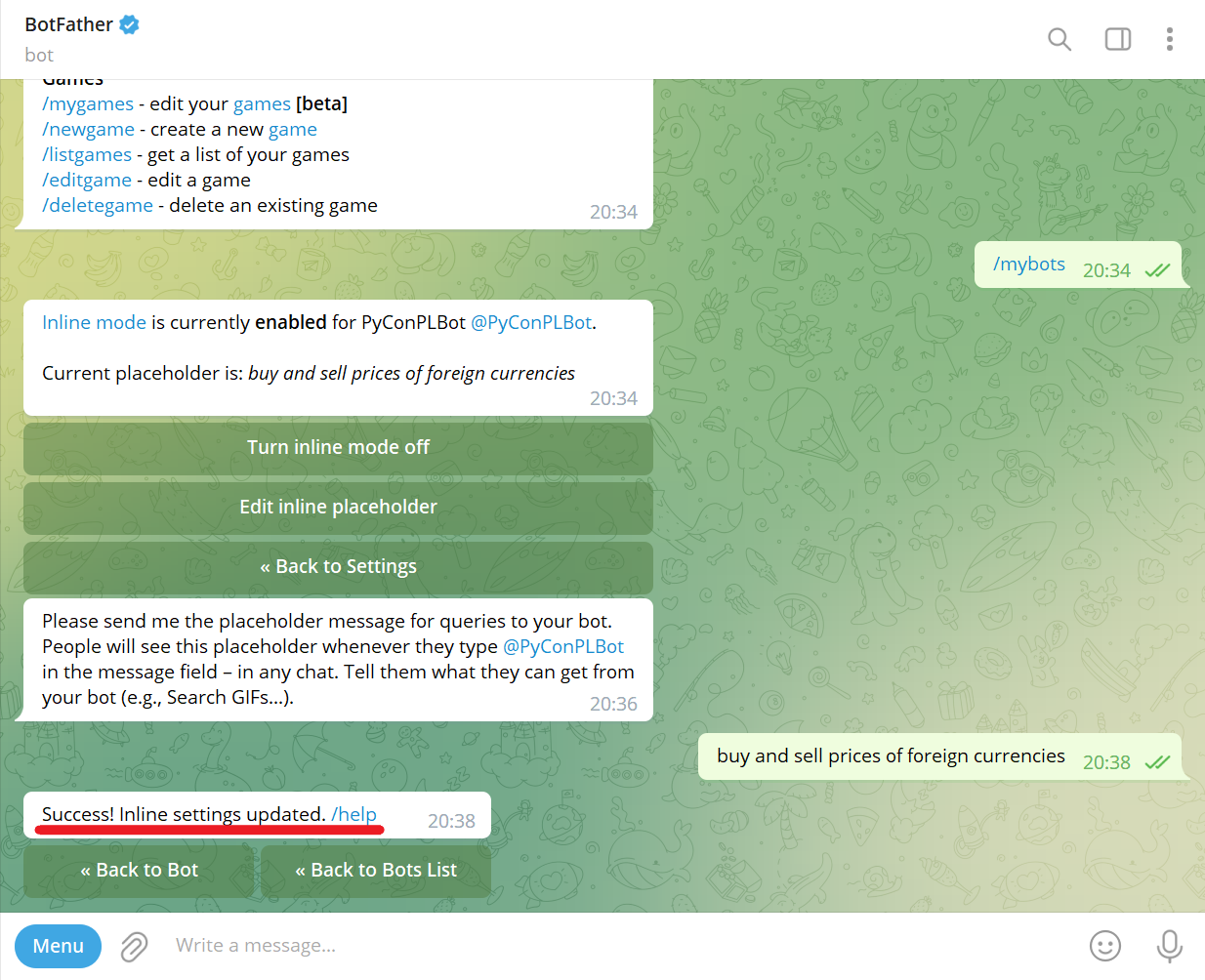
Navigate to @BotFather Telegram bot and send /mybots command:
Choose a bot from the list (e.g., @PyConPLBot):
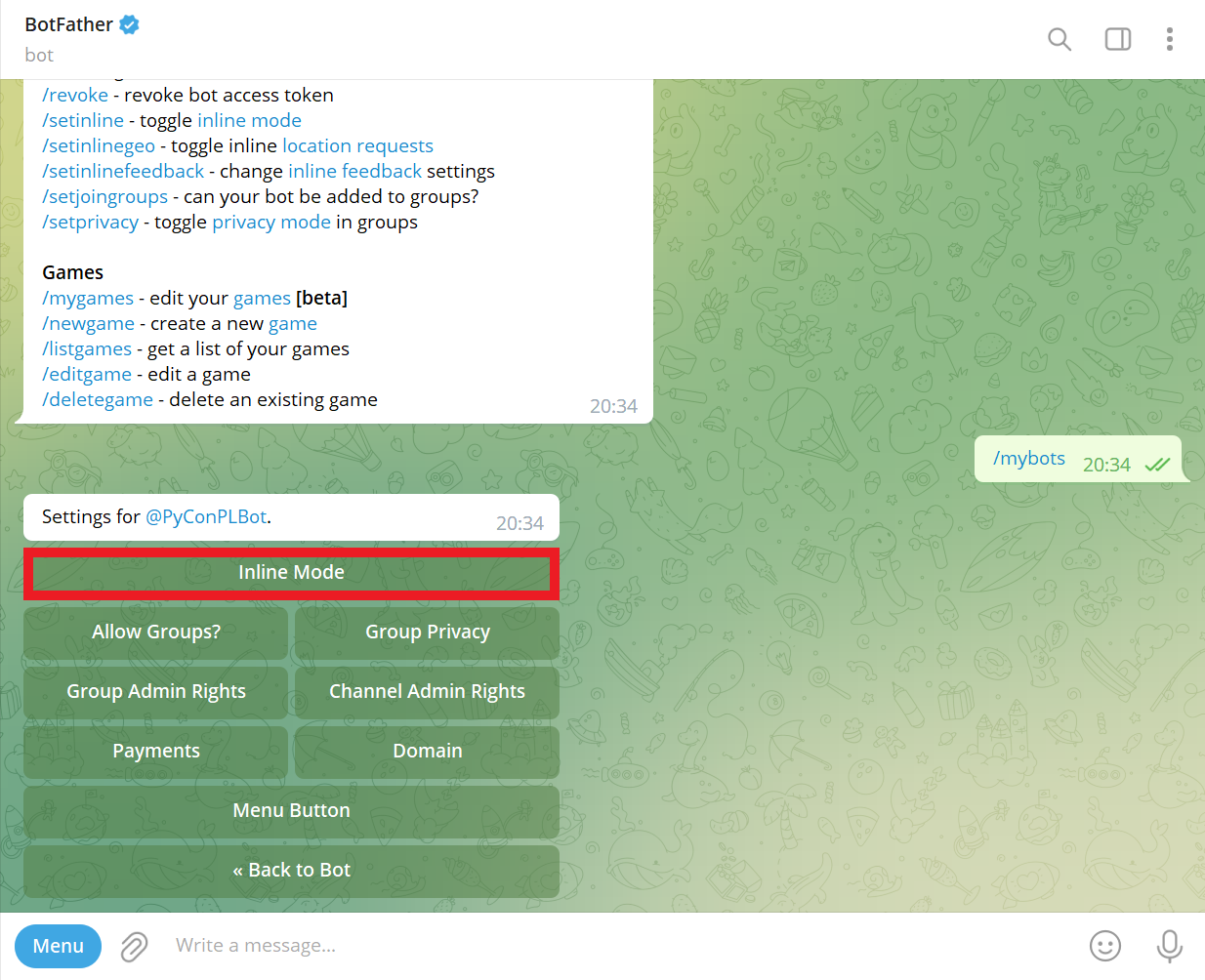
Click Edit inline placeholder button:
Send placeholder (e.g., buy and sell prices of foreign currencies):
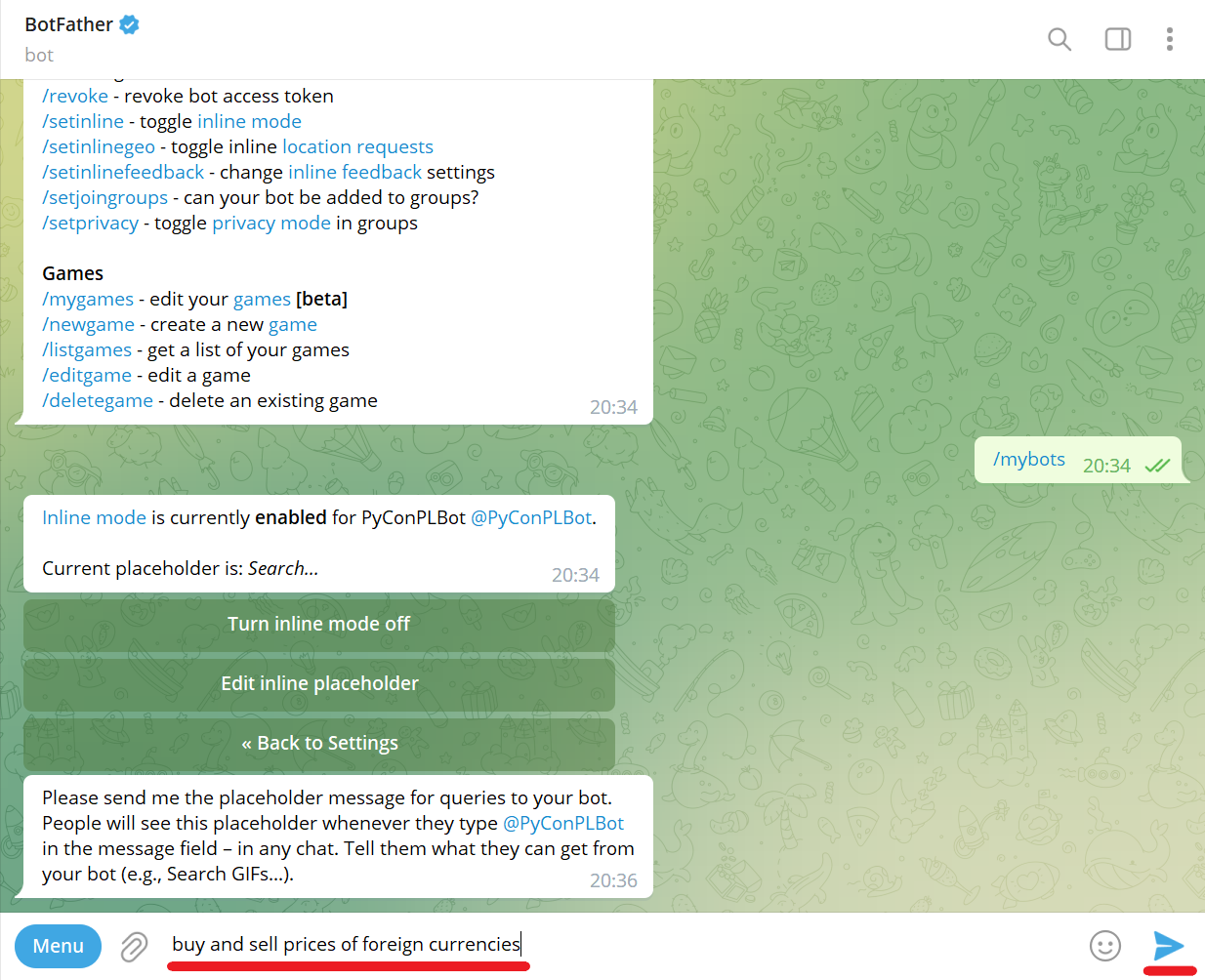
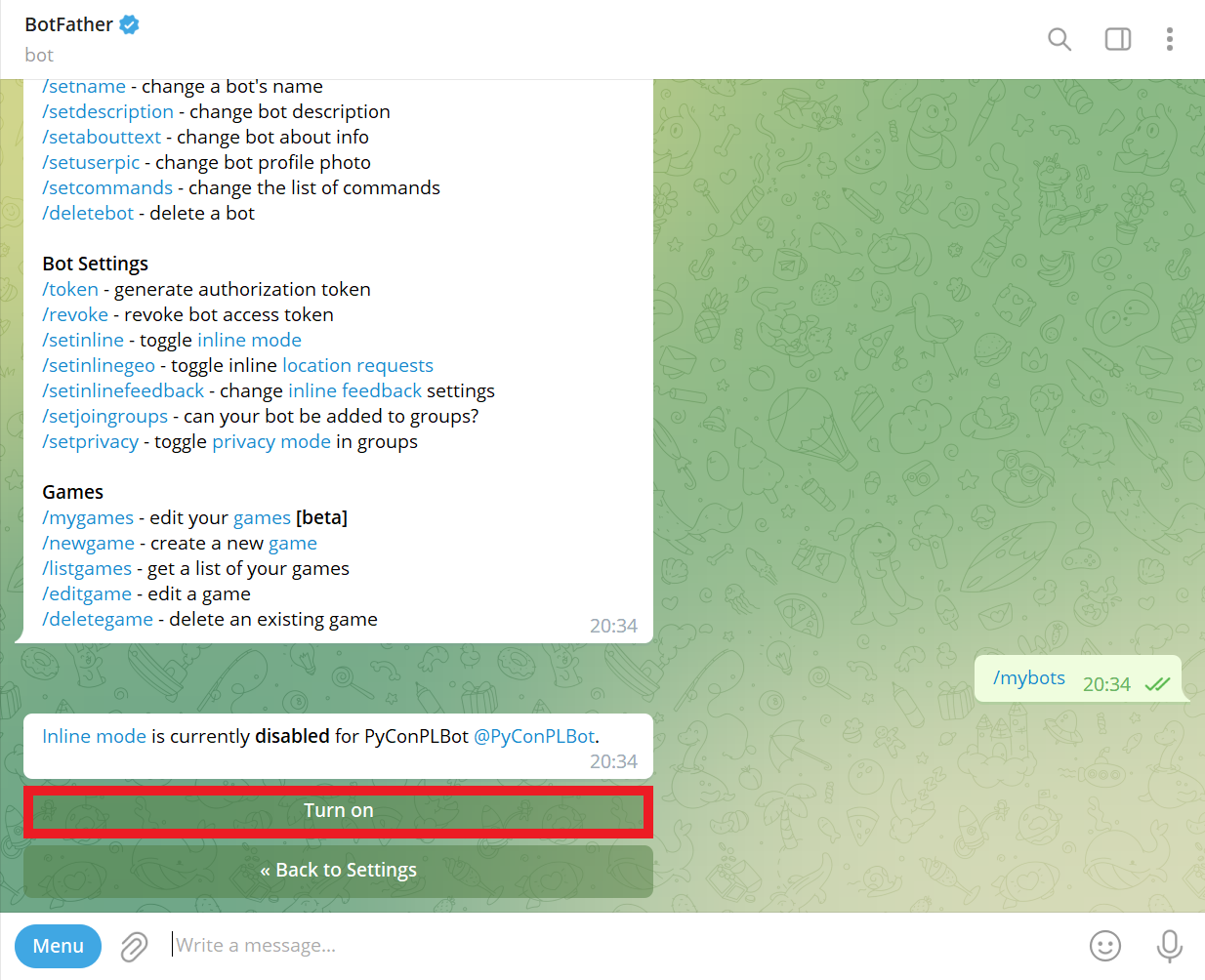
Success! Inline setting updated:
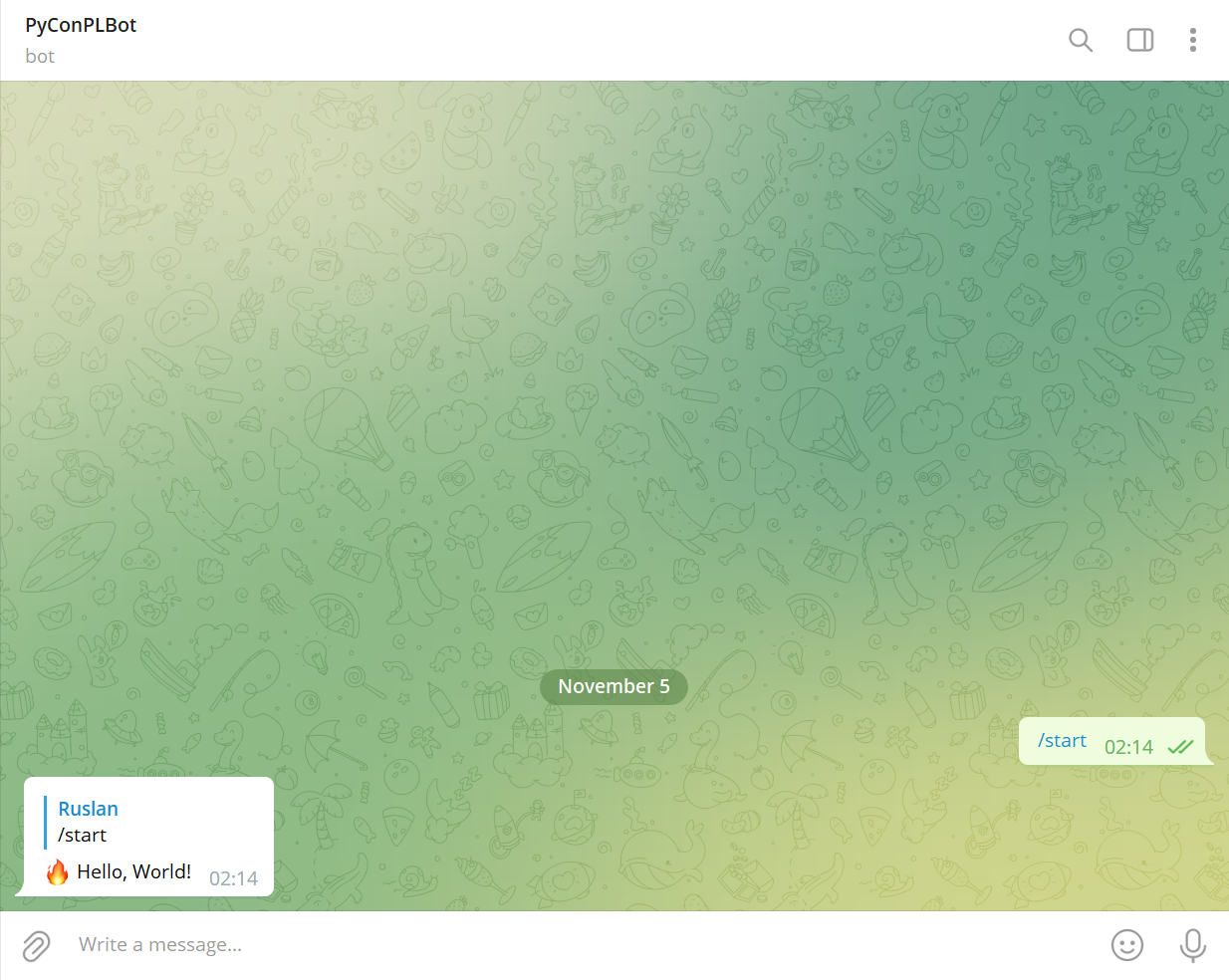
Lets start with Hello, World! bot written with pyTelegramBotAPI.
$ git clone https://github.com/korniichuk/telegram-pycon-pl-2022.git
$ cd telegram-pycon-pl-2022Install requirements:
$ pip install -r requirements.txtCreate .env file with token:
$ touch .envCopy and past token to .env file:
$ echo TOKEN=<TOKEN> > .env
Example:
$ echo TOKEN=5741693832:AAFyfYpqWRHaGVhTt9CO4edV7bTlNR7bvaA > .envStart Hello, World! bot:
$ python3 bot1.pyNavigate to your Telegram bot (e.g., @PyConPLBot) and click START button:
You can achieve the same result with /start command.
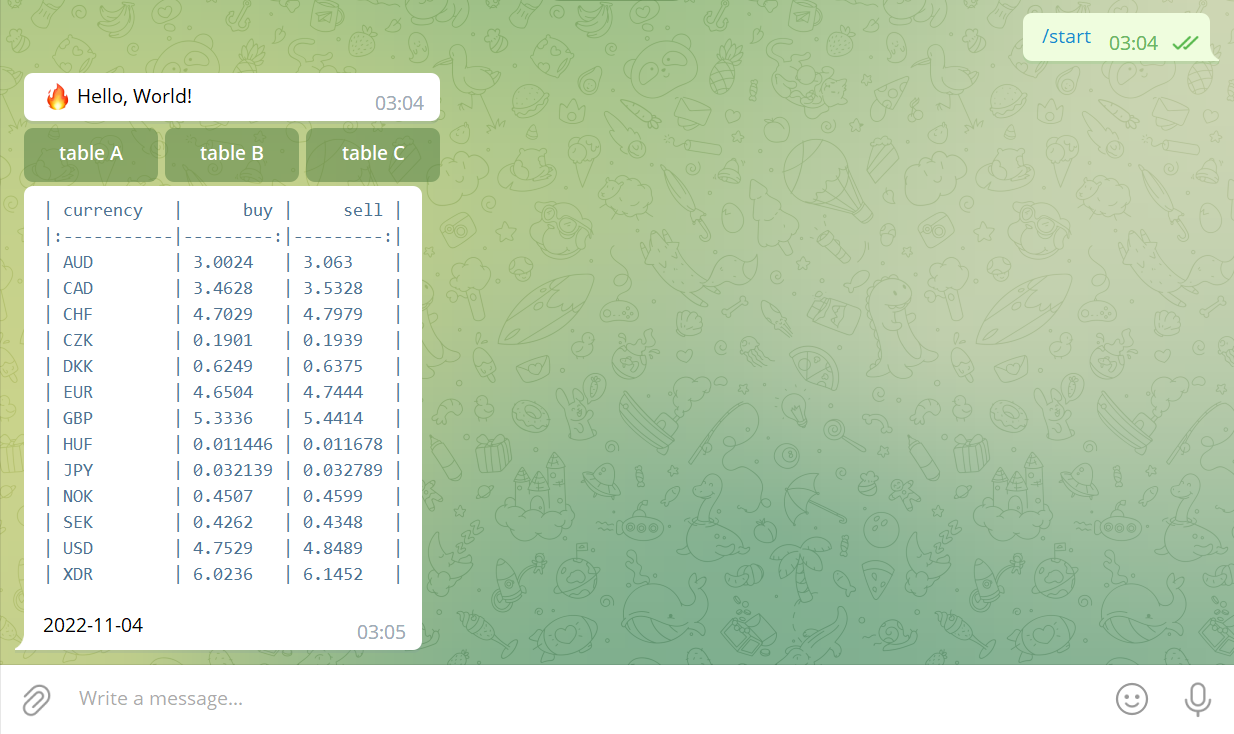
$ python3 bot2.pyNavigate to your Telegram bot (e.g., @PyConPLBot) and send /start command.
Test table A, table B, and table C buttons:
Send /a, /b, and /c commands:
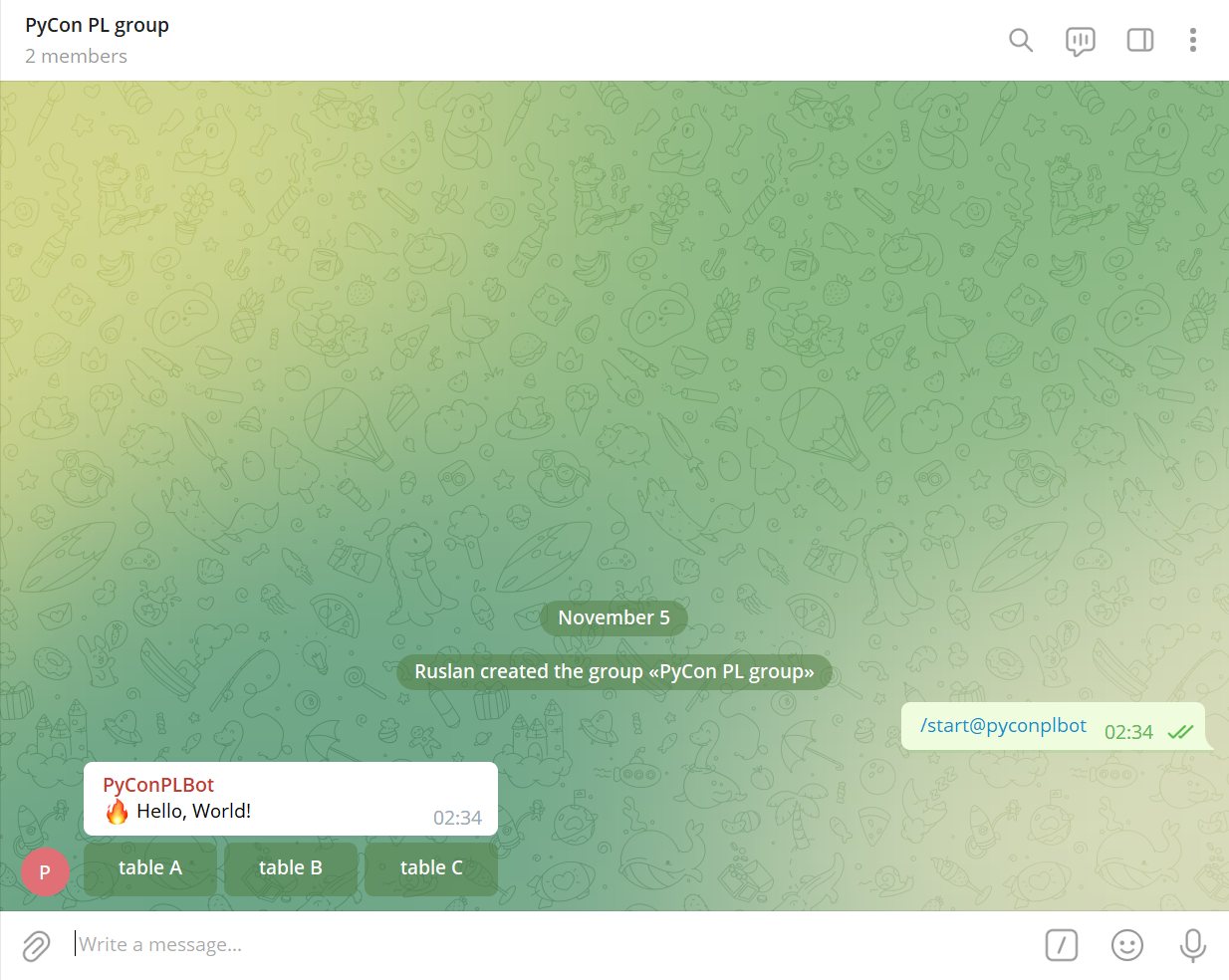
Create a new Telegram group (e.g., PyCon PL group).
Add your Telegram bot (e.g., @PyConPLBot) to the group.
Add your friend(s) (optional).
Test /start@<you_bot_username> (e.g., /start@pyconplbot) command:
Communication with Telegram bots is not always easy. You had to send them messages in separate chats or add them to your groups.
With the inline mode, bots become omnipresent and can be used as a tool in any of your chats, groups or channels – it doesn't matter, whether the bot is a member or not.
Open chat with your friend(s) or create a new Telegram group, and type the username of your bot (e.g., @pyconplbot).
You can see inline placeholder now (e.g., buy and sell prices of foreign currencies):
Type space and rate command (e.g., @pyconplbot rate):
$ python3 bot3.py$ python3 bot4.py$ python3 bot5.pyNote: Parse mode Markdown is legacy since Telegram Bot API 4.5, retained for backward compatibility. Source: https://core.telegram.org/bots/api#formatting-options
$ wget https://github.com/aws/aws-sam-cli/releases/latest/download/aws-sam-cli-linux-x86_64.zip
$ unzip aws-sam-cli-linux-x86_64.zip -d sam-installation
$ sudo ./sam-installation/install
$ sam --versionSource: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/install-sam-cli.html
Insert your token to lambda_function.py file. For example, from:
TOKEN = "<TOKEN>" # token from @BotFather for your Telegram bot
to:
TOKEN = "5741693832:AAFyfYpqWRHaGVhTt9CO4edV7bTlNR7bvaA"
$ cd ..
$ cd aws-serverless-application-model
$ sam build$ sam deploy --guidedEnter Stack Name (e.g., telegram). Enter AWS Region (e.g., eu-west-1).
Confirm changes before deploy [y/N]
Enter Y.
Allow SAM CLI IAM role creation [Y/n]:
Enter Y.
Disable rollback [y/N]:
Enter N.
MyLambdaFunction Function Url may not have authorization defined, Is this okay? [y/N]:
Enter Y.
Save arguments to configuration file [Y/n]:
Enter Y.
Enter SAM configuration file name (e.g., samconfig.toml).
Enter SAM configuration environment (e.g., default).
Copy and save the Lambda URL Value from terminal (e.g., https://avi4v7gy25zo4lizhqqzh3dtom0zufol.lambda-url.eu-west-1.on.aws/).
All you have to do is to call the setWebhook method in the Bot API via the following url:
https://api.telegram.org/bot{TOKEN}/setWebhook?url={URL}/
Where:
TOKEN-- token you got from BotFather when you created your bot,URL-- Lambda URL for the MyLambdaFunction (must be HTTPS).
Exmaple:
https://api.telegram.org/bot5741693832:AAFyfYpqWRHaGVhTt9CO4edV7bTlNR7bvaA/setWebhook?url=https://avi4v7gy25zo4lizhqqzh3dtom0zufol.lambda-url.eu-west-1.on.aws/
{"ok":true,"result":true,"description":"Webhook was set"}
Source: https://xabaras.medium.com/setting-your-telegram-bot-webhook-the-easy-way-c7577b2d6f72
To delete Telegram bot WebHook:
https://api.telegram.org/bot{TOKEN}/setWebhook?url=
Example:
https://api.telegram.org/bot5741693832:AAFyfYpqWRHaGVhTt9CO4edV7bTlNR7bvaA/setWebhook?url=
{"ok":true,"result":true,"description":"Webhook was deleted"}
To delete the sample application that you created, use the AWS CLI:
$ sam deleteThe following example is written on pyTelegramBotAPI. See aiogram example: https://stackoverflow.com/a/64911415
Install AWS CLI:
$ curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
$ unzip awscliv2.zip
$ sudo ./aws/install
$ aws --versionInstall EB CLI:
$ pip install awsebcli
$ eb --versionSource: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/eb-cli3-install-advanced.html
Navigate to aws-elastic-beanstalk folder and initialize the directory with the EB CLI:
$ cd aws-elastic-beanstalk
$ eb initSelect a default region (e.g., eu-west-1). Enter a new application name for your Elastic Beanstalk application (e.g., telegram).
It appears you are using Python. Is this correct?
(Y/n):
Enter Y.
Select a platform branch (e.g., Python 3.8 running on 64bit Amazon Linux 2). Details: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/platforms/platforms-supported.html#platforms-supported.python
Do you want to set up SSH for your instances?
(Y/n):
Enter Y.
Create a new Elastic Beanstalk environment:
$ eb createEnter environment name (e.g., telegram-dev).
Enter DNS CNAME prefix (e.g., telegram-dev).
Select a load balancer type (e.g., application).
Would you like to enable Spot Fleet requests for this environment? (y/N):
Enter N.
To set Telegram token as an environment variable in the EB CLI, run the following command:
$ eb setenv TOKEN=<TOKEN>Example:
$ eb setenv TOKEN=5741693832:AAFyfYpqWRHaGVhTt9CO4edV7bTlNR7bvaASource: https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/elastic-beanstalk-pass-variables/
To deploy new source code to the environment:
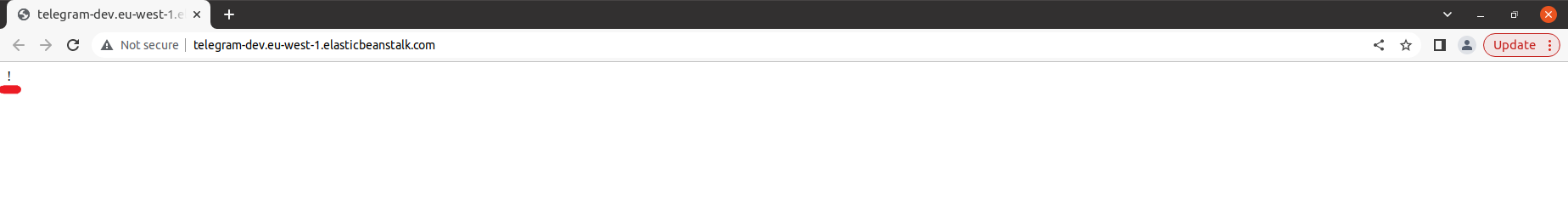
$ eb deployOpen the EB application URL in a browser:
$ eb openIf you can see exclamation mark, Telegram bot deployed successfully:
This part is out of workshop scope!
We need to purchase and configure a custom domain name (e.g., telegrambot.click for 3 USD) for our Elastic Beanstalk environment.
This part is out of workshop scope! We need use HTTPS to allow secure connection.
