MIPS Assembly Language Examples
Files:
macros.asm: Common macros (MARS macros)sle.asm: Solve systems of linear equations (Ax = b)mult-table.asm: Print out multiplication tables from 2 to 9ary-stack.asm: Implement a stack using an arrayqsort.asmImplement quick sort algorithm
Use MARS MIPS simulator to run the codes.
sle.asm
Solve systems of linear equations (Ax = b) (A: 5x5, x: 5x1)
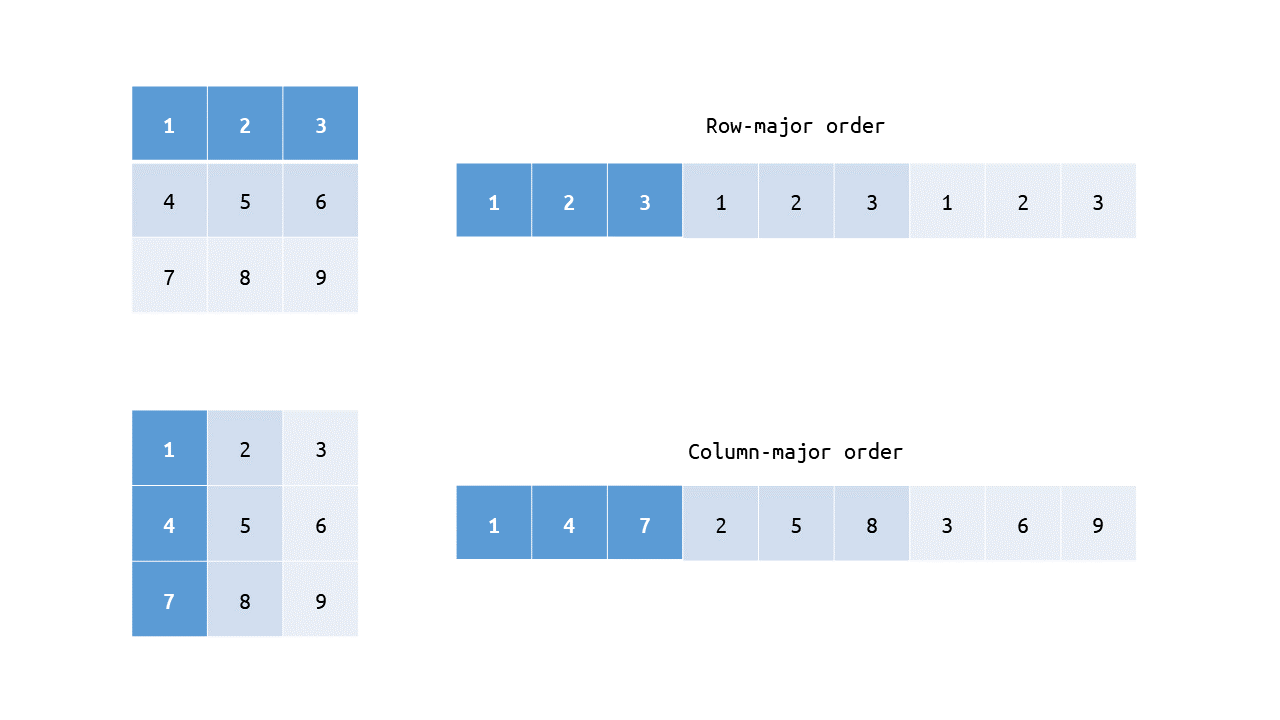
Each matrix is assumed to be supplied in column-major order.
Matrix:
| 7 1 7 9 3 | | 4 | | ? |
| 8 8 6 5 6 | | 2 | | ? |
| 4 1 3 7 8 | x | 6 | = | ? |
| 8 8 0 4 5 | | 6 | | ? |
| 4 4 2 1 7 | | 5 | | ? |
In memory:
# Matrix A
mat_A: .word 7 8 4 8 4
1 8 1 8 4
7 6 3 0 2
9 5 7 4 1
3 6 8 5 7
# Matrix x
mat_x: .word 4 2 6 6 5
# Result matrix
mat_b: .word 0 0 0 0 0Result:
Result:
| 141 |
| 144 |
| 118 |
| 97 |
| 77 |
mult-table.asm
Print out multiplication tables from 2 to 9
Result:
2 times table:
- 2x1 = 2
- 2x2 = 4
- 2x3 = 6
- 2x4 = 8
- 2x5 = 10
- 2x6 = 12
- 2x7 = 14
- 2x8 = 16
- 2x9 = 18
3 times table:
- 3x1 = 3
- 3x2 = 6
- 3x3 = 9
- 3x4 = 12
- 3x5 = 15
- 3x6 = 18
- 3x7 = 21
- 3x8 = 24
- 3x9 = 27
...
ary-stack.asm
Implement Stack using an array (stack capacity: 10)
Push/pop:
:: Usage:
:: - Input a zero or positive number => push
:: - Input a negative number => pop
> Input: 1
:: Stack: (size: 1) [ 1 ]
> Input: 2
:: Stack: (size: 2) [ 1 2 ]
> Input: 99
:: Stack: (size: 3) [ 1 2 99 ]
> Input: -1
:: Popped item: 99
:: Stack: (size: 2) [ 1 2 ]
> Input: -1
:: Popped item: 2
:: Stack: (size: 1) [ 1 ]
> Input: 77
:: Stack: (size: 2) [ 1 77 ]
> Input:
Stack capacity exceeded:
:: Usage:
:: - Input a zero or positive number => push
:: - Input a negative number => pop
> Input: 1
:: Stack: (size: 1) [ 1 ]
> Input: 2
:: Stack: (size: 2) [ 1 2 ]
> Input: 3
:: Stack: (size: 3) [ 1 2 3 ]
...
> Input: 9
:: Stack: (size: 9) [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ]
> Input: 10
:: Stack: (size: 10) [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ]
> Input: 11
:: WARN: Stack capacity exceeded! Your input has been discarded
:: Stack: (size: 10) [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ]
> Input:
Stack is empty:
:: Usage:
:: - Input a zero or positive number => push
:: - Input a negative number => pop
> Input: -1
:: WARN: Stack is empty!
:: Stack: (size: 0) [ ]
> Input:
qsort.asm
Implement quick sort algorithm
The array is stored in the stack and its capacity is increased if needed. Check resize_array() macro.
C language version of the sort function:
void sort (int *arr, int low, int high) {
if (low >= high) return;
int pivot = partition(arr, low, high);
sort(arr, low, pivot - 1);
sort(arr, pivot + 1, high);
}Result:
> Input: 1
:: Array: (size: 1) [ 1 ]
> Input: 2
:: Array: (size: 2) [ 2 1 ]
> Input: 3
:: Array: (size: 3) [ 3 2 1 ]
> Input: 4
:: Array: (size: 4) [ 4 3 2 1 ]
> Input: 99
:: Array: (size: 5) [ 99 4 3 2 1 ]
> Input: 0
:: Array: (size: 6) [ 99 4 3 2 1 0 ]
> Input: -1
:: Array: (size: 7) [ 99 4 3 2 1 0 -1 ]
> Input: 124
:: Array: (size: 8) [ 124 99 4 3 2 1 0 -1 ]
> Input: 5
:: Array: (size: 9) [ 124 99 5 4 3 2 1 0 -1 ]
> Input: -5
:: Array: (size: 10) [ 124 99 5 4 3 2 1 0 -1 -5 ]
> Input: -3
:: Array: (size: 11) [ 124 99 5 4 3 2 1 0 -1 -3 -5 ]
> Input: