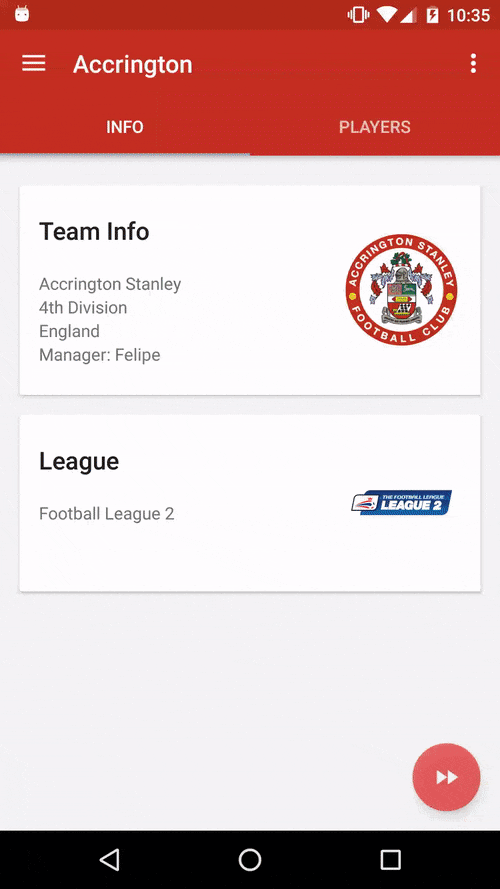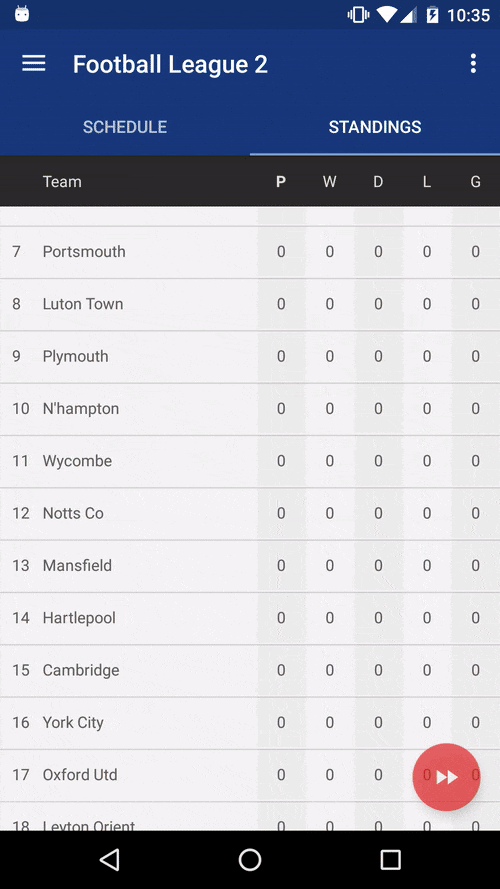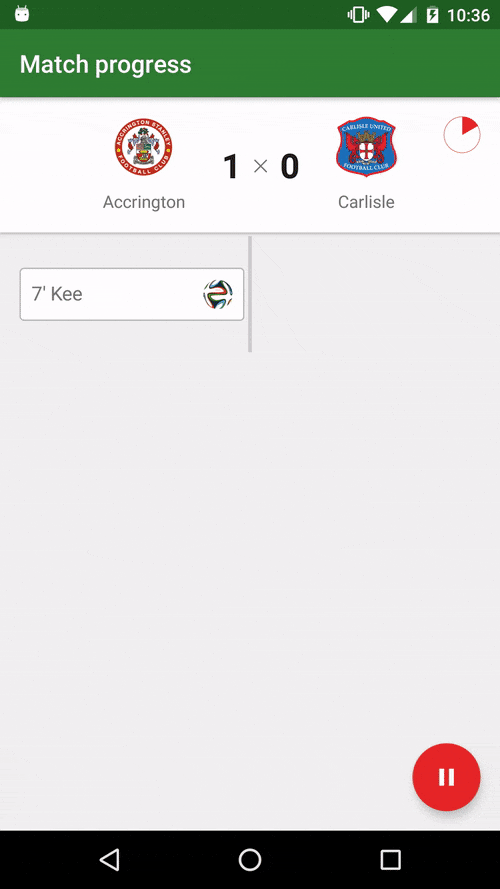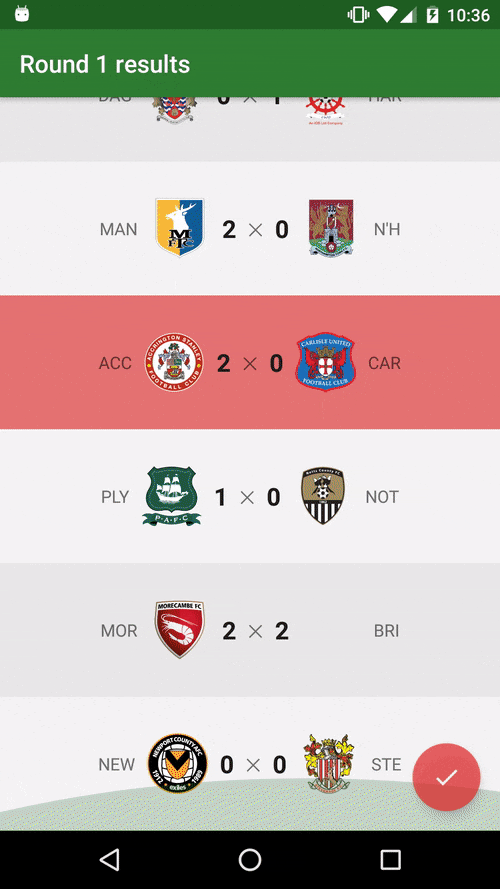
You can also watch the Youtube video.
This is an Android open source "football manager style" game inspired on the classic "old but gold" Windows game Elifoot 98 based on the FIFA 15 Ultimate Team data. Check out the original Medium post for a more detailed introduction and motivation.
Besides being a fun soccer manager game, this app also aims to follow the best practices on Android development and be some kind of reference implementation, both in terms of engineering (code) and design (follow platform UI/UX standards). We're trying to showcase and promote here some core concepts of Android development and advanced usage of some libraries.
Below is a non-comprehensive list of the libraries/plugins/patterns used:
- Dependency Injection using Dagger
- Image caching and loading using Picasso
- Unit testing using JUnit and Robolectric
- Reactive programming using RxJava and RxAndroid
Viewbinding using ButterKnife- JSON manipulation using Moshi
- Value classes using AutoValue
- Networking using OkHttp
- HTTP client using Retrofit
Activity/Fragmentstate management using Icepick- Reactive
SharedPreferencesusing rx-preferences - Reactive SQLite data using SqlBrite
- Code-generation based
Parcelableimplementation using auto-value-parcel - Code-generation based Moshi JSON adapters using auto-value-moshi
- Code-generation based Cursor adapters using auto-value-cursor
- Additional Java utility classes provided by Guava
- Debugging using Stetho
- Material design widgets using AppCompat and the Support Design Library
Run ./gradlew check to compile and run the unit tests. If everything passes, you can run the