To set up SSL we need to obtain SSL certificate:
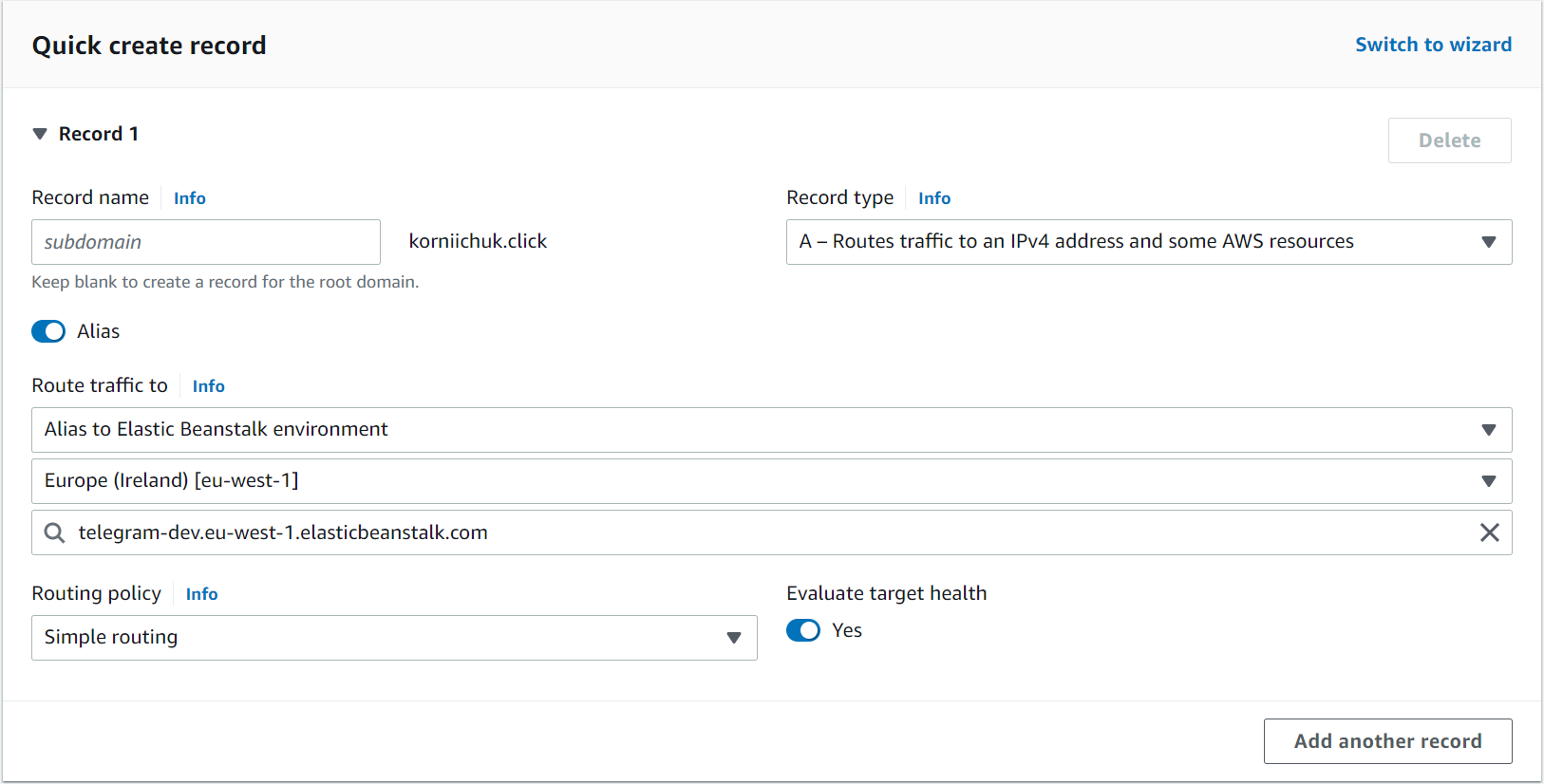
- Navigate to AWS Certificate Manager (ACM).
- Click
Request certificatelink orRequestbutton. SelectRequest a public certificate. ClickNext. - Add two domain names: one for website (e.g.,
korniichuk.click) and one wildcard domain (e.g.,*.korniichuk.click). It will cover all subdomains including www or any other. - Select
DNS validationand clickRequestbutton.
Because we delegated domain management to AWS, we need to validate ownership by expanding any domain and clicking Create records in Route 53.
SSL certificate will be issued after a while (it can take up to 48 hours - usually within 30 minutes after nameservers delegation is completed).
Source: https://dev.to/bnn1/deploying-dockerized-nextjs-app-to-aws-eb-part-3-setting-custom-domain-45bm
This part is out of workshop scope!
- Open the Elastic Beanstalk console, and in the Regions list, select your AWS Region (e.g.,
eu-west-1). - In the navigation pane, choose
Environments, and then choose the name of your environment from the list (e.g.,telegram-dev). - In the navigation pane, choose
Configuration. - In the
Load balancerconfiguration category, chooseEdit. Note: If the Load balancer configuration category doesn't have anEditbutton, your environment doesn't have a load balancer. - On the
Modify Application Load Balancerpage, chooseAdd listener. - For
Port, type the incoming traffic443port. - For
Protocol, chooseHTTPS. - For
SSL certificate, choose your certificate. ChooseAdd. Scroll down and clickApply
Important: Adding listener this way (via Elastic Beanstalk) will fix security group automatically. For adding listener via EC2 you need to fix security group manually.
Source: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/configuring-https-elb.html
This part is out of workshop scope!
To delete bot from AWS cloud, terminate the environment:
$ eb terminate