app on any emulator or device with API > 21 with ./gradlew assembleDebug installDebug.
By default, the app will be pointing to the production API. You can change that to use your local
development API by setting the API_ENPOINT constant in the build.gradle to $devApiEndpoint:
buildConfigField "String", "API_ENDPOINT", "\"$devApiEndpoint\"".
Generate a
google-services.json file for Google Analytics and replace the placeholder in the app/src/release directory.
In order to build a signed release app, you'll also need to define a few environment variables:
ELIFUT_CERT_PASSWORD: path to your certificate passwordELIFUT_FABRIC_API_KEY: fabric.io API key
Create an Organization and App on Fabric dashboard and create a string fabric_api_key
with your Fabric API key
- Check out the latest master to make sure the feature hasn't been implemented or the bug hasn't been fixed yet
- Check out the issue tracker to make sure someone already hasn't requested it and/or contributed it
- Fork and
git clonethe project - Start a feature/bugfix branch, eg.:
yourname/fix-bug-xyzoryourname/implement-feature-abc - Commit and push until you are happy with your contribution
- Make sure to add tests for it. This is important so I don't break it in a future version unintentionally.
- Open a Pull Request and describe your motivation and changes. Make sure the Travis build passed on your branch by making sure it has a green checkmark
- Squash the commits so we can keep a clean history
Huge thanks to Square and their Android team for releasing such a huge number of very high quality libraries. As you can see from the list above, the vast majority of them are created and maintained by Square.
Copyright 2015 Felipe Lima
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